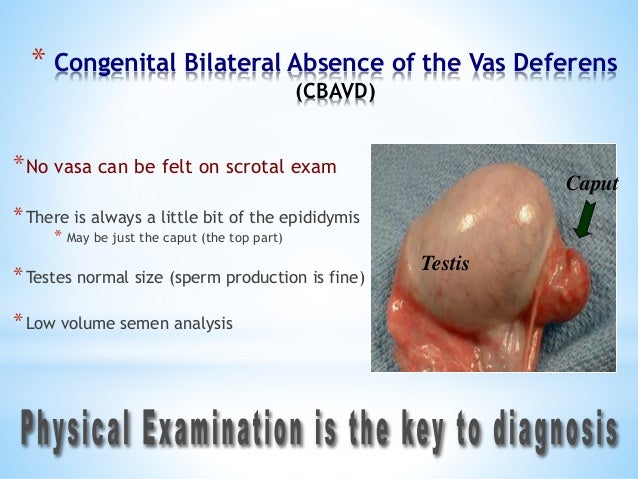
Congenital absence of the vas deferens
A CBAVD ( Congenital bilateral aplasia of engl. the vas deferens for " two-sided Congenital absence of the vas deferens ", short for Congenital aplasia also CAVD of vas deferens ) may be isolated or occur as a mild form of cystic fibrosis. The disease is an autosomal recessive trait and is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene. In contrast to the classical form of cystic fibrosis, the clinical picture of CBAVD limited mostly to an absence of the vas deferens. In patients with CBAVD the formation of sperm cells in the testes is normal. However, as the vas deferens is missing, the sperm in the testis formed only into the epididymis and not escape to the outside.
Cause
In CAVD can be distinguished according to the number of defective vas deferens between a bilateral ( CBAVD ) and unilateral ( CUAVD ) form. One of congenital aplasia of one or both sides is based on a mutation in the CFTR gene ( "cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator " ) in 75-90 % of cases. People with such a mutation usually have a mild form of the cystic fibrosis ( cystic fibrosis), in which only the seed head is affected. If a mutation of cystic fibrosis or CAVD leads depends on the severity of the mutation in both alleles from.
Pathogenesis
We do not know yet how a CFTR mutation leads to the absence of the vas deferens. Believed to be a disorder of the vas deferens caused during fetal development. When tested fetuses with CFTR mutation of the 12th and 18th week of pregnancy, however, no abnormalities regarding the vas deferens was established. Therefore, rather than cause a blockage of the channels by viscous secretions very likely.
Reproduction
Affected with a genital cystic fibrosis are carriers of classical form. Their offspring have an increased risk of cystic fibrosis.
Therefore, should be tested in a possible CFTR mutation of / partners /. If the test is negative, a residual risk remains, as it is only tested to the most frequently occurring mutations and the sensitivity of the test is only 90 %.
Clinical Diagnostics
A CAVD can be detected with the help of a sperm analysis. By CFTR mutation secretions water is withdrawn as a result of the osmotic effect. Thus the sperm of CAVD patients has a lower pH, less volume and less fructose than normal semen.
Treatment
Operative treatment is not possible. A desire to have children through artificial insemination can (intracytoplasmic sperm injection ) are complied with.