Broca's area
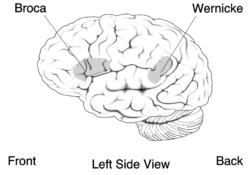
The Broca's area, Broca's area or Broca's language region is a region of the cerebral cortex and is considered along with the Wernicke's area as one of the two main components of the Language Centre. Broca's area takes on a motor function. Is named Broca's area after the French surgeon Paul Broca (1824-1880), who discovered it in 1861.
Localization
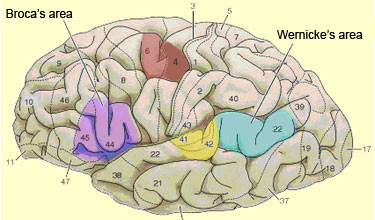
Broca's area is a region of the cerebral cortex, which is located in the pars triangularis of the inferior frontal gyrus usually on the left hemisphere of the brain. After the division of Korbinian Brodmann, it is located in the area of Brodmann areas 44 and 45. Broca's area is above the arcuate fasciculus with the Wernicke's area in conjunction.
Function
The neural networks in the Broca's area is maintained primarily responsible for the grammatical aspects of languages. Children aged up to approximately three years form their language in this center. Later learned second languages are stored separately in adjacent areas of the brain near the Broca's area.
Recent studies using non-invasive imaging techniques such as positron emission tomography and Functional magnetic resonance imaging have shown that the Brocazentrum is responsible for speech motor skills, articulation, sound analysis, articulation and the formation of abstract words. Proven was also found that Wernicke's speech center is responsible for the auditory sensory and logical language processing. Both areas are connected by the arcuate fasciculus.
However, the modern method also showed that the neuronal circuitry of the areas involved in language processing is much more complex than assumed long and other areas of the brain are involved (see the Language Centre ).
Damage
An injury to the brain in Broca's area leads to aphasia, ie an acquired language disorder in which language comprehension remains largely intact. The individual in question, however, it is ( almost) impossible to talk yourself. Some patients are still able to formulate sentences with great effort, but which are incomplete ( telegraphic ). There is no paralysis of the muscles of the need for articulation organs. In Broca 's aphasia is the so-called motor aphasia ( expressive aphasia synonym ). This is in contrast to sensory aphasia, which goes back to an injury to the Wernicke's center.