Bramwald
P1f1p5
Dep1
The Bramwald in Lower Saxony's Göttingen district is one to 408.1 m above sea level. NHN high and wooded mountain range in the Weser mountain country.
Geography
Location
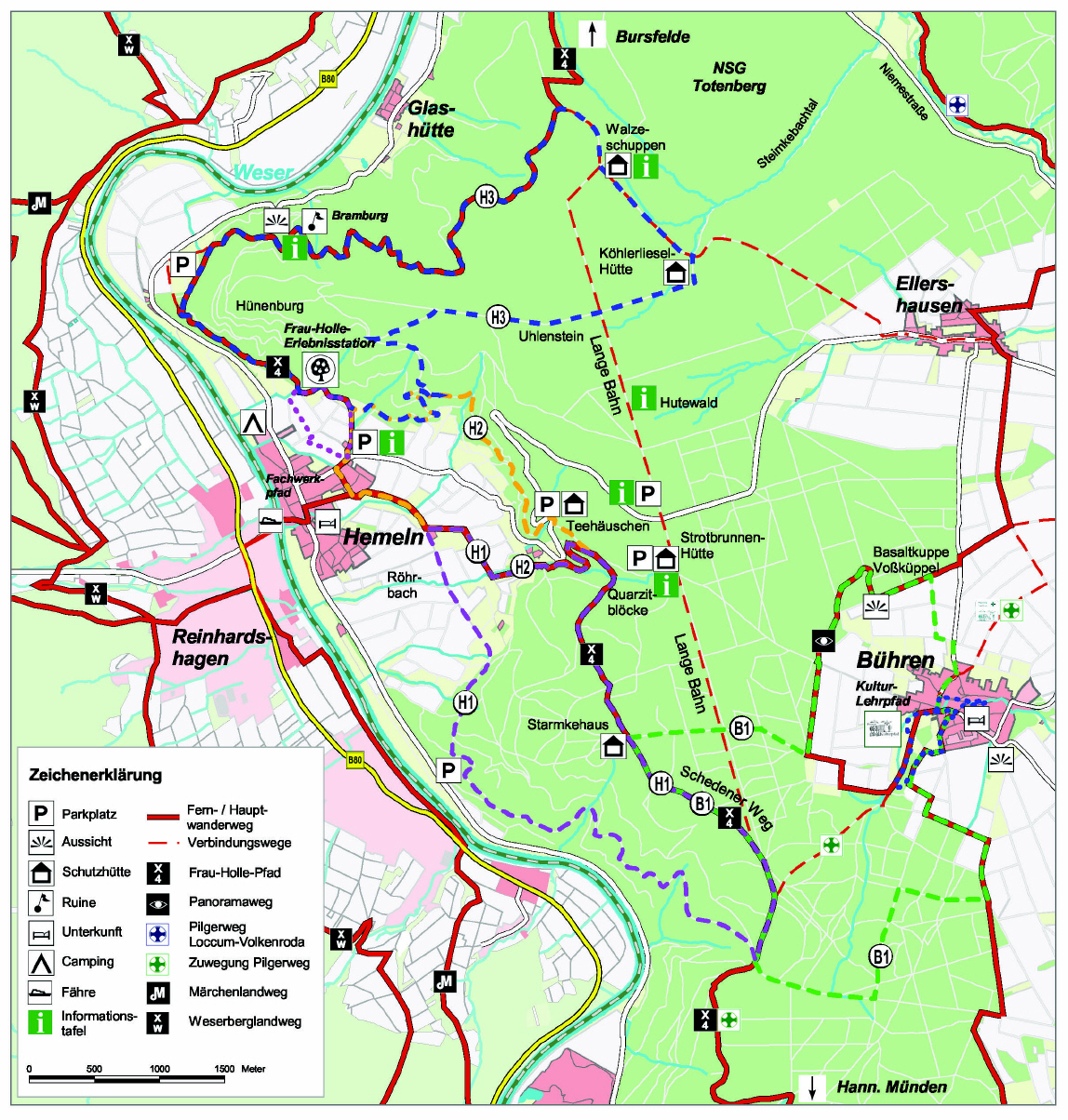
The Bramwald located in South Lower Saxony in the northwest of the Natural Park Munden 20 km (air line ) west of Göttingen and 5 km north of the main town of Hann. Munden. He lies to the east of the upper southern section of the Upper Weser, at the western shore there is the wide Reinhard forest in northern Hesse. To the north passes over the countryside to the Solling, the Schwülme separates the two areas from each other. Each bit in the east rises the Dransfelder Urban Forest in the south of Kaufunger forest.
The elongated Bramwald is in the range from State Forest Forestry Department Munden. Its highest mountain is the Totenberg ( 408.1 m), which lies off the north of the forest and a nature reserve (see below) is reported.
Nature Spatial allocation
The Bramwald forms in the natural spatial feature unit group Weser -Leine Bergland (No. 37) and in the main unit Solling, Bramwald and Reinhard Forest ( 370), the subunit Bramwald ( 370.5 ) located in natural areas Hemelner Bramwald ( 370.50 ), Schedetal ( 370.51 ) and Mündener Bramwald ( 370.52 ) splits. To the north the landscape passes over ( 370.1 ) through the valley of Nieme to Kuppigen Solling. To the east, it falls into the Schedener Rötsenke ( 371.11 ), to the south in the Fulda- Werra- Mündener Talung ( 370.6 ) and westward into the Weserdurchbruchstal ( 370.3 ).
