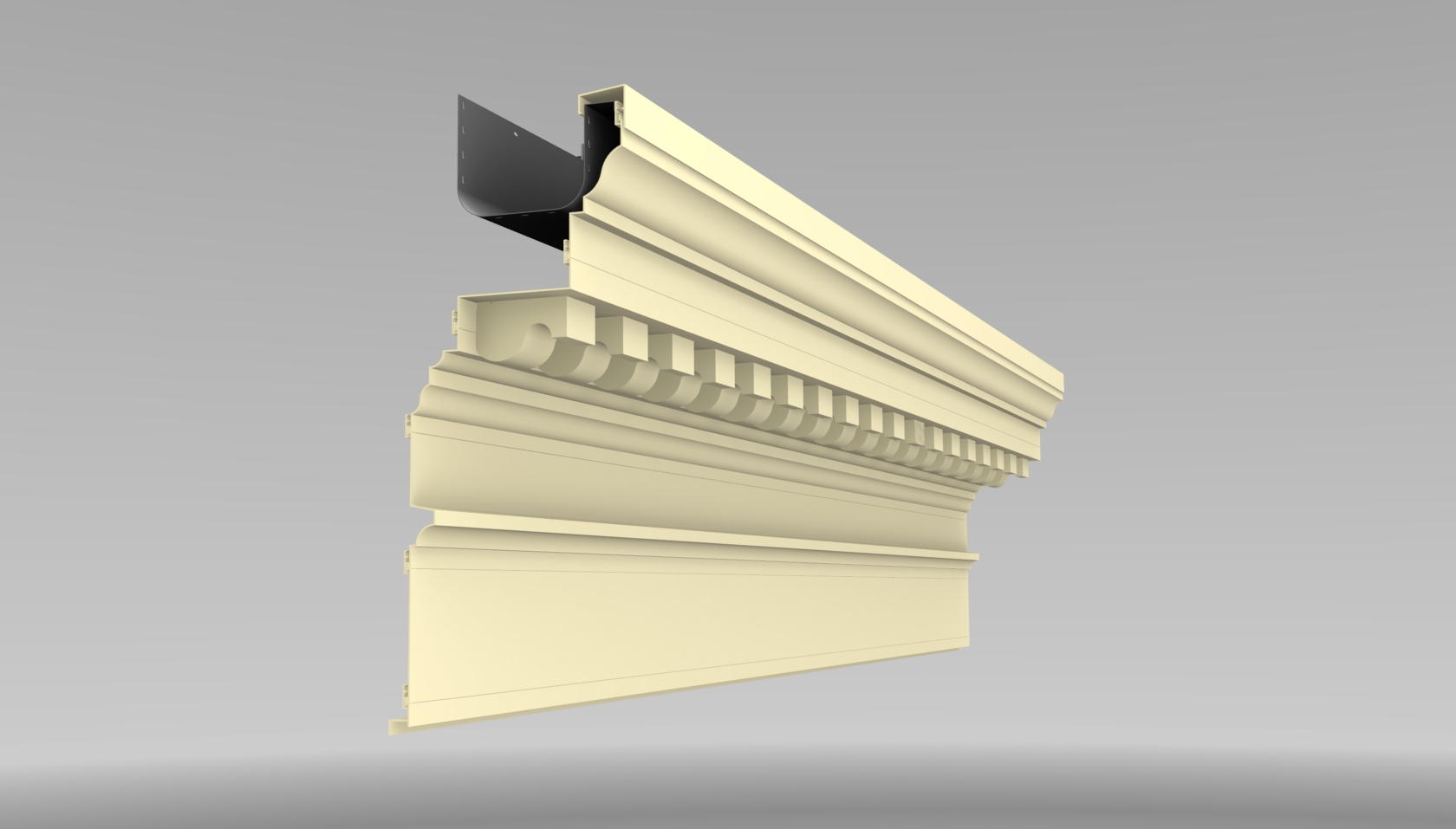
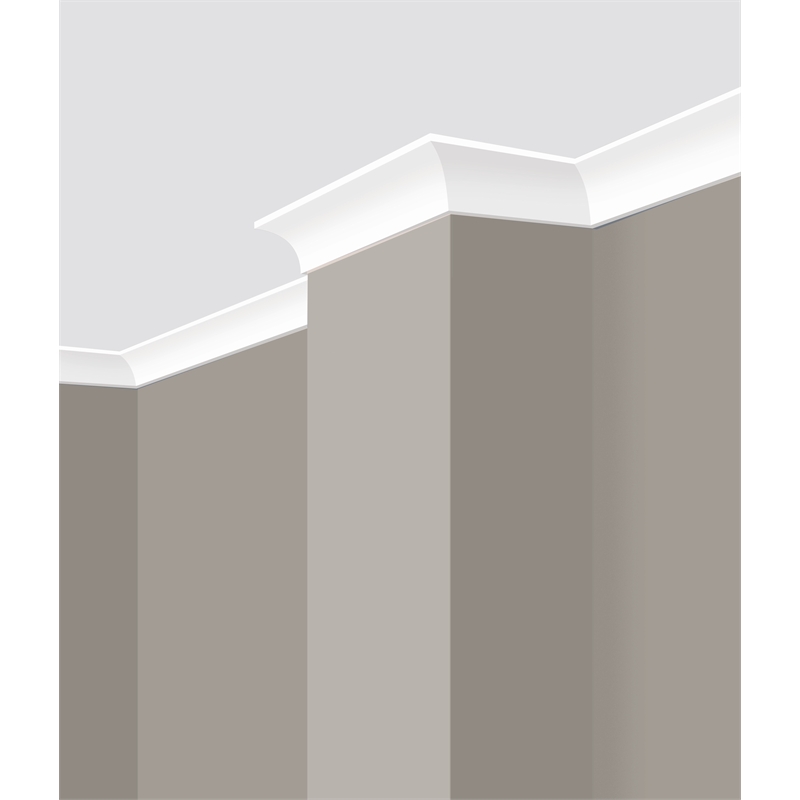
Cornice
Cornice also ledge usually is a horizontal member which protrudes from a wall. A cornice is used together with vertical architectural elements such as pilasters, pilasters and columns of the structural design (outline ) of walls and facades.
The cornice is an old and important instrument of European architecture. As the origin geison of Greek architecture of antiquity is considered. In epochs of architectural history, the meaning and the execution of cornices were subject to severe changes, they are so far compared with friezes. Short, decorative Gesimsabschnitte as crown above doors and windows are also called is roofed. In the modern architecture since the beginning of the 20th century cornices lost their decorative and artistic importance.
In addition to the design had cornices in historic buildings and a constructive function, to protect the lower position wall from the weather. In this context, a Gesimsstein is a form of brick, which was incorporated into cornices, for example, as a nasal stone with attached nose shape as a drip edge.
Terms
After the location on a structure it may be:
Verkröpftes cornice
A shoulder piece (especially in older sources also offset ) is in the architecture of the run around a horizontal cornice to a vertical wall projection. This creates a protruding edge, which is also known as the crop edge. Vertical wall projections may be in this context, for example, columns, piers or pilasters.
Plastering Tape
A cleaning tape is created when the horizontal member and not profiled simply, that is flat and rectangular in cross section, is frilly. It may be arranged on the facade, as well as the moldings described above.

.png/220px-Cornice_(PSF).png)





.png)