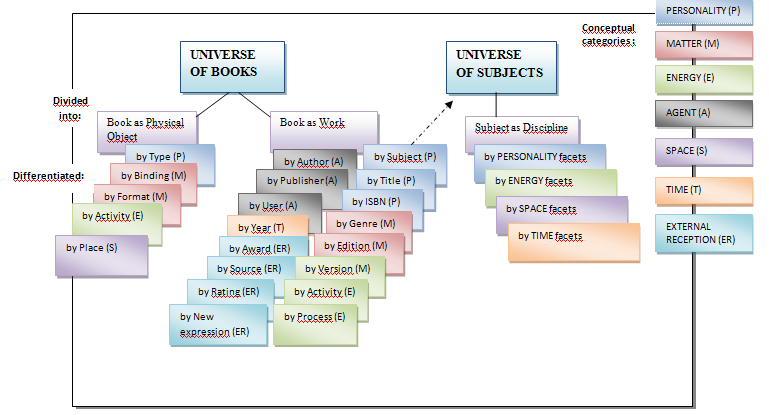
Faceted classification
A faceted classification (also analytic- synthetic classification ) is a classification system in which the objects of a knowledge domain can not be incorporated into a relatively inflexible tree structure, as is the case with purely hierarchical systems. Instead, the classification of an object by assigning multiple independent terms. On this point, it is a so-called facets that represent a particular point of subdivision (example: " Gender "). The concrete expressions of a facet are called foci or single classes (example: " male ", " female "). An object foci of several facets are assigned in this case typically, so it is a polyhierarchisches classification system. A Focus heard but always to exactly one facet. The foci of a facet may have a hierarchical structure. It can be associated with an object several foci of a facet, a faceted classification can thus be used polydimensional.
The classification of an object results from the combination of the associated foci, which is referred to as a post- combination - as opposed to a pre-combination, in which the combination takes place even at the formation of the terms of the classification system. For the notation of the object classification the identifiers of the foci are connected, resulting in the overall notation.
The best-known faceted classification is the Colon Classification. In the field of architecture and construction, there is the BRD / SfB system, which is constructed in the form of a faceted classification.
Pros and Cons
A big advantage of a faceted classification compared to pre-combined classification systems lies in the greater flexibility and expandability. In particular, the number of required classes is considerably lower at a faceted classification. For example, the amount of required classes could be reduced by about a factor of 40, if you would map the "Literature" section of the Universal Decimal pre-combined in terms of a faceted classification. It follows that the cost of maintenance of the classification catalog is significantly lower.
Pre-combined and particularly mono- hierarchical classification systems give as opposed to a faceted classification the access path before using the top- down principle. They are therefore particularly suitable for cases in which there is a typical access path also provides a predefined access path for Investigative guidance dar. the other hand are suitable facet classifications especially if access is typically carried out from different perspectives.
When electronic access is the design of an intuitive user interface when using a faceted classification rule, demanding compared to a pre-combined classification. Also, the need for resources upon execution of a search is typically higher in systems that support a faceted classification as the combination of the various terms occurs only when performing the search.
Example
In the example, two variants are outlined by classification systems that could represent a section of the field of " shoe stores ". The top in this case represents a mono-hierarchical catalog in which a pre-combination is made. In the lower variant is a faceted classification. To the right is shown how the same concrete object - a Brogue, a men's shoe model in size 49 - would be classified in both systems. In the pre-combined system of this object would be associated only with the class "Lord street shoe Oversized ". In a faceted classification, however, it would be the three, namely " Men's Shoes ", " street shoe " and " oversize ".
One is interested in a specific shoe model, the pre-combined system, from top to bottom along allows the tree to find the right most detailed node. If one is interested, however, how large is the total range of shoes plus size, you would already consider four different classes in the pre-combined system. Particularly marked difference between the two systems is then, if one imagines that a differentiation to Upper material classification system is to be supplemented. When pre-combined system, this differentiation should take place at many different points of the tree. In faceted classification, however, " textiles", would merely add a new facet to the foci " leather ", " synthetic ", etc. are introduced. With the introduction of further differentiations, such as when orthopedic shoes are to be included in the range, the number of required classes in the pre-combined system grows exponentially.