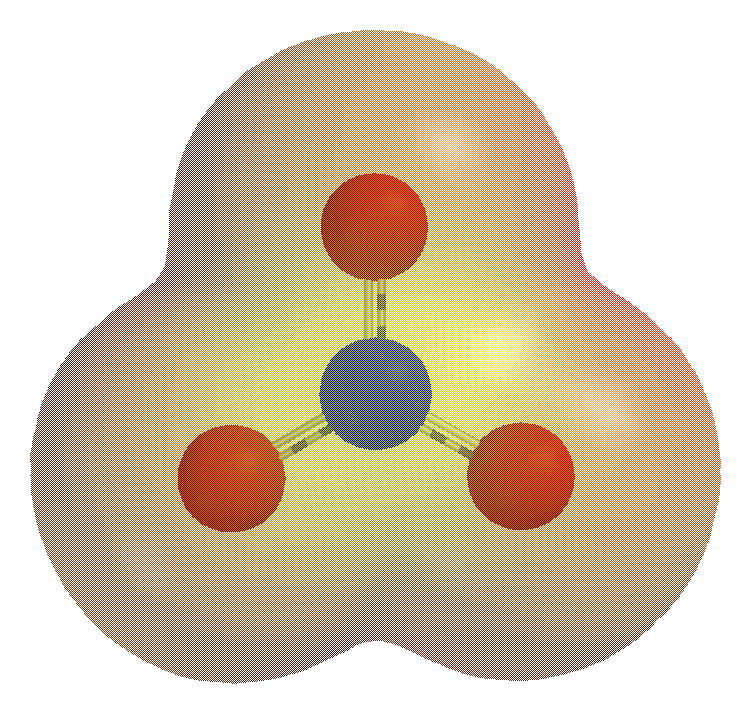
Ion
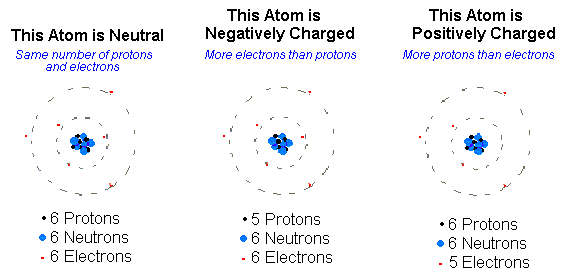
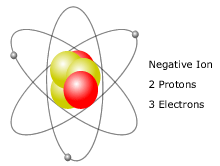
An ion [io ː n] (. AltGr ἰών or ἰόν ión "outgoing" ) is an electrically charged atom or molecule. Atoms or molecules are in the neutral state as many electrons as protons. Electric charge is formed, and thus the ion, when an atom or molecule having one or more electrons is less or more than in the neutral state. Ions are negatively charged at electron deficient positively and in an excess of electrons.
Fast ions moving in a direction to be studied in atomic physics, nuclear physics and particle physics or used, refer to ion irradiation, ion source or particle accelerators. A plasma (eg in the interior of stars) is a random ensemble of fast ions and electrons, which move at high temperature in all directions, like the molecules of a gas.
The following comments relate primarily to slow or stationary ions.
Positively charged ions are cations, negatively charged anions called because they each migrate in an electric field to the cathode (negative terminal ) and anode ( positive pole). In a solvent to form a solvation shell (see hydration shell ).
Formation of ions
Ions are formed from atoms when deliver or store these electrons. Although the separation of charges causes an expenditure of energy, the ions formed can be energetically favorable if they have particularly stable configurations, for example, satisfy the octet rule.
Cations
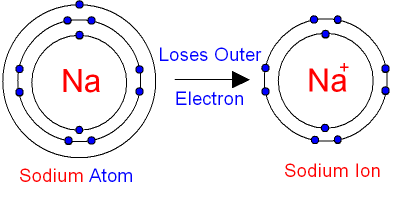
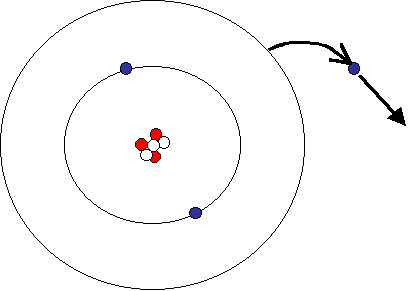
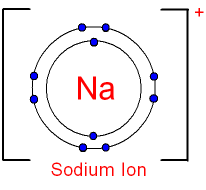
Positively charged ions, called cations, are formed when atoms give up electrons. Since the nucleus is still a positive charge has identical ( in the neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus of the exact number of the surrounding electrons), the ion appear in its entirety as a positively charged particle.
