Flocculation
Flocculation or flocculation (Latin flocculus, tufts of wool small ') to be coagulated finest suspended or colloidal impurities of the water in order to be able to better separate out from water by sedimentation or filtration and remove. This is superficially seem a purely physical- technical process.
In general, chemical complex formation also play a role. It is possible to remove dissolved substances from the water by means of flocculation, such as phosphate, or fractions of the dissolved organic carbon. This is done by means of suitable chemicals, referred to either as a flocculant or flocculants. The chemicals are divided into organic and inorganic polyelectrolytes primary flocculants, mostly Hydroxidbildnern such as calcium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide or iron hydroxide. It therefore is a mixed chemical and physico- technical process.
Application in water treatment and waste water technology
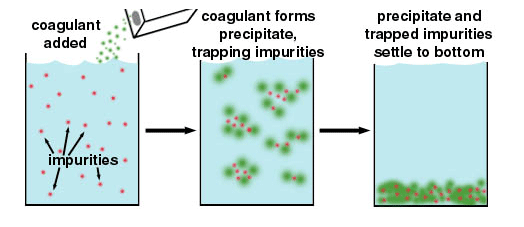
If it is in turbidity in turbid waters are colloidal particles (< 1 micron ), for example, in surface water to plankton, humic substances, clays or hydroxides, then the density difference is so small that it does not drop sedimentation. The particles are loaded on its surface mostly negative and repel each other by electrostatic effects. A measure of these forces (diffuse double layer ), the zeta potential. If these forces overcome by appropriate conditions or addition of flocculants, the small particles agglomerate into larger macro-flocs.
The time required for the formation of the macro flocs destabilization of the microparticles can be effected by cations, especially by trivalent carrier such as Al or Fe Hydroxidbildner (aluminum chloride, aluminum sulfate, sodium aluminate, ferrous chloride, ferrous sulfate ) or lime ( calcium hydroxide). The adjustment of the optimum pH is crucial. However, the coagulation can often be achieved with cationic polyelectrolyte, preferably with polyamines. For the agglomeration macroflocs high molecular weight polyelectrolytes ( in common parlance "polymeric flocculants " ) are used mostly copolymers based on acrylamide, which may be anionic or cationic.
Coagulation and agglomeration usually run in parallel. In the practical application of flocculation mixing conditions ( stirring ) and ripening time can play an important role in the efficiency of the deposition, especially for systems with a low solids content (eg, surface water). Flocculation is also used for sludge dewatering or in sewage and drainage processes of the industry ( paper manufacturing, mining, chemical processes). However, it can also be used for removing phosphate from surface waters such as in the OWA ( surface water treatment) in Berlin Tegel to avoid eutrophication of natural waters.
Occurrence in metallurgy
Larger workpieces of alloy steel tend to undesirable material separation by resignation of hydrogen solid solution with a reduced diffusion capacity. Flocculation is preventable by pre-heating the aggregates, by alloying additions and special forming processes with delayed cooling.