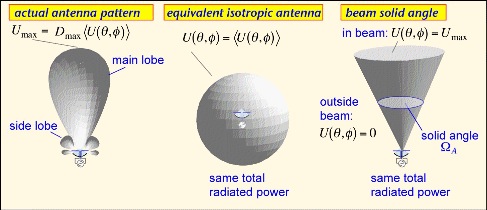
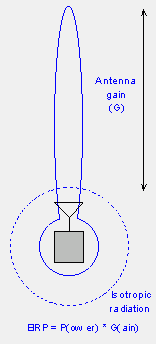
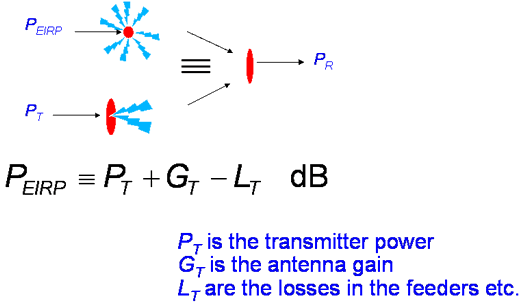Equivalent isotropically radiated power
The equivalent isotropic transmission power (English equivalent isotropically radiated power, EIRP ) is the product of the fed in a transmitting antenna power multiplied by the antenna gain ( relative to isotropic radiator a ). If no direction is specified, the value for the main beam direction of the transmitting antenna, the antenna gain is their greatest simultaneously applies.
- Gi: antenna gain over an isotropic radiator (dimensionless)
As a reference antenna for the antenna gain of the isotropic radiator is used here. To make the reference antenna in the antenna gain is expressed in dBi indicated that, with the units of dB trailing " i" stands for the reference antenna " isotropic radiator ". An isotropic radiator has a gain of 1 (corresponding to 0 dBi ).
As ERP and EIRP differ only in the reference antenna for the antenna gain ( a half-wave dipole has a gain over an isotropic radiator of 1.64 - 2.15 dBi accordingly ), there is the following relationship:
Or exemplified in logarithmic units:
Spellings
The German term for the EIRP is relatively uncommon. Often, for example, the formulation is radiated power ( EIRP) used (although not, effective radiated power, as it relates to a half-wave dipole and is abbreviated ERP).
EIRP is often treated as a physical quantity ( electric power). You therefore is assigned a unit ( watts). Another possibility is EIRP to get behind the unit in brackets, eg watts ( EIRP).