Coronary circulation
As coronary or coronary artery or a vein is called, supplying the heart muscle with blood and this discharges from it. The coronary arteries are arranged in a ring around the heart. The word comes from the Latin coronary, meaning crown or wreath shaped.
Coronary arteries
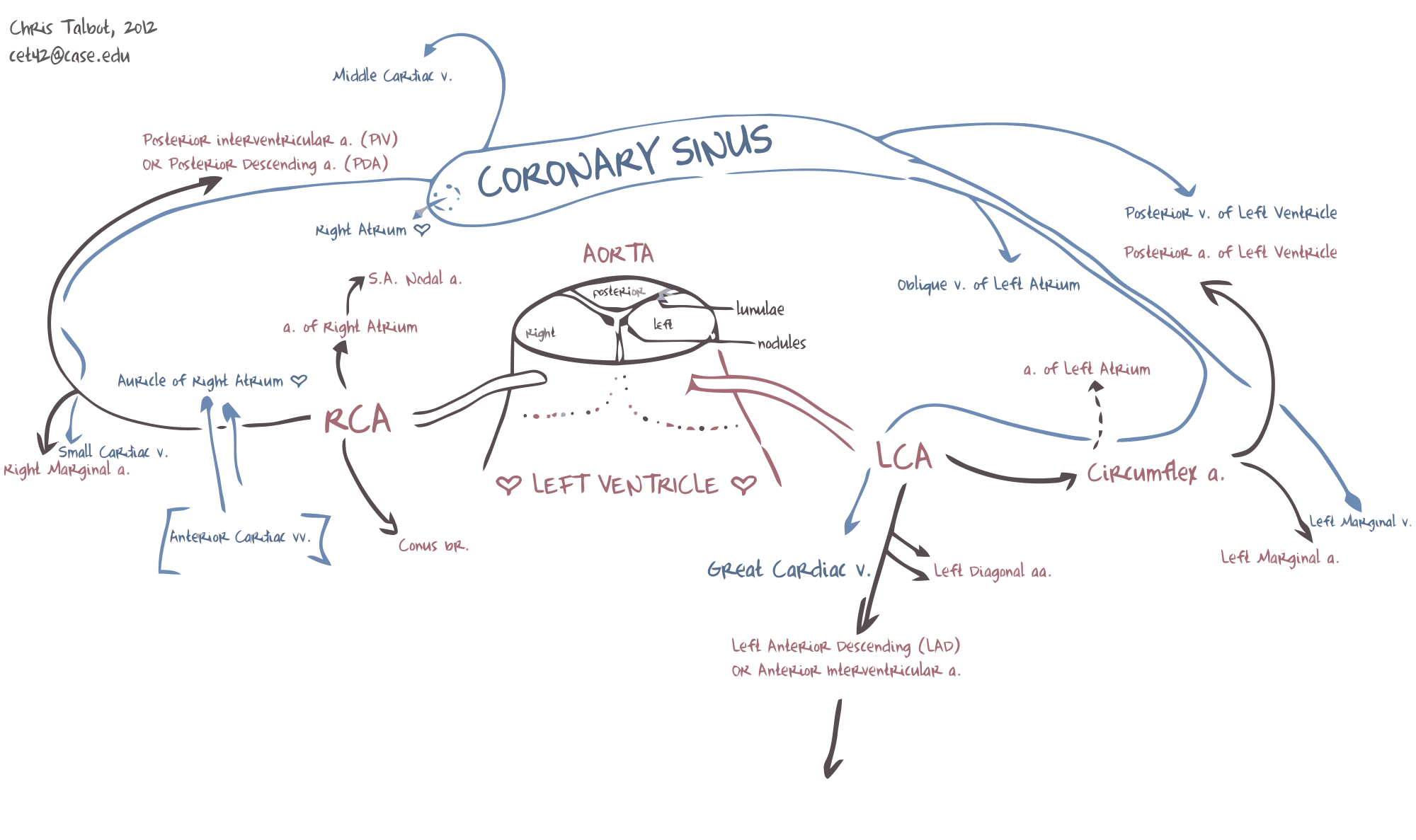
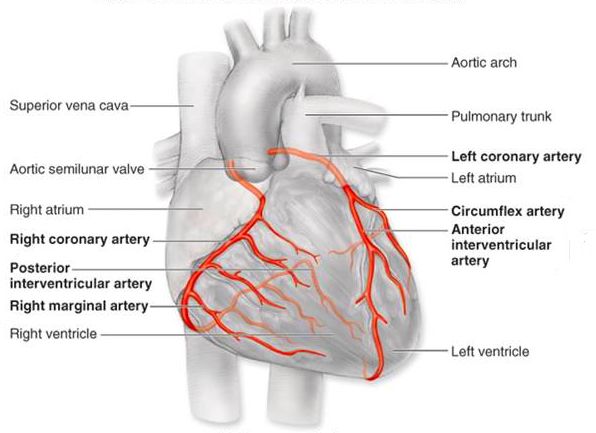
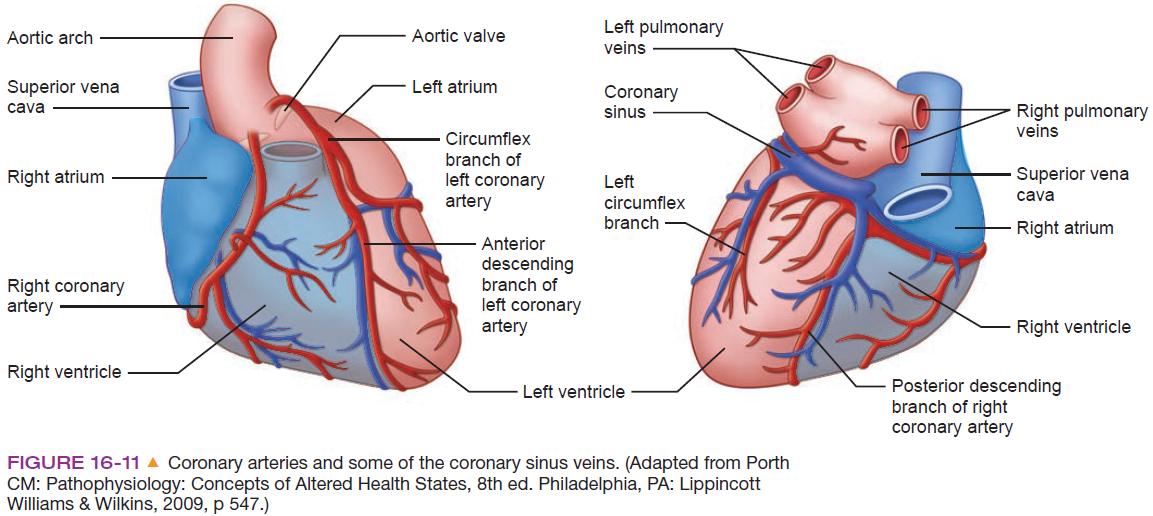
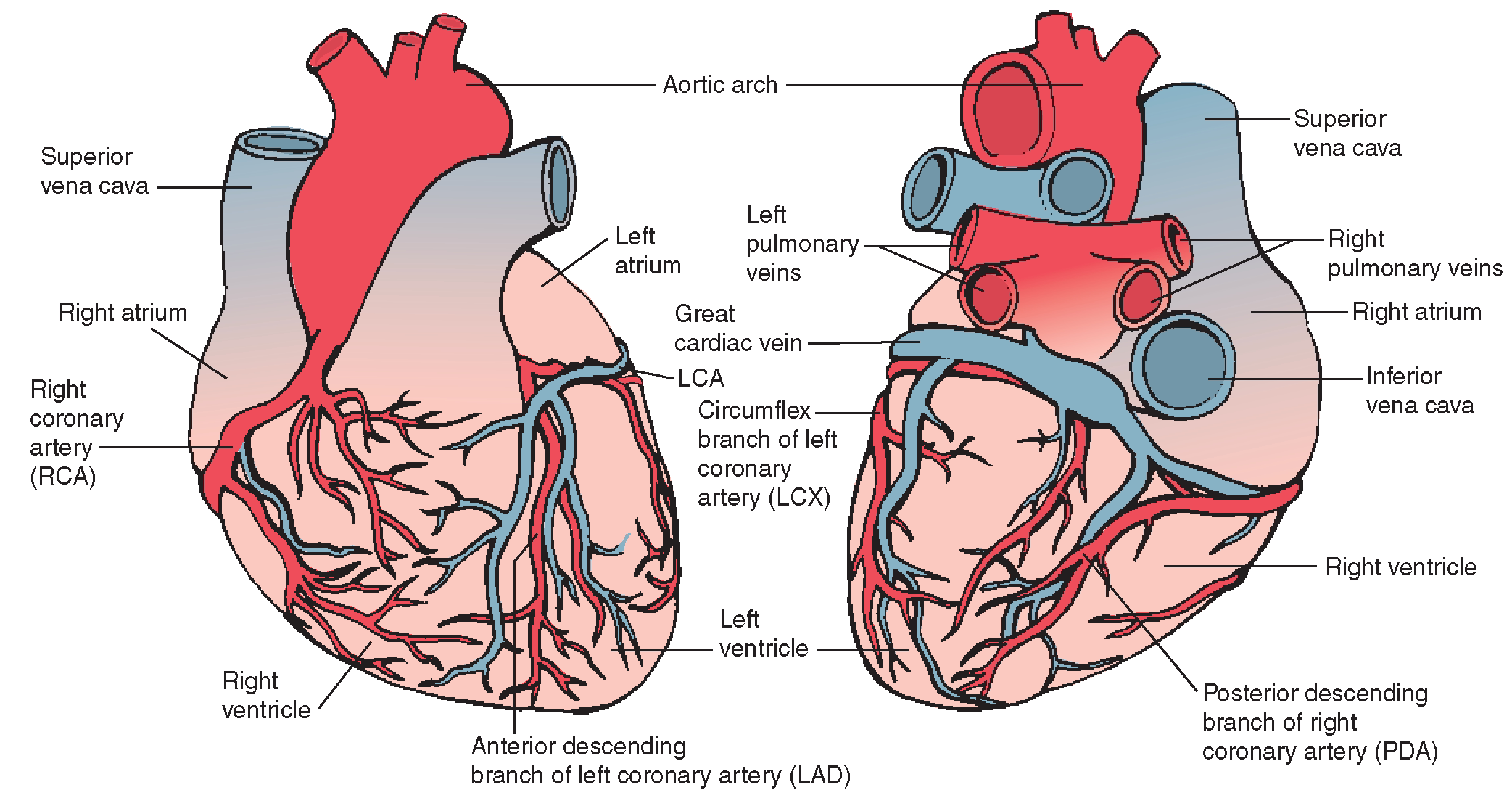
The coronary arteries ( arteries coronariae ) arise from an indentation of the aorta just above the aortic valve. There is a left (arteria coronaria sinistra ) and right coronary artery (arteria coronaria artery ).
The left coronary artery ( LCA) is divided by about 1 cm in the left circumflex artery ( RCX ) and the left anterior descending artery (LAD, English:. Left anterior descending, LAD), which the front moves between left and right ventricular apex of the heart on. Until the bifurcation is called from the main trunk (truncus communis). Sometimes the main trunk divides into three vessels, the medium is termed the ramus intermedius. The left artery supplies the heart front wall, the side wall and the septum.
The right coronary artery ( RCA) has a main branch, the ramus posterior interventricular ( RIVP, English:. Posterior descendent artery, PDA). The rear wall and the sinus and AV nodes are powered normally by the right coronary artery, as well as the right ventricle and the right atrium and left ventricle partly shares.
