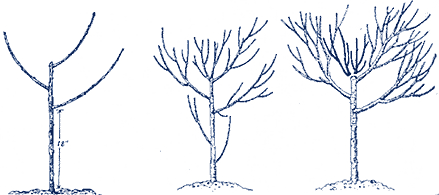
Fruit tree forms
The term cultivated form refers to the apparent growth form of the relevant fruit trees. The desired type of use, the requirement for different forms. For the orchard, the trees must be robust and allow convenient mowing the lawn under the trees. In the garden trees will often be convenient to harvest and therefore be selected with a shorter stem and a smaller crown volume. The " commercial horticulture " ( for example, by Otto Schmitz -Pretty ) requires its plants favorably in direct access without having to use ladders and is dependent on a rapid onset of yield phase. Here the smallest forms of the fruit trees are used.
The shapes generated by the nursery as the high - and half - tribes, as well as the bush trees give, with their combination, the root, as the power-determining base and the variety determined scion, an output structure from that of by the owner with the help of fruit tree section is developed and maintained throughout the lifetime of the tree. Of course, the average for all tree shapes uses the same physiological principles, but its implementation to the requirements of the relevant forms must be adapted. In the article, pruning trees, some instructions are called, which are suitable for the high - and half- tribe. Due to the complex structure of the tree crowns this should be supplemented by appropriate training essential. For usual also in the form of fruit growing sectional shapes such as Slender spindle, columns and espalier fruit trees exist adapted their own instructions and sometimes training.
- 4.1 Ecology at high strains
- 4.2 Ecology at Busch trees
Tree shapes
Standard tree
As a high trunk is called fruit trees whose crown base is at least 180-220 cm height ( valid definition around the year 2000). To achieve this form in the nursery, in the first years after sowing, all side branches and in the third year, all branches removed below the desired crown height. The young tree is implemented in this period several times for example by means of a ball cutter, pronounced " transplants " to obtain a concentration of roots on a compact bales, and thus enhance the growth at the final location.
Between 1950 and 1995, was the request to the nurseries "at least 160-180 cm ". The change in the desired strain level at high strain corresponds to the change of use and the growing tractors to perform a mechanized section of the orchard can.
In nurseries, the term is also indicated for the qualities of other trees and shrubs in sales. A high trunk is here einstämmiges, trained wood with crown base at the appropriate height.
For the current situation infection with fire blight are the high strains a possible way dar. While the dwarf forms, in the case of an infection, usually the whole plant needs to be cleared, a high strain can sustain a vigorous pruning the affected areas.
Half -and low- strain
As half tribes are called trees whose crown base is approximately between 100 cm and 160 cm. At low strains, the crown begins from 80-100 cm in height.
Older forms of use (Y- crown)
The former method, low strains build up in combination with a strongly growing base are possible in principle, however, there is no use for this now needs more for the professional fruit growing. The result would be a tree with the crown volume of a high strain and a barely discernible trunk height. The old form of the Y- or longitudinal - crown represented such use, however, the necessary crown section of the inlet of the income phase later and the yield in relation to the required area is complicated, worse, compared to the currently used Slender spindles.
Bush tree
Bushes and spindle bushes have a stem length of about 40-60 cm. This tree shape is achieved by choosing a correspondingly weak growing base and a pruning to plant the crown forming branches. Although a low strain requires a life, adapted to its physiology section, but the overall size of the plant is almost completely determined by the performance of the root surface. In addition, this root is so weak, that the more conventional forms also permanently need a supporting post or tethering to a wire system.
For use on a trellis the plants are to be selected in each case according to the desired crown volume. For this purpose, usually weaker documents are used. However, in appropriate space even more documents are possible.
A Slender spindle is usually grafted on a very slow-growing surface. The fruit wood is brought directly to the center, real scaffold branches ( Leitäste ), as in big-crowned fruit trees usual, are completely absent. Because of the early entry earnings and fitness for rational work processes, this form has prevailed in the low- strain - commercial fruit growing.
History of professional fruit growing bush with trees
Low ethnic fruit trees were cultivated systematically only with advent of acquisition fruit crops in the 19th century. For they bring (compared to high strains ) earlier and higher yields with better quality; Moreover, they are much easier to harvest and maintain because no ladders are necessary.
Initially, the low -growing forms were preferably used for trellises, topiary and limited in space allotments. Was due in part to the desired shape of the fruit tree (eg U - palmettes ) more important than the earnings.
