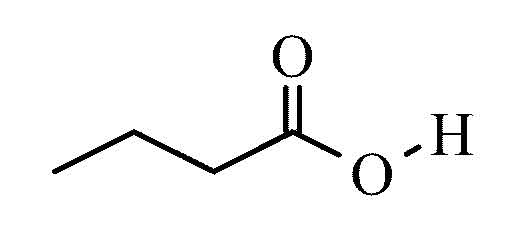
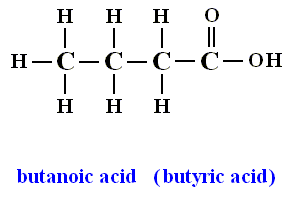
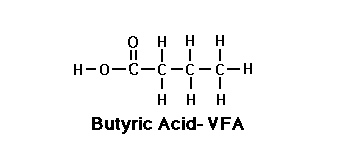
Butyric acid
- Butanoic acid
- N- butyric acid
- Propylcarboxylic
Colorless, unpleasant smelling liquid
Liquid
0.96 g · cm -3 ( 20 ° C)
-5 ° C
163 ° C
0.9 hPa ( 20 ° C)
4.82
Miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether
1.3980 (20 ° C)
Risk
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Butyric acid is the trivial name of the butanoic acid, a carboxylic acid, while the fatty acid easily. It is produced in nature by butyric acid fermentation. The salts (see below) and esters ( see butyric ester ) of butyric acid called butyrate ( also systematically butanoates ).
Butyric acid is a colorless liquid at room temperature, which accounts for the unpleasant smell of vomit or rancid butter, in essence, from where the name originates. Their vapors are irritating to eyes and the respiratory tract.
Metabolism
In the human colon butyric acid is mainly produced in the breakdown of prebiotic carbohydrates by intestinal bacteria. The associated pH -shift in the acid range, the medium for salmonella and other pathogens is unfavorable. Butyric acid also seems directly stimulate the bowel movements and serves the epithelial cells of the colon as an energy source.
Odor
The smell of butyric acid can be perceived by humans and some animals in small traces. Man rated the smell negative, the housefly positive. Ticks is the smell of butyric acid to locate their hosts.
Butyric acid propionic acid, in addition, hydrogen sulphide and volatile sulfur-containing organic compounds ( methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide ) cause of bad breath in humans.
Since the formation of butyric acid is a sign of decay, odor perception can be understood as a warning odor. The odor of butyric acid can be reduced with bases such as sodium hydroxide, solutions of carbonates, etc.. Here, the corresponding butyrate, which no longer smell form.
Salts
Butyrate ( also systematically butanoates ) is next to a name for butyric acid esters also the name for the salts of butyric acid. These consist of butyrate anions C3H7COO and a cation. Examples are sodium butyrate ( NaC3H7COO ) Magnesiumbutyrat (Mg ( C3H7COO ) 2) and Ammoniumbutyrat ( NH4C3H7COO ). When moisture they have the same characteristic odor such as butyric acid. If a butyrate salt treated with a stronger acid, butyric acid, in turn, arises.