Both coronary arteries ( arteries coronariae ) indicate in their course from smaller branches, which are often subject to variations depending on the supply type. In the following the anatomical names are listed in parentheses are the clinically common names are called, the relevant, since most vigorous, vessels are in italics.
Branches of the circumflex artery ( RCX ):
- Ramus marginalis sinister ( ramus marginalis )
- Ramus atrialis
- Posterior rami ulcer sinistri
Branches from the left anterior descending artery (LAD ):
- Rami lateral ( Ramus diagonalis )
- Rami interventriculares septal ( Septaläste )
Branches from the arteria coronaria artery (RCA):
- Ramus nodi sinuatrialis ( sinus node artery)
- Ramus coni arteriosi
- Ramus atrialis
- Ramus marginalis dexter
- Rami atrioventriculares
- Division ( bifurcation ) of the RCA in the field of " crux cordis " in Ramus posterior interventricular ( RIVP, often anastomosed to the LAD ) with its Rami interventriculares septal ( often form collaterals to the Septalästen LAD ) and
- Posterolateral ramus dexter ( RPLD )
Supply types
When the left coronary artery along- and the rear wall and the node, it is called a left- catering type, whereas one speaks of a right supplier type in a (joint) supply the front wall by the right coronary artery; the normal case is referred to as intermediate type.
