Cherokee language
Spoken in
- Iroquois language family südirokesische languages Cherokee
-
Cherokee ( Ꮳ Ꮃ Ꭹ " Tsalagi ") is the language of the Cherokee people and is used by up to 22,000 people have spoken. Cherokee is part of the Iroquoian language family and is the only language in the südirokesischen group, which is still spoken. The original self-description of this language was Aniyunwiya, the present name Tsalagi has been derived from the English word Cherokee.
- 2.1 Classifiers for texture in some verbs
Phonology
Consonants
The consonant inventory of Cherokee of North Carolina can be described as:
Vowels
Cherokee has six vowels: a, e, i, o, u, and a nasal vowel, the un sounds like French and is mostly written in Latin script as v. This vowel is available in all Iroquoian languages. All vowels can be short or long:
At diphthongs there, except in foreign words, only one: ai.
Emphasis
Cherokee is a tonal language with six tones: high, low, rising, falling, high and rising, low and falling. However, only in very rare cases cause a false note another meaning of the word. In addition, the signature marks the tones do not, and also in Latin transliteration they are usually omitted. In many areas simplifies the sound system, especially in careless pronunciation, while other speakers, especially older consciously hold it.
Grammar
How many Indian languages also Cherokee polysynthetic. This means that many morphemes can be packed into a single word, which can be very long. The verbs of the Cherokee have the most important part of speech information contained much more than German words. They include not only the subject (I, you, ...) with a, but also the object ( me, you, ...) and some of its properties ( see below). A verb must consist of at least four parts: the prefix for the pronoun, the verb root, a suffix for the aspect, and a suffix for the mode. Thus, gega the verb form, " I go (even) ", the following elements:
How many languages (eg Turkish) Cherokee knows no distinction between "he", "she" and "it." There knows a dual (two numbers ) as Slovenian, Tagalog and Tamil and as an inclusive and exclusive we. This can be seen in the conjugation of the verb in the present tense -e- see:
The time used here is the progressive present tense ( " I 'm going "). Cherokee differentiates between progressive and even stricter habitual present tense (I'm often / usually) than English. The shapes of the habitual present tense for I go (usually), you're going (usually), he, she, it does not (usually ) hot gegoi, hegoi, Egoi ( in Scripture Ꭸ Ꭺ Ꭲ, Ꭾ Ꭺ Ꭲ, Ꭱ Ꭺ Ꭲ ).
Classifiers for texture in some verbs
About 20 of the Cherokee verbs require special syllables that qualify the direct object according to its nature. These include the verbs for " cancel ", " store ", " take ", " wash ", " hide", "food", "draw", " have ", " hold ", " put in water ", " fire in place "and" are ". The classifiers can be divided into five categories:
1 Alive 2 Supple (most common) 3 Long ( narrow, not flexible ) 4 Liquid (or container ) 5 Indefinite (solid, relatively difficult)
Example:
There are reports that recent Cherokeesprecher only use the indefinite forms and begins to disappear the classification system.
Word order
Simple declarative sentences follow a word order of subject-object - verb ( SOV ). Negated sentences have a different position. Adjectives in front of nouns. Are they after, they form a sentence with " is " ( the word "is " is unnecessary ): Ꭰ Ꭹ Ꮩ Ꮣ Ꭴ Ꮤ Ꮎ agidoga utana ("my father is great" ). Demonstrative at the very beginning of a noun phrase: Ꮎ Ꭰ Ꮝ Ꭶ Ꮿ Ꭰ Ꭹ Ꮩ Ꮣ na Asgaya agidoda ( " this man is my father " )
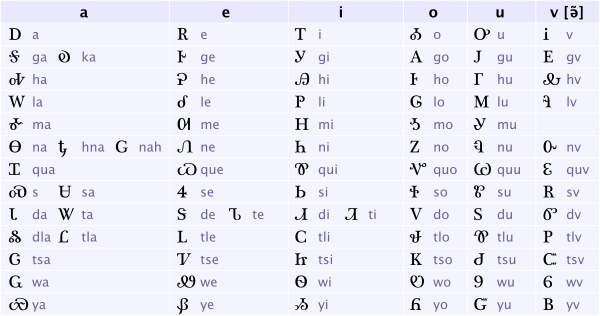
Font
Cherokee is written in its own syllabary, which was developed by the Indian Sequoyah. Some characters resemble Roman letters or Arabic numerals, but the meanings are independent.