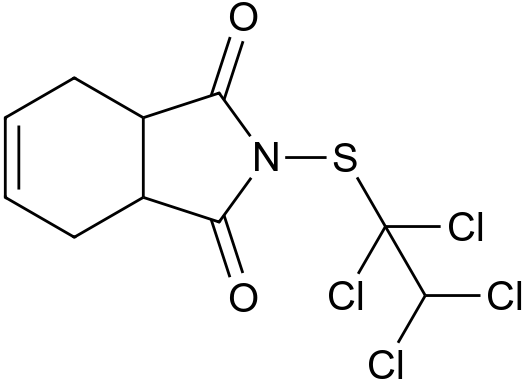
Captafol
Colorless solid
Fixed
160-161 ° C
Practically insoluble in water
Risk
- 2.500 mg · kg -1 ( LD50, rat, oral)
- 15,400 mg · kg -1 ( LD50, Rabbit, transdermal)
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Captafol is a chemical compound from the group of phthalimide and is structurally related to Difolpet and captan.
Production and representation
Captafol can be obtained in benzene 1,1,2,2- Tetrachlorethylsulfenylchlorid by reaction of the sodium salt of tetrahydrophthalimide.
Properties
Captafol is a flammable colorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It decomposes when heated. It slowly hydrolyzes in aqueous solutions but rapidly under basic conditions.
Use
Captafol has been used since 1961 as a fungicide in fruit growing, vegetables, ornamental plants and in viticulture and is also used for seed treatment. The effect is due to inhibition of enzymes in carbohydrate, amino acid and phosphate metabolism. Based on the findings in animal experiments carcinogenic effect of phthalimide 1986, the approvals of such compounds have been withdrawn in the FRG.
The use as an active ingredient of pesticides is banned in the EU.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no plant protection products containing this active ingredient are allowed.
Safety
Captafol can cause contact allergy and has been classified as a carcinogen.
The World Health Organisation classifies captafol as "extremely hazardous " one. For international trade, with the substance of the Rotterdam Convention is to be observed.