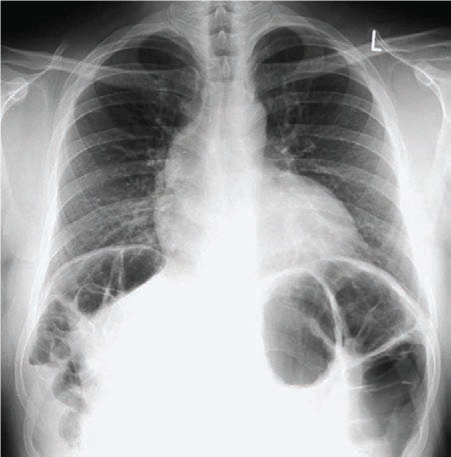
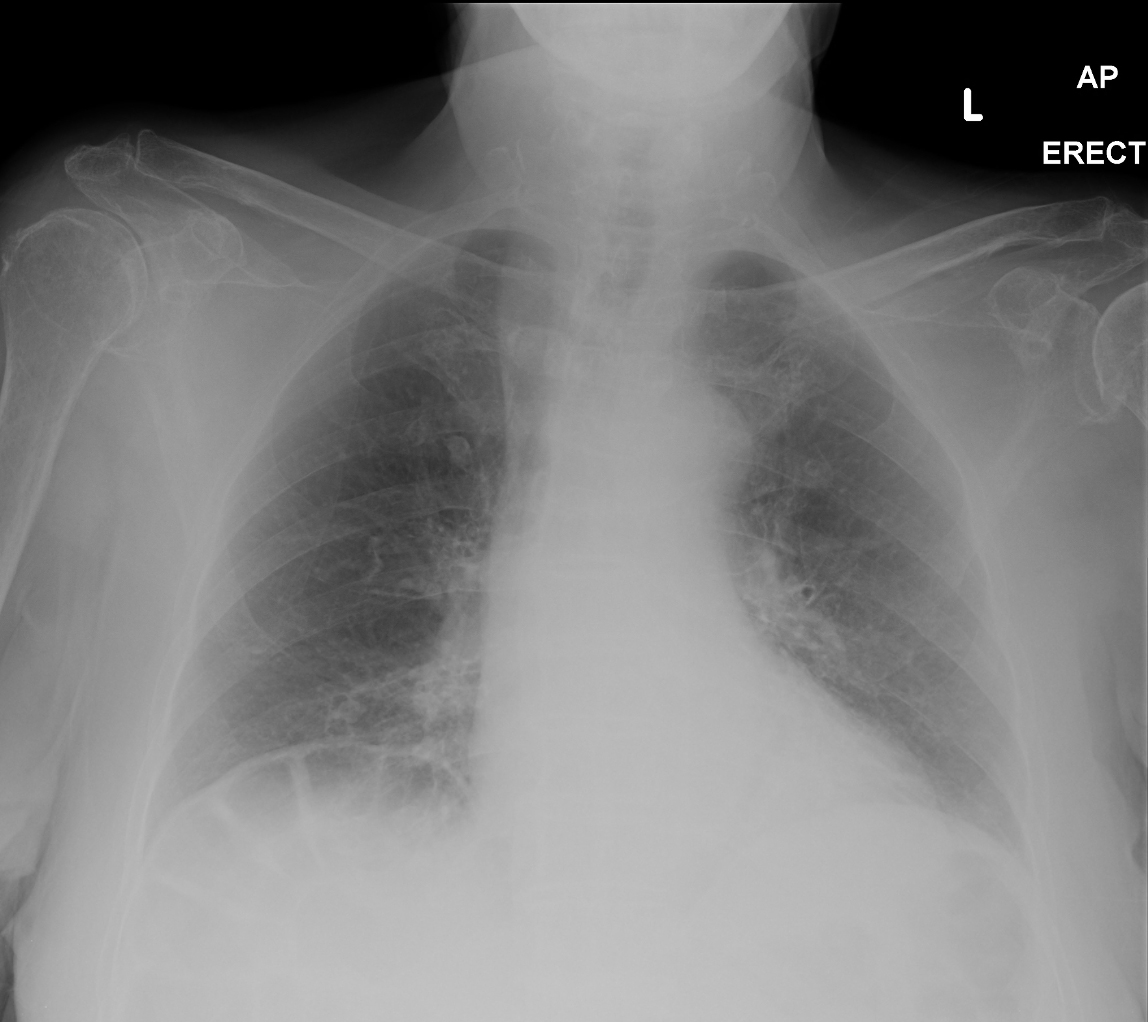
Chilaiditi syndrome
The Chilaiditisyndrom or Chilaiditi syndrome describes a shift in medicine and rotation of the colon and small intestine of rare proportions of further footwards after cephalad ( cranial) between the diaphragm and liver. Normally found in this region, no gut. The syndrome is an anatomical variant, and not necessarily of clinical significance.
Name
Synonymous with the term Interpositio coli hepato - diaphragmatic ( Greco- Latin " displacement of the colon between the liver and diaphragm " ) will be used. The syndrome was named after the Greek radiographers Dimítrios Chilaiditi, born in 1883, who lived in Vienna and Istanbul.
Occurrence
The syndrome is rare (less than 1 %) and is usually identified as an incidental finding on radiographs of the lungs. Computed tomography of the upper abdomen, it also falls on. In ultrasound, it may be recognized, but heavier than the radiograph. In operations on the liver, especially in liver punctures, is the knowledge of this anatomical variant of importance.
Anatomy / Pathophysiology
There are portions of the colon - shifted or more rarely of the small intestine between the right lobe of the liver and right diaphragm - ( flexure ), especially his right upper bend. The syndrome may be associated with abnormalities of the liver, diaphragm, or large intestine.
Twisting ( torsion ) of the right colon bending about the longitudinal axis of the gut to the blood supplied mesentery ( the Mesocolons for the thickness or the mesentery of the small intestine ) can be obtained by the digestion movements of the intestine ( peristalsis ) a dangerous rhythmic closing of the intestine cause or its blood supply.
Discomfort
Most patients are asymptomatic. However, it can also lead to the impoundment before interponierten colon, which bloating and pain to a life-threatening intestinal obstruction can cause ( a ileus) ( see above).