The normal case ( around 75 % of the population ) represents the balanced type
The arteria coronaria sinistra ( left coronary artery ) supplies here:
- The left atrium,
- The musculature of the left ventricle,
- The major part of the interventricular septum,
- A portion of the front wall of the right ventricle.
The arteria coronaria artery (right coronary artery ) supplies:
- The right atrium,
- The muscles of the right ventricle,
- The rear part of the interventricular septum,
- The sinus node,
- The AV node,
- A portion of the posterior wall of the left ventricle.
Coronary heart disease
→ Main article: Coronary heart disease
The coronary arteries are terminal arteries, there is no collateral circulation, which could take over a supply in an emergency. In the event of closure, the unserved area dies ( heart or myocardial infarction). If the coronary artery is damaged, it is called coronary heart disease ( CHD).
Coronary veins
The large coronary veins (venae cordis ) run in parallel over long distances to the coronary arteries and flow through the transverse current coronary sinus into the right atrium. Smaller coronary veins empty directly into the right atrium or other heart spaces, such as the veins ulcer dextri ( right ventricle) and the veins cardiacae minimae or Thebesiusvenen ( inner chambers of the heart ).
The large coronary veins (venae cordis ) are:
- Vena cordis magna
- Vena cordis media
- Vena cordis parva
- Anatomy of the heart
- Aorta