Ectromelia virus
The ectromelia virus ( ECTV, mice pox virus) is the only member of the virus family Poxviridae ( smallpox virus ) that can cause disease in mice. The disease caused by the ECTV was first described in 1930 and recognized in 1948 the serological similarity to the vaccinia virus.
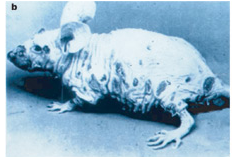
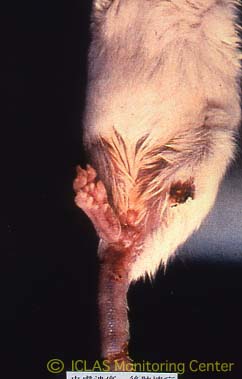
The ECTV causes two different diseases: A mild, chronic form with typical, pox -like skin lesions (mouse pox ) and an acute disseminated infection, which is often fatal with the involvement of various internal organs. In mouse embryos, the ECTV causes a severe malformation of the long bones ( ectromelia ), after which the virus is named. A disease caused by ECTV was observed only in laboratory mice. The virus itself was also suspected in wild mice. It is spread very easily within laboratory populations by droplet and contact infection.
Morphology
The genome of the ECTV consists of a linear double-stranded DNA (dsDNA ) of about 210 kbp. As a member of the genus Orthopoxvirus that ECTV has a rectangular shape with a diameter of about 200 nm and a length of 250 to 300 nm To date, two subtypes described ( Belo Horizonte - virus and ECTV type Moscow). The ECTV is closely related to the monkeypox virus, and vaccinia virus.
Importance
The ECTV is used in the research into the disease mechanisms of various viral pathogens as a model virus to which the animal model, the distribution of the virus in the organism can be studied in exanthemischen viral infections or specific defense mechanisms of the immune system. With the investigation of the ECTV important mechanisms of the immune system have been discovered and elucidated, the importance of cytotoxic T cells for the healing of a virus infection, the viral immune evasion and the importance of nitric oxide in the function of macrophages and dendritic cells. In addition to the function of various viral proteins as immunomodulators or activation mechanisms for natural killer cells and the significance of Toll-like receptor 9 for the defense of smallpox virus in the ECTV model could be shown. The ECTV is also used for testing of vaccines and antivirals against smallpox viruses.
Swell
- RM Buller et al. Poxviridae, genus Orthopoxvirus. In: CM Fauquet, MA Mayo et al.: Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. London, San Diego 2005 p 122f ISBN 0-12-249951-4 p 122 f
- David M. Knipe, Peter M. Howley ( ed. -in- chief): Fields' Virology. 5th edition, Philadelphia, 2007, Volume 2, page 2967 ISBN 0-7817-6060-7
- DJ Esteban and Buller RM: ectromelia virus: the causative agent of mousepox. J. gen. Virol. (2005) 86 (Pt 10): pp. 2645-2659 (Review) PMID 16186218