Coenzyme Q – cytochrome c reductase
- CAS Number: 9027-03-6
The enzyme cytochrome c reductase, more coenzyme Q: cytochrome c oxidoreductase called ( systematic name ), cytochrome bc1 complex or complex III of the mitochondrial respiratory chain is a protein complex. The enzyme acts as an oxidoreductase, it catalyzes in a coupled reaction (Q- cycle), the oxidation of a coenzyme Q, the reduction of cytochrome c and the translocation of protons from the matrix space (M ) in the intermembrane space (IM). Mutations in the MT- CYB gene are rare genetic diseases such as myopathies and optic neuropathy type liver (LHON ) the cause.
Structure
Mitochondrial cytochrome c reductase is a transmembrane protein consisting of eleven subunits. The minimal functional complex consists of only three essential catalytic subunits with four cofactors:
- Cytochrome b with two b heme ( bL and bH )
- Cytochrome c1 with a heme c
- Rieske iron - sulfur protein (ISP engl. Iron sulfur protein) with a [2Fe · 2S ] center
Function
The function of cytochrome -c reductase is in the
- Transfer of electrons from coenzyme Q ( two- electron carriers ) to cytochrome c ( A - electron carriers )
- Transport of protons by coenzyme Q ( two- proton carrier ) from the electronegative side of the membrane (matrix space M) to electropositive side of the membrane ( intermembrane space, IM)
The electron transfer and proton translocation are coupled in the cytochrome c reductase by the so called Q- cycle ( Q engl. Quinones ).
The enzyme has two binding or reaction centers ( Qo and Qi ) for the substrate coenzyme Q:
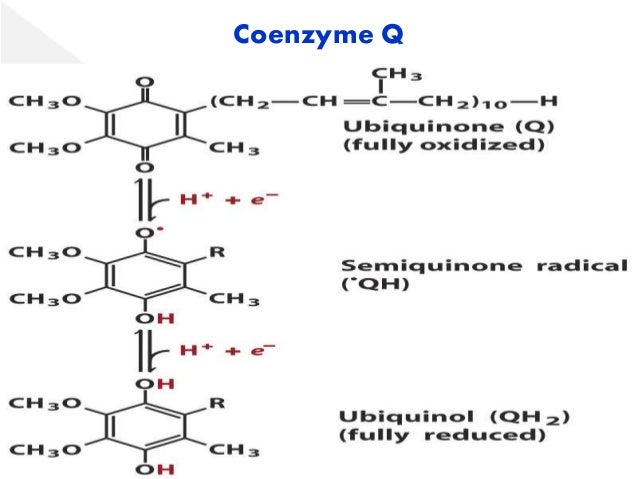
- Qo or QP center (o engl output, P eng positive site. . ): Here binds reduced coenzyme Q ( Ubihydrochinon, QH2 ) and is oxidized to ubiquinone (Q).
- Qi or QN- center (i engl input, N Engl negative site. . ): Here binds oxidized coenzyme Q ( ubiquinone, Q) and is reduced to Ubihydrochinon ( QH2 ).
On these two reaction centers following reactions take place:
At the Qo center binds a Ubihydrochinon. Ubihydrochinon ( QH2 ) transfers an electron via FeS and heme center C1 to the heme group of a bound cytochrome c. The resulting Ubisemichinon (Q · - ) on Qo center transmits another electron BL via heme and heme bH two protons to the positively charged membrane side (P ) from. The resulting ubiquinone (Q ) now leaves the binding site. This half cycle will run through a second time.
On Qi - center binds a ubiquinone. Ubiquinone (Q ) captures an electron via heme bL and heme bH. The resulting Ubisemichinon (Q · - ) receives another electron via heme and heme bH bL and two protons of the negatively charged membrane side (N). The resulting Ubihydrochinon ( QH2 ) now leaves the binding site. Thus a ubiquinone is regenerated per cycle.
Two ubihydroquinones ubiquinone to be in the course of a complete cycle of Q thus on the one hand on the Qo center oxidized, on the other hand on a Ubihydrochinon Qi center recovered. Two cytochrome c are ( Cyt c ) reduced. Furthermore, two protons of the negatively charged membrane side (N) are removed and four protons on the positively charged side of the membrane (P) is discharged. In contrast to complex I and complex IV to complex III is not a proton pump.
Inhibitors
- At the Qo - center: myxothiazol, stigmatellin, Methoxyacrylsäureester ( MOA), strobilurin
- On Qi - center: antimycin A
Alternative names
- Coenzyme Q: cytochrome c oxidoreductase
- Cytochrome reductase
- Complex III of the respiratory chain
- Cytochrome bc1 complex