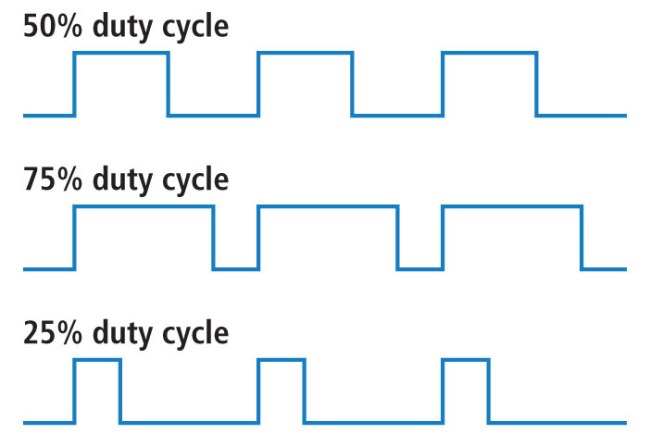
Duty cycle
The duty cycle (also drive level, english duty factor or duty cycle) 60469-1 specifies the ratio of the pulse duration to the period of a periodic sequence of pulses according to DIN IEC. The duty cycle is specified as a dimensionless ratio with a value from 0 to 1 or 0 to 100%. This is explained in the ideal pulses that form a square wave.
Especially for the duty cycle τ / T = 0.5 = 50 % results in a symmetric pulse.
The term duty cycle does not occur in the above standard and is not used consistently in the literature; it is used for both the duty cycle and its inverse as well as the relationship between pulse and pause duration. The last variant corresponds to the occurring in the same standard term on-off ratio, defined as the ratio of pulse duration to pulse interval, ie
With a value from 0 to ∞.
Use and importance of
By varying the duty cycle, the arithmetic mean value of the electric voltage can be changed. Since this setting is almost no power loss due to switching - in contrast to the setting with a series resistor - this digital technical method is a common method for controlling electrical voltage and power. Applications include switching power supplies, and burst control for heating systems.
The underlying pulse width modulation is a modulation for producing continuously variable DC voltage, in which the demodulation through a low-pass behind the pulsweitenmodulierenden circuit for averaging. Despite the on-off switching creates an analog signal because the duty cycle is an infinitely adjustable size. At sufficiently sluggish applications will dispense with the low-pass, because for averaging alone is the inertia of the system is sufficient, for example in heating systems.
Also, some digital - to-analog converter work with adjustable duty cycle. With a square-wave voltage with a constant period of time, the digital input information is determined in this case gradually adjustable pulse width, and thus the average output voltage proportional thereto.
Wherein the phase angle control motor speeds are set by means of the variable duty cycle of a sinusoidal voltage. The same applies to the chopper control.