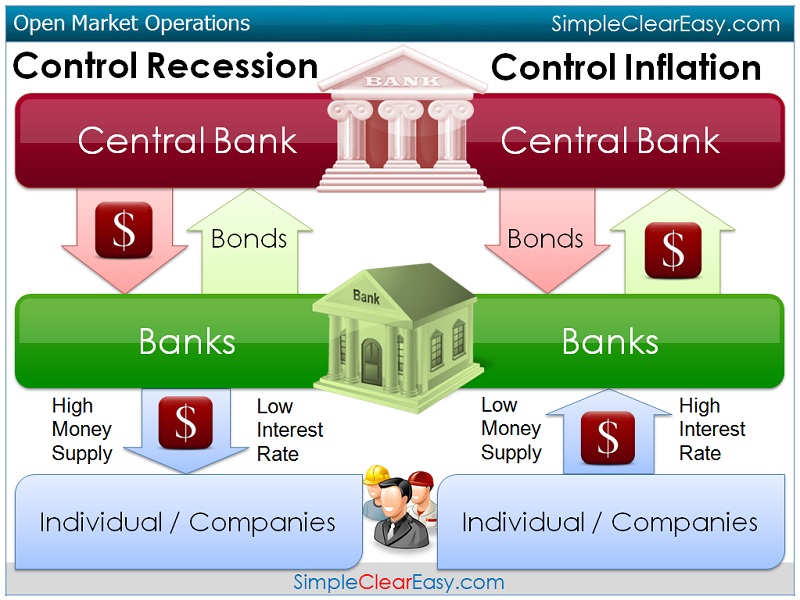
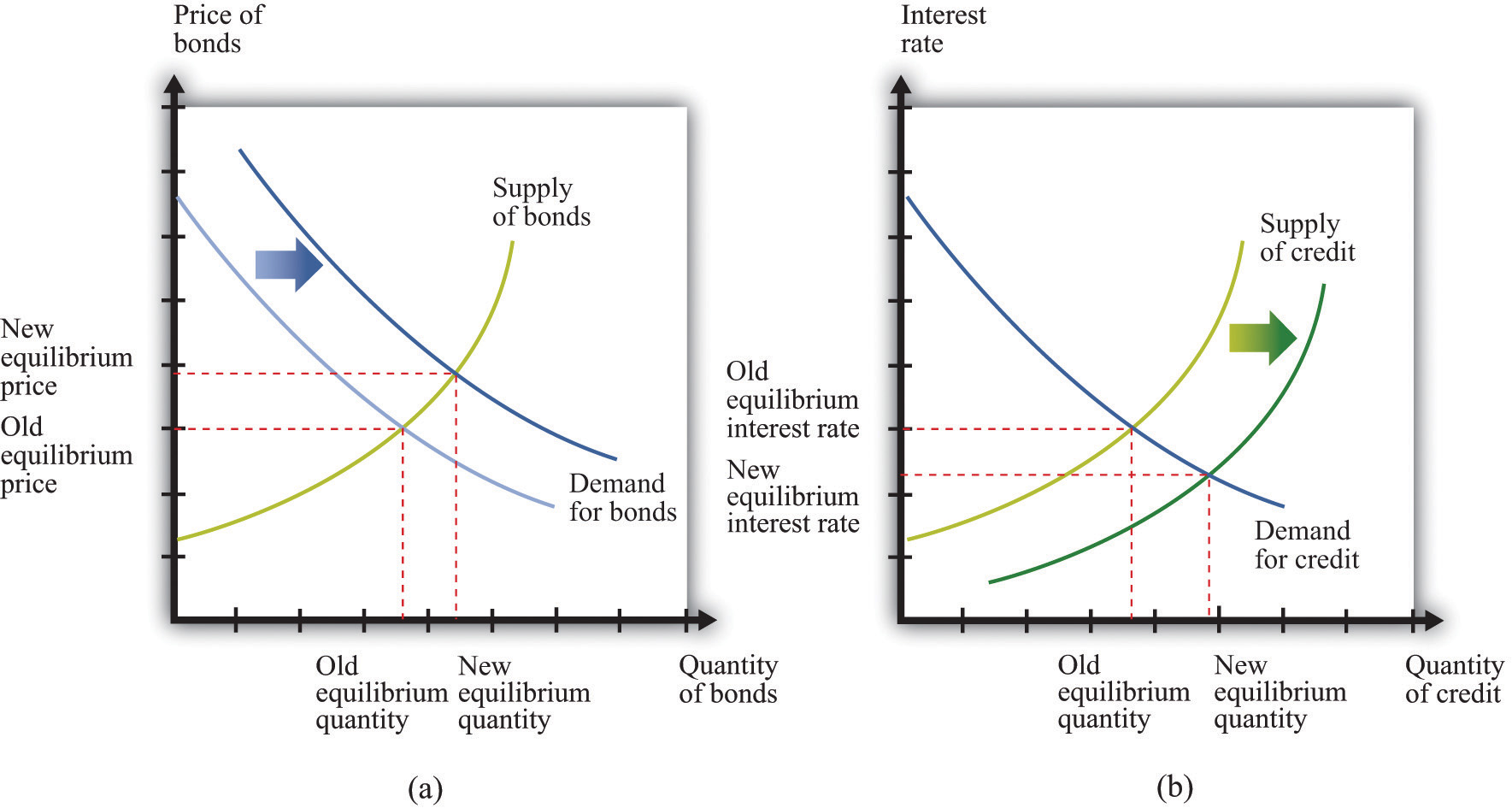
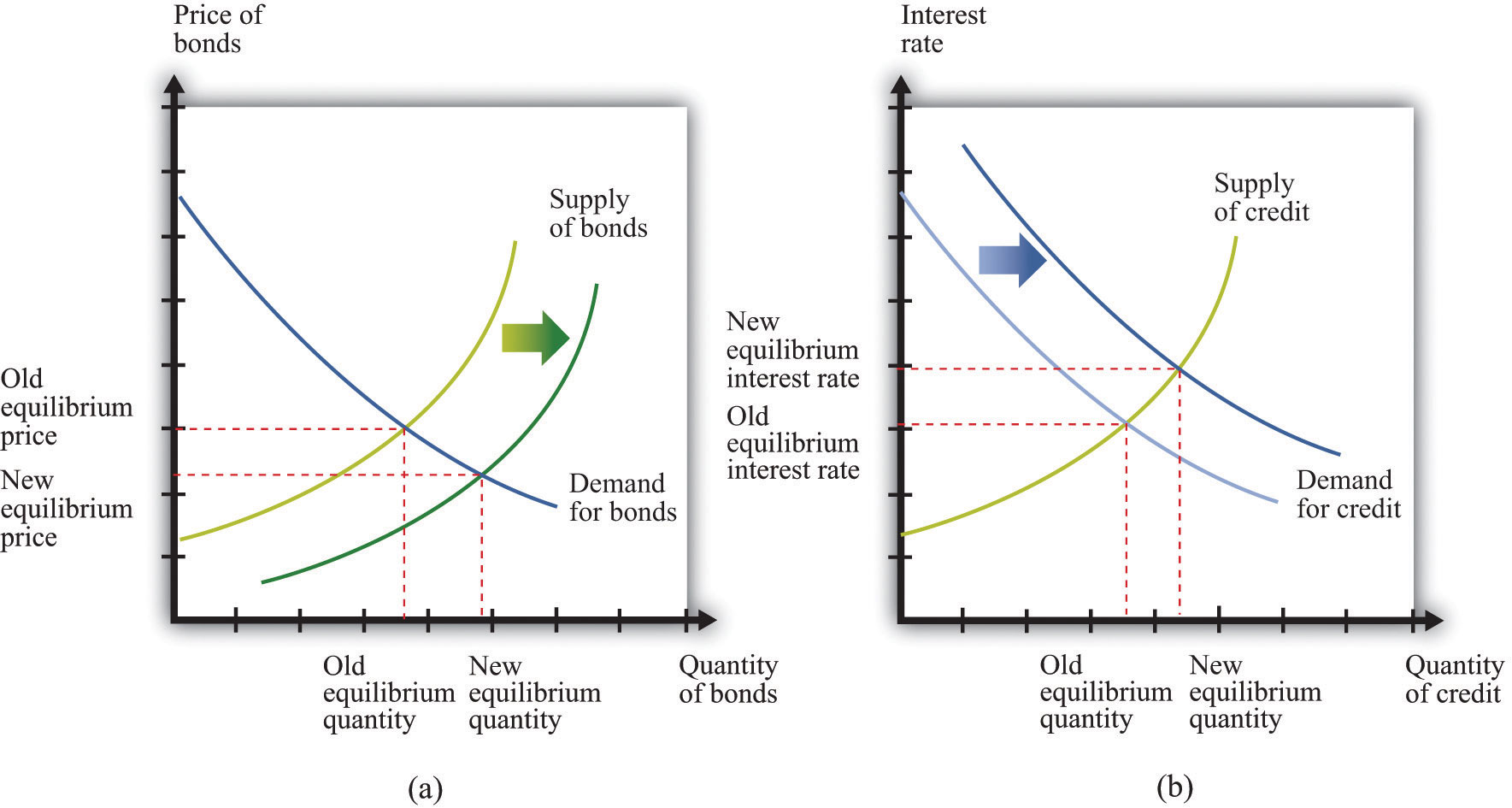
Open market operation
The open market policy is the main instrument of monetary policy, with the money creation affects the Central Bank ( by commercial banks ). The central bank provides the commercial banks to certain fixed income securities to buy or even buy securities from commercial banks ( open market operations ).