Mountains
To the mountains and elevations of Bramwalds include those without the Kiffings - sorted by height in meters ( m) above mean sea level ( MSL ):
- Totenberg ( 408.1 m), with nature reserve Totenberg
- Heidelberg (approx. 402 m), with transmission tower
- Klingenberg ( 399.5 m)
- Giant head ( 388.5 m), with Bramburg and a Hünenburg
- Sandberg ( 382.3 m)
- Action mountain (about 381 m )
- Vaaker mountain ( 380.1 m)
- Speer mountain (about 378 m)
- Schiffenberg ( 377.4 m)
- Klingenberg (approx. 373 m)
- Mountain hut ( 360.3 m)
- Langeliethstrasse ( 345.5 m)
- Spieker mountain ( 312.5 m)
- Miihlberg (approx. 212 m)
Watercourses
In and near the Bramwald centers include those running in predominantly east-west direction running waters:
- Hassel ditch - rises in the northern part of the forest and empties into the Thiele Bach
- Hesse Bach - rises in the extreme north part of the forest, flows to the northeast, and is part of the catchment area of the Schwülme
- Nieme - rises in Bramwald, later forms its northern boundary and empties into the Weser
- Rehbach - opens into the Nieme
- Schede - rises in the southern part of the forest, it happens south and empties into the Weser
- Schwülme - rises in the Solling, runs about 3 km northeast of the Bramwalds and empties into the Weser
- Thiele Bach - rises in the Solling, later runs north of Bramwalds and empties into the Weser
- Weser - created south of the forest by the confluence of the Fulda and Werra and it happens in the West
Towns
The Bramwald is uninhabited, lie only at its edges villages.
- In the north: Fürstenhagen (district of Uslar )
- Mielenhausen (district of Hann. Munden )
- Bühren (municipality )
- Niemetal (municipality with the villages Ellershausen and Löwenhagen )
- Hilwartshausen (district of Hann. Munden )
- Gimte (district of Hann. Munden )
- Volkmarshausen (district of Hann. Munden )
- Hemeln (municipality with Bursfelde and glassworks; district of Hann Munden. )
- Reinhard Hagen (municipality with the villages Veckerhagen and Vaake at the other or western Weser river in northern Hesse )
- Upper Weser ( with the villages Gottstreu and Gieselwerder at the other or western bank of the Weser and Oedelsheim in Northern Hesse )
Reserves
( 4.37 km ² CDDA-Nr. 165935; ; reported 1989) and almost equal in area, the Fauna- Flora-Habitat area Totenberg ( FFH-Nr. 4423-305; 4.32 To the north of Bramwaldes the nature reserve Totenberg is km ²). On the Bramwald parts are protected landscape Weser Uplands Kaufunger Forest ( CDDA-Nr. 325317; 1989; 285.02 km ²).
History
About property rights possessed in the Middle Ages the monasteries there Bursfelde, Lippold mountain and especially Hilwartshausen. Advocacies had temporarily Sigebodo II of Scharzfeld, Ludolf of Dassel II and the Earls of goat mountain. Even in the era of Henry the Lion, first won the Archbishopric of Mainz influence. 1224 the forest was mentioned in a document with " silve que dicitur Bramwaldt ".
The Bishop of Mainz, Gerhard I. was in 1256, together with Count Konrad III. of Everstein on a campaign by the location in Göttingen area. The campaign was intended for the relief of the Asseburg. The Guelph Duke Albrecht I took both captured and then killed the Count cruel. The bishop, he was released in 1257 against two things: First Albrecht conceded I. 5000 marks which was available to the bishop, because Richard of Cornwall gave him 8,000 marks, so this gave him his voice in the double election of 1256/57. Secondly, after the bishop cede the castle to Gieselwerder Albrecht I.. A little later, also the Bramwald was owned by the Guelphs.
Attractions
Among the attractions, natural and cultural monuments of Bramwalds include:
- Ruin Bramburg ( between Hemeln and glassworks )
- Over beech (east of Vaake )
- Hedwig Oak ( north of Volkmarshausen )
- Several tumuli (eg east of Vaake )
- Wallburg Hünenburg near the Bramburg ( between Hemeln and glassworks )
- Koehler Liesel Hut ( south of the Dead Mountain )
- Fairy tale book ( between Hemeln and glassworks )
- Quartzite blocks (east of Hemeln )
- Quartzite blocks at Voßköppel (northwest of Bühren )
- Sweden -Hills (northwest of Volkmarshausen )
- Totenberg house ( north of the Dead Mountain )
- Wilhelm- skimmed Kurt Oak (east of Hemeln )
Transport and Hiking
By Bramwald lead a few narrow streets, such as a section of the national road 560, the Hemeln and Reinhard Hagen connects to the west with Niemetal - Ellershausen in the east and on the runs a piece of Mother Hulda route of the German Fairy Tale Road through the forest. In west-east direction by pulling it a section of the trail Mother Hulda path and in north-south direction of such an Upland -Weser mountain country lane.