The German fruit growing pioneer Otto Schmitz -Pretty laid in 1896 at the first apple and pear orchards with low strains and thus developed what is now known as sealing planting or high-density planting. Schmitz -Pretty it was also the beginning of the 1930s the spindle bush ( Slender spindle) in Bornheim -Merten introduced. This work was further developed in 1950 in England by Grodon McLean under the name Pillar. Again on Dutch plantations, the Slender spindle was reintroduced in 1960 in southern Hesse. However, this form of cultivation only began in the second half of the 20th century by the world. Today, about nine out of ten apple trees in Europe spindle bushes.
Other bush tree shapes
Currently pillars trees are as developed eg Ballerina For private garden. This is in principle slender spindles that meet this growing pattern more or less independently and form short fruit wood. The weak base allows for easy holding the plant in the bucket. The disadvantage of many of these varieties is usually not completely satisfying taste. Moreover, almost all fruit species and varieties can be kept as a potted fruit with appropriate support and care. Lately also different varieties like Cox, offered as a dwarf apple trees for the balcony bucket.
Confusion with other forms of care
About the stem height also a bonsai tree could be viewed as a low strain, but are bonsai usually not refined to weak monitoring documents. The reduction of plant size is achieved here by a far more extensive Astschnitt and in particular an additional root pruning. The format of bonsai shows, however, that almost all fruit species and varieties can be kept as a potted fruit with appropriate support and sometimes very intensive care.
Vulnerabilities of bush trees
For the current situation infection with fire blight weak -growing low strains are less suitable. The dwarf forms after an infection is usually only possible to clear the entire plant, since the necessary pruning ( starting from the infected site ) hardly leaves are the remains of the plant. However, a high strain can a correspondingly massive pruning of individual infestation sites cope relatively easily.
Vigor and refinement
It is a common misconception that high strains generally larger crowns trained as a half - or low strains. At the same root documents all of the above forms of similar form large crowns. However, in practice it is usually so that high strains on fast-growing base, half trunks are grafted on strong or medium strong base and low strains or bushes on medium-to slow-growing surface.
A free-standing tree, of whatever kind, is first not form a high trunk without human intervention. The first of crown is formed at the first random branching of the young seedling. However, when many trees to observe with age by their own shading of lower crown parts, the effect of self - Aufastung. Trees in a narrow forest inventory form usually up to about 10 meters high knot-free logs from. Since fruit trees are typically upgraded, you can not speak of a natural crown approach to this. However, old, unkempt fruit trees also tend to continual " aufzuasten " since the forming screen crowns shade the lowest crown branches, making the tree it can no longer obtain.
Mostly need fruit trees on medium-or slow-growing base due to their weak root systems artificial life support devices ( pole guy wires, trellis, etc.).
History
Low ethnic fruit trees were cultivated systematically only with advent of acquisition fruit crops in the 19th century. For they bring (compared to high strains ) earlier and higher yields with better quality; Moreover, they are much easier to harvest and maintain because no ladders are necessary. The German fruit growing pioneer Otto Schmitz -Pretty laid in 1896 at the first apple and pear orchards with low strains and thus developed what is now known as sealing planting or high-density planting. Schmitz -Pretty it was also the beginning of the 1930s the spindle bush ( Slender spindle) introduced. Because of the world wars and initial resistance of fruit growers, both innovations were as late in the second half of the 20th century by the world. Today, about nine out of ten apple trees in Europe spindle bushes.
Ecology
Ecology at high strains
Großkronige fruit trees are an asset to the landscape and ecological value, as they offer different species of bird and insect species that are on the Red List of endangered species habitat. This ecological function returns one hand, from the above-described problems, to manage them efficiently. So it is with standard trees instead of only extensive farming and the use of insecticides is not profitable. Second, high strains are able to absorb more damage. Thus the remains necessary for many insects dead wood in the tree or put up caves for multiple uses.
Some fruit recyclers carry high- strain - products in their range. In Switzerland Hochstamm Suisse is responsible for the non-profit promoting these cultures.
Ecology at Busch trees
Spindle bushes are in contrast to the big-crowned fruit trees, only a small addition to the landscape and have only a limited ecological function, they offer virtually no nesting. This restriction is on the one hand from the size of the plants, no large, hollow branches for nests, barely old textured bark that would be suitable as an insect hiding place and the need to manage them efficiently. Major damage can not cope with such a small tree, so that can do that for many insects necessary deadwood or even Asthöhlen not keep.
It takes place with spindle bushes only one intensive cultivation ( monoculture ) held in an extensive use of the tree would quickly suffer from the surrounding vegetation, senile and die without the constant care section quickly. The use of insecticides in conventional orchards is common, however, intensive organic farming is also possible and is an improvement of the habitat for many creatures dar.