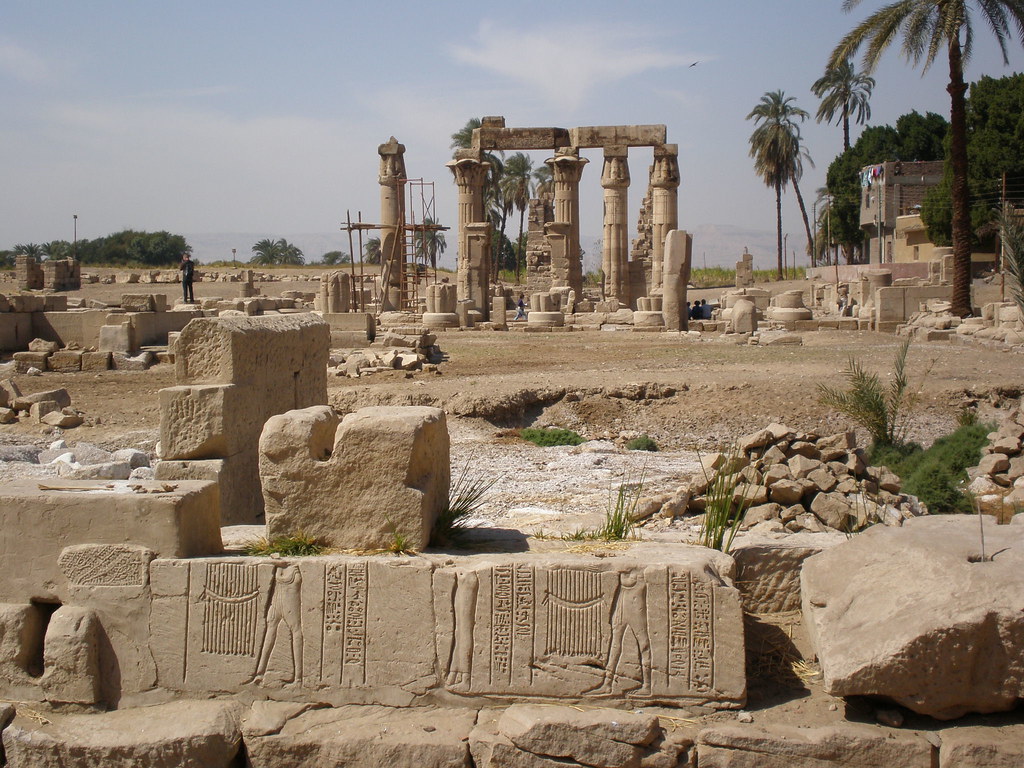
Medamud
Al - Madamud (also Medamud, Médamoud, Medamut, Medamot, Arabic المدامود al - Madāmūd, completely نجع المدامود Nadsch 'al- Madamud, DMG Naǧ ʿ al - Madāmūd, Weiler al - Madāmūd ', ancient Egyptian: Madu, Coptic: Ⲙ Ⲉ Ⲧ Ⲉ Ⲙ Ⲟ Ⲩ Ⲧ, Metemout ) is still inhabited village in Upper Egypt ( Egypt) north of Karnak, or approximately 8 km northeast of Luxor. In the west of the village is the Month Temple an archaeological site.
Meaning and function of the location in the ancient world
The ancient Egyptian place Madu ( M3dw ) is the location of the Month - temple occupied since the end of the Old Kingdom and the 1st split. The place name is obtained from the Coptic today. Obviously, the place had no other function. The local temple is one of the oldest archaeologically proven temple in Egypt.
Dear deities
The local temple was dedicated to the gods triad of Madu, these are the god of war mostly bull -faceted represented in the Late Period Month, his companion Rat- taui ( " Council of the two countries "), a female sun goddess, and their son Hor -pa - re -pa - chered ( " Horus -Re, the child "). Before the introduction of Amun as the main god in the Theban nome Month was the chief god of the Gaus. In the Theban area the Month temples have been dedicated to this god at Karnak and in at- death.
In Ptolemaic ( Greek ) Time is worshiped here in the same degree of wind and fertility god Amun, whose worship in this temple but already begun in the New Kingdom.
Architectural History
A first simple temple was located in the east below the present temple. It dates to the end of the Old Kingdom or in the First Intermediate Period, but prior to the 11th Dynasty. From the north was reached by two consecutive pylons in a double cave shrine, whose underground chambers were marked on the surface with mounds. These mounds were certainly the function of Urhügeln. With the rise of the water table since the construction of the Aswan Dam in 1970, this early temple was lost.
Sesostris III. ( 12th Dynasty, Middle Kingdom ) had build over these first temple with a temple of their own. The approximately 60 × 100 m wide, oriented from north to south temple was built of mud bricks. Only the doorways and columns, including the architraves were built of limestone. The entrance of the temple was located in the north. From the found fragments of two goals could be reconstructed. The sed festival portal that. At the coronation anniversary of Sesostris III recalls, is now in the ground floor in the Egyptian Museum of Cairo, the second in the open-air museum in the temple of Karnak.
In the 13th Dynasty, the temple was expanded and embellished particular Sobekhotep II. In the New Kingdom Thutmose III had. build his own 21 × 32 m large temple in the west of the temple from the Middle Kingdom. He was oriented in the east-west direction and consisted of a columned room offering table room and barqueshrine. The temple complex is thus already taken precisely at this time a double temple.
In Greco- Roman period, the temple was demolished, replaced by a new and greatly expanded. Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II (about 180-116 BC) leaves a pronaos in the west of the temple, supplement stand upright from the still five pillars including architrave. The Roman emperor Antoninus Pius ( 86-161 ) had the temple to another, the western courtyard with a double row of columns expand - the temple now had a size of about 75 m length and 42 m width. Emperor Tiberius Caesar Augustus ( 42 BC - 37 AD ) was a goal for the enclosure at the end of the avenue of sphinxes build.
To the west of the temple is a 200 m long avenue of sphinxes follows, which led to the quay.
At the end of the 4th century, a Coptic church is built on the temple area.
History of Research
The exploration of the temple was 1925 - 1932 by the French Egyptologist Fernand Bisson de la Roque, Alexandre Varille and Clément Robichon on behalf of the Musée de Louvre. Part of the collection is now exhibited in the Louvre and the Museum of Fine Arts in Lyon.