Buy the commercial banks securities by the central bank, this reduces their account balances at the central bank. Sold a commercial bank securities to the central bank, it receives in return ( asset swap ) central bank money (bare, non-cash reserves), which may use them for the fulfillment of the minimum reserves to credit creation.
The open market operations may, in particular on the choice of open market instruments (such as reverse transactions, foreign exchange swaps, outright ), the maturity of the instruments, the through seduction process, the implementation rate ( regular or irregular) and the allocation process can be distinguished.
The open market transactions, so-called reverse transactions dominate, that is those credit transactions in which the central bank buys eligible collateral in the context of short-term repurchase agreements with variable interest rates. These main refinancing operations ( main tender ) take the form of repurchase agreements or collateralised loans. In repurchase agreements, the collateral (usually securities) are transferred from the commercial banks to the Central Bank in accordance with the term to repurchase agreement ( also given in "Pension "). The commercial bank will in turn receive cash in the form of central bank money (secondary liquidity). In mortgage lending, the securities owned by the banks remain.
More open market operations are longer -term refinancing operations (basic tender), fine-tuning operations and other structural operations.
The methods for initial placement of securities through tenders are added in amounts and interest Tender ( " Tender" = tender ) differed ( auction). The ( administrative ) implementing procedures vary in standard and quick tenders procedures and in other bilateral procedures.
- 2.1 Standard Tender
- 2.2 Quick Tender
- 3.1 fixed rate tender
- 3.2 Interest Tender
Open market operations of the ECB
Open market operations are the most important instruments of the ECB and are the focus of monetary policy of the ESCB. They are used to control interest rates, liquidity, and to show the monetary policy stance. Through open market operations, commercial banks receive the bulk of their money against the pledge of collateral (such as securities). The initiative to open market operations is based on the ECB.
Main tender
The main tender is the main refinancing operation of credit institutions, which ( until the beginning of 2004 two weeks duration ) offered by the ECB every week with typically one week duration. The tender is carried out by the national central banks. He has a certain signal for banks. On the grounds of a high financing needs of banks at the end of 2007, the ECB has initially one-time increase on 19 December 2007, the maturity again in two weeks. The reason for this was the increase to 4.8 % interest for ECB monetary one hand, and the fact that banks have each other scarcely borrowed money due to the banking crisis. This extension led to a cut in interest rates on the money market in advance.
Base Tender
Fine-tuning operations
Fine-tuning operations are used to provide liquidity or absorb liquidity to counter unexpected changes in bank liquidity and thus to prevent excessive interest rate fluctuations in the money market. The implementation method is made in rapid tender or through bilateral procedures.
Structural operations
Structural operations are comprehensive measures for fundamental and lasting influence on the liquidity position of the financial sector relative to the central banking system.
Implementing procedures
Standard Tender
The standard tender is a method used in Euro system tender process, which is in contrast to the quick tenders conducted within 24 hours. The standard tender can be carried out either as fixed rate tender procedures as well as variable rate tenders. It is usually used for main refinancing operations ( main refinancing operations ) and longer -term refinancing operations (basic tender) used.
Quick Tender
To compensate for variations in liquidity quickly, there is the quick tender which belongs to the fine-tuning operations of the ECB. This is a tender procedure for monetary policy fine-tuning. The settlement of such a business and the money allocation occurs within 1-2 hours and is often performed with a limited number of banks. This tender may be withdrawn from the market of money or fed. It takes place only when necessary. The award may be limited to certain business partners.
Allocation process of the central bank money
The ECB conducted from 1 January 1999 when allocating a first rate tender, but changed due to the Überbietungsproblematik on 27 June 2000 to variable rate tenders. In the wake of the financial crisis, the ECB moved in October 2008 to re- rate tender procedure.
Rate tender
In the fixed rate tender procedure, the interest rate offered for central bank money is fixed. Commercial banks make bids in the amount of desired amounts of money that they wish to acquire. The allocation ratio is calculated by dividing the total proposed allotment is based on the total bid amount. The problem of the fixed rate tender is that the commercial banks tend due to the low interest rate to emit higher quantity bids than they actually need ( Überbietungsproblematik ). Called In the subsequent rate averaging ( pro rata allocation ), also scaling down, then they cut better.
Rate tender
With the method of variable rate tenders, the central bank can perform its open market operations. The Bank shall appoint to be emitted amount of money and also specifies a minimum bid, ie, the minimum interest rate at which it conducts open market operations ( as a signal of the monetary policy stance ).
The commercial banks then pass off their offered interest rates.
The allocation of central bank money will be made after the end of the bids:
The ECB used the American rate tender procedure. However, in the wake of the financial crisis, it is switched to the fixed rate tender procedures with full allotment. Settlement will be made by OMTOS ( Open Market Tender Operations System).