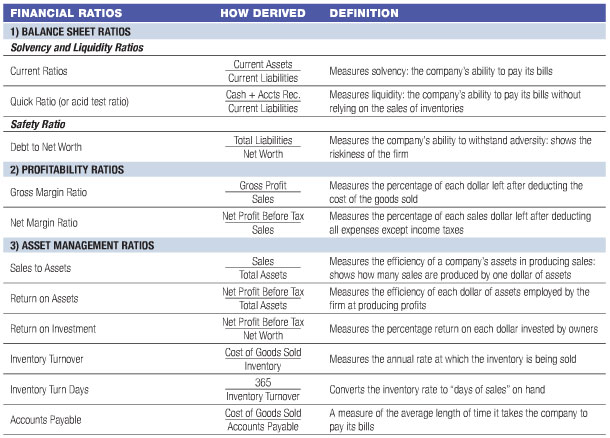
Financial ratio
An economic indicator is used within the business for the evaluation of companies. It serves as a basis for decisions ( problem identification, identification of operational Stark and vulnerabilities, information extraction ), the control ( target-actual comparison), the documentation and / or coordination ( behavior control ) important facts and relationships within the company. A measure is selected from the wealth of existing companies in numbers of accounting as particularly meaningful size. A relative figure, two selected variables into a suitable reference are to each other. Measures provide a condensed information. Especially expanded are financial ratios and performance measurement systems in commercial establishments.
Performance indicators will be published in part by the companies themselves. A number of indicators can be determined from financial statements beyond.
The exact calculation of ratios is not standardized in most cases. So many figures depend, for example from the underlying accounting principles, which differ internationally. A comparability between companies in different countries is therefore limited.
Metrics that relate to each other can be combined into performance measurement systems. Major performance measurement systems are the DuPont system of metrics that ZVEI performance measurement system and the RL- indicator system.
Of particular importance are key figures in the comparison operation as well as in the so-called benchmarking. The number of the " best company " represents the benchmark (also "best practice ") that, on the other companies can follow.
- 3.1 Key performance indicators
- 3.2 Liquidity ratios
- 3.3 Profitability Ratios
- 3.4 Key figures for capital structure ( accounting ratios )
- 3.5 Key figures for turnover
Types of indicators
KPIs can be fundamentally divided into absolute and relative indicators.
- Absolute figures: for this purpose are business individual values , sum values , difference values and mean values into account. Your information content is defined by the significance of the value itself; For example, cash flow, contribution margin, EBIT, total assets, size of company.
- Relative ratios: connecting two business management values them as an indicator of increased and / or specific significance. The strength of a relative ratio depends primarily on the factual context of the compared variables. A distinction must be three types of relative indicators: Relationship indicators: ratio of two dissimilar but of equal sizes; eg return on equity;
- Index Indicators: Comparison of two similar and its peers sizes with different time reference. In general, index numbers always refer back to a base date (year, month, day, etc.), which is equal to 100 in order to analyze the development over time as compared with the baseline time point can; For example, sales growth, price development;
- Structure characteristics: comparison of two similar but ungleichrangiger sizes, ie a subset to a higher total amount; eg equity ratio.
Functions of key figures
Decision function
Indicators form the basis for business decisions. Decision-makers need information, the impact of the decisions taken by them. The information should also enable the identification of problems and opportunities. These ratios are kept clear. During the aggregation of data is important to note that this lost detail information. Representation and presentation of the indicators is important for the correct perception and interpretation by the decision makers. By conciseness and clarity, these are supported in the problem identification and pattern recognition.
Control function
Indicators are used to check ex ante and ex post planned the achieved result.
Coordination function
Key support for the enforcement of decisions in the coordination of different entrepreneurial areas and in the control of behavior by employees. In addition, documented issues with them.
Behavior control function
Especially in larger companies measures are used to move employees to specific, positive behaviors for the company. It should be noted that, for a remuneration on the basis of a measure of employees is primarily interested in increasing this number. An incorrectly selected measure may thus lead to mismanagement.
Vision and Strategy
Performance measurement systems for the implementation of vision or strategy form the basis of a balanced scorecard.
Outline of key figures
KPIs can be according to the underlying facts to be expressed by them, broken down into key performance indicators, liquidity ratios, profitability ratios and indicators for net assets structure ( accounting ratios ) and the turnover frequency.
Performance indicators
Key performance indicators are used to determine the company's success. Relative performance indicators based on either the profits or shareholder value. The latter originated from the shareholder value approach and the frequent criticism of profit-oriented metrics such as ROI. A decisive advantage of the company's value-based indicators is their cost of capital.
Key performance indicators include
- Profit before tax
- Net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT )
- Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes ( NOPLAT )
- Net income Adjusted net income
- Cash flow Free Cash Flow
- Operating Cash Flow
- EBIT
- EBIRT
- EBITA
- EBITDA
- EBTA
- Economic Value Added
- Product result
- Mark-up
- Gross
- Total operating income
- Personal power ( "Personal Productivity " )
- Space power ( " land productivity " )
Liquidity ratios
- Cash ratio
- Acid Test Ratio
- Current Ratio
- Assets ratio
- Catchment liquidity
- Working Capital Net working capital
Profitability Ratios
- Return on assets
- Return on equity
- Return on sales
- Return on Capital Employed
- Return on Investment
- Cash Flow Return on Investment
Key figures on the capital structure ( accounting ratios )
- Equity ratio
- Debt ratio
- Gearing
- Investment intensity
- Berry - Index
Key figures for turnover
- Capital turnover
- Inventory turnover
Criticism, failure modes and risks
The generally applicable indicators for criticism of a unilateral focus, misinterpretation and promotion of undesirable behavior also applies to financial ratios. As a well-known example is considered here, the economic measure of "chicken efficiency" leads instead of the intended increase in efficiency to customer and revenue losses.