For example, metal ions are positively charged in the rule. Equation for the sodium ion form: Na → Na e - Equation for the magnesium ion formation: Mg → Mg 2 2e - Equation for the aluminum ion formation: Al → Al3 3e - Equation for the tin ion formation: Sn → Sn 4 4e -
Anions
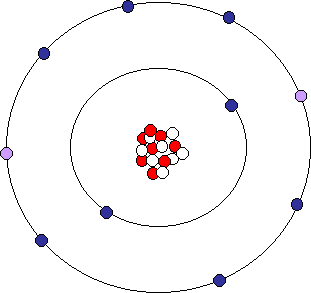
Negatively charged ions ( anions) are formed by atoms accept electrons. This results in an excess of electrons ( negative charge carriers ), which will be the existing protons ( positive charge carriers ) not balanced - outweigh the negative charges of the ion is negatively charged.
Example: non-metal ions are negatively charged in the rule. Equation for the chloride ion formation: Cl e - → Cl - Equation for the sulfide ion formation: S 2e - → S2
Moving ions form spontaneously when salts are dissolved in polar solvents (water ), eg
The subscript " aq" stands for aquatisiert, the subscript " s" stands for solid (English for proof).
As an example, the aqueous milieu of cells and organisms (electrolyte solution) may be mentioned. Here they play a crucial role in the electrical processes in membranes, especially for the excitability ( membrane potential, action potential ).
Identification
The ionic charge are the number of positive or negative electric charges having an ion. It is indicated by a superscript Arabic numeral form of the following a plus or minus sign. The general form is An- An respectively.
Examples are:
- Na - sodium ion ( n is omitted here, since N is equal to one)
- S2 - sulfide ion
- NH4 - Ammonium ion, a composite ion
For complex ions, the molecule is enclosed in square brackets and the ionic charge in superscript after the parentheses indicated.
Properties of the ion
The radius of ions differs from that of the corresponding atom. The cation radius is smaller - due to non- occupation of the outer atomic orbitals -, the anions mostly higher, as the outer orbitals filled with electrons and / or other orbitals are filled. Depending on the ratio of charge to radius ions act differently polarized in chemical bonds.
Ions of different charge formed by the ion binding salts. Solutions containing ionic substances that conduct electricity and therefore are called electrolytes. The reason for the conduction of the electrical current is the translational mobility of the ions within the solution. Information about the translational mobility of ions in the electrolyte solution, such as the diffusion coefficient, or the mobility in the electric field can be obtained through field gradient NMR methods. However, the measure can also be done with the "classical " method of the "moving boundary " (moving boundary ).
A cyclic ion is an ion which is configured in a ring structure ( cyclic compounds ).
Occurrence
Ions with more than three or excess charges rarely occur in chemistry.
In physics, ions are generated at specific experimental purposes, for example, with ion sources, but they also occur in nature, such as in the solar wind, the Rekombinationsleuchten of meteors, Polar lights, with a lightning bolt or a St. Elmo's fire (see also electric meteors ).
Gas ions play in the management processes in fluorescent lamps and other gas discharges ( electric sparks, lightning ) play a role. An ( almost) completely ionized gas is called a plasma.
Ionized noble gases can form ionic bonds. Noble gas-halide compounds can be used in excimer lasers.
For molecules with two or more functional groups, it is possible that they in a group a positive bearing on another a negative charge ( total of the molecule is then neutral). Such polar molecules are also known as zwitterions.
Electrolytes play an important role in metabolic processes and in batteries, such B.Lithium - ion batteries.
Configuration
After release or absorption of electrons Valenzelektronenschale has a different number of electrons than before. If the number of electrons of the ion in all shells equal to the normal constellation of a noble gas atom, one speaks of a " noble gas configuration ".