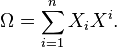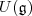Casimir element
The Casimir operator ( also Casimir invariant, named after the physicist Hendrik Casimir ) is studied in the mathematical field of algebra and differential geometry. He is a special item from the center of the universal enveloping algebra of a Lie algebra. A typical example is the squared pulse rotary operator, which is a three-dimensional rotation of the Casimir invariant group.
Definition
Suppose that is a -dimensional semisimple Lie algebra. Be
Any basis and
Is the dual basis of respect to a fixed invariant bilinear form (eg the Killing form). Casimir the square element is represented by the formula
Given element of the universal enveloping algebra. Although the definition of the Casimir element refers to the direct election of a basis in the Lie algebra, it is easy to show that the generated element is independent. In addition, implies the invariance of the bilinear form that was used in the definition that the Casimir element commutes with all elements of the Lie algebra and therefore is in the center of the universal enveloping algebra.
Be an arbitrary representation of the Lie algebra on a (possibly infinite-dimensional ) vector space V. Then the corresponding quadratic Casimir invariant is defined by
Given linear operator on V.
Applications
A special case of this construction plays an important role in the differential geometry, or the global analysis. Operates a connected Lie group G, then the elements of first order described by differential operators with associated Lie algebra on a differentiable manifold M on M. Be the representation on the space of smooth functions on M. In this case, the given by the above formula Casimir invariant of G -invariant differential operator of second order on M.
One can also define more general Casimir invariants; this happens for example in studies of pseudo - differential operators in the Fredholm theory.