Pascal's law
Hydrostatic pressure (Greek ὕδωρ hydor, water), and gravitational pressure or gravity pressure is the pressure that is. Within a quiescent fluid is a liquid or a gas, set by the influence of gravity The term is contrary to the word meaning " water " used for other liquids, and even gases. Dynamic pressure by fluid currents, such as the dynamic pressure is not detected by the hydrostatic pressure, it considers only static, static fluid.
- 2.1 stars in equilibrium
- 2.2 Examples of stars in the imbalance
Incompressible fluids in a homogeneous gravitational field
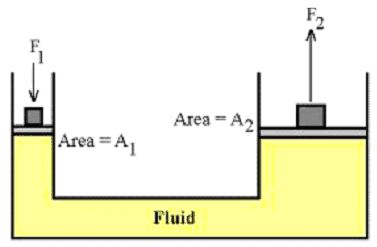
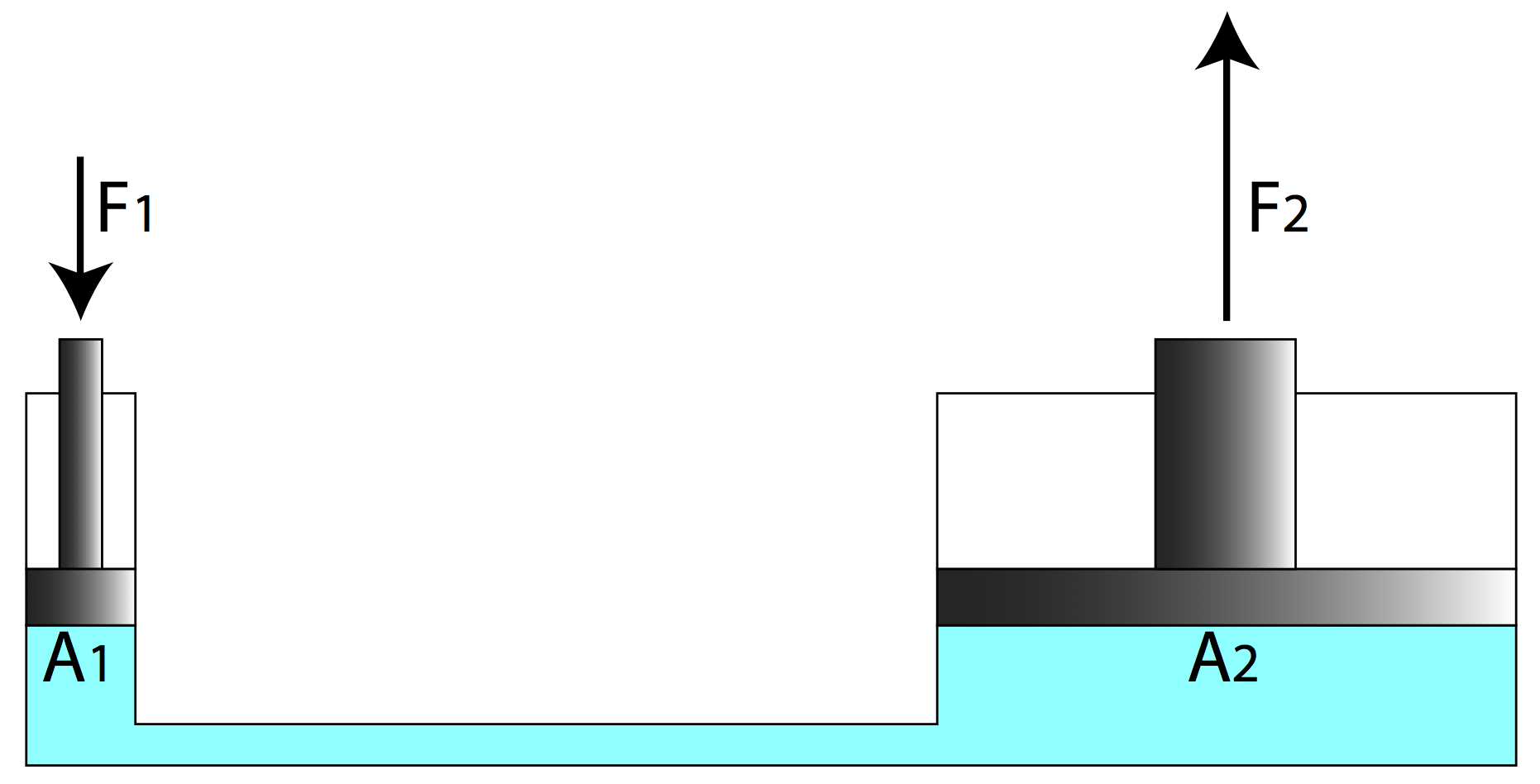
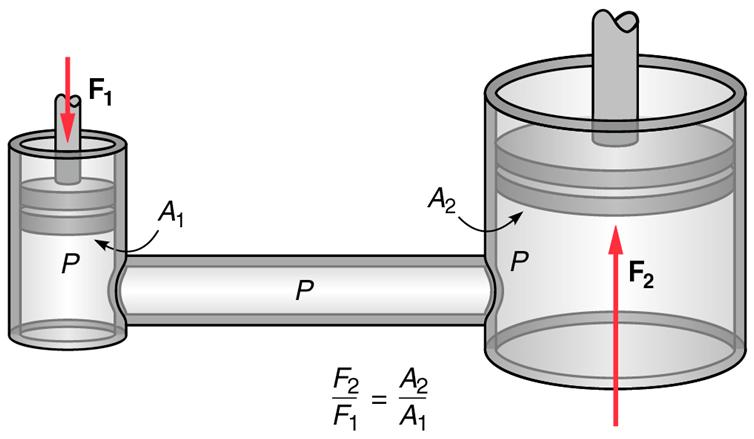
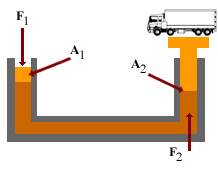
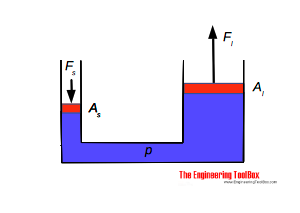
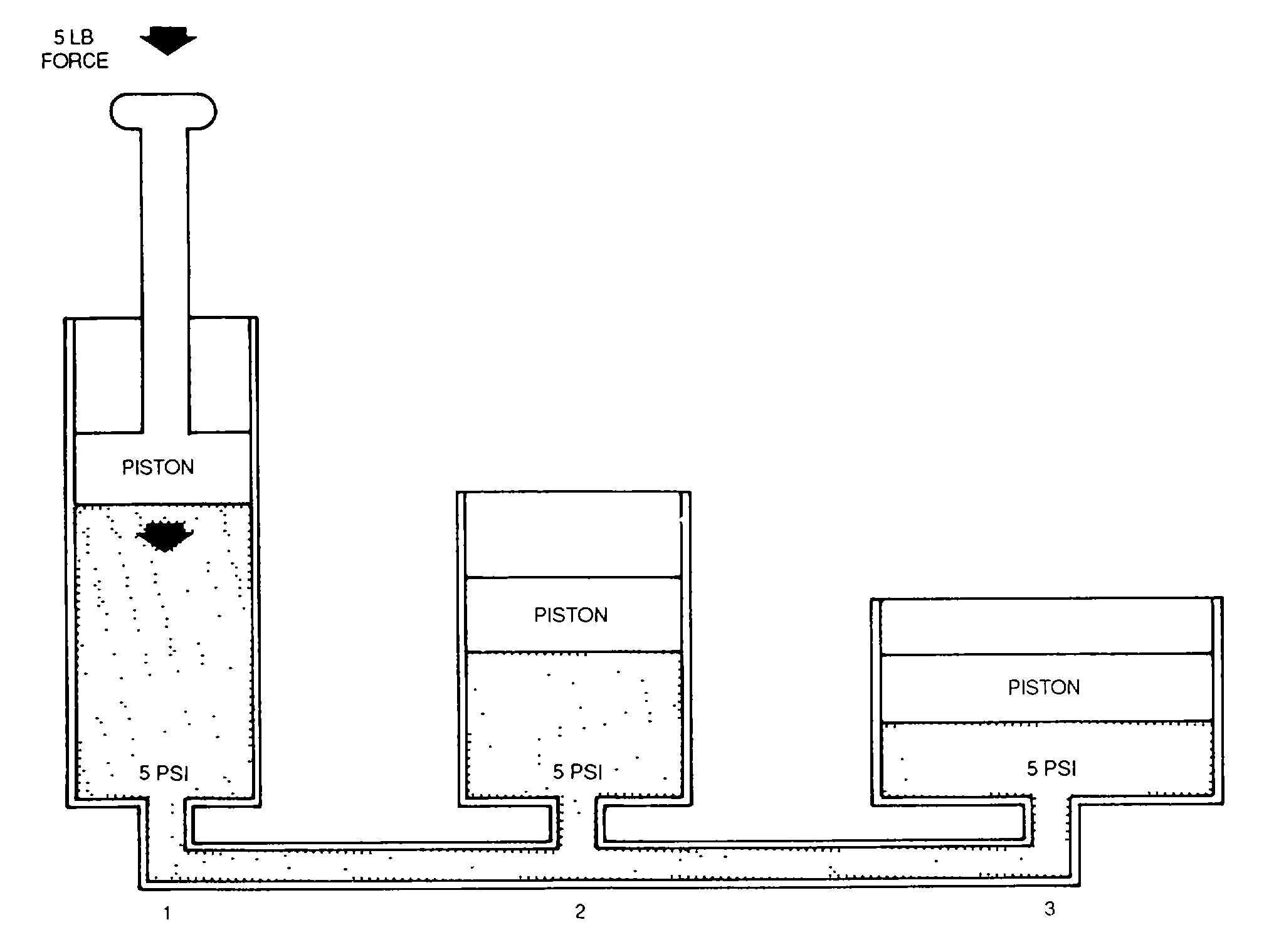
Pascal's law
The hydrostatic pressure for fluids with constant density in a homogeneous gravitational field (eg liquids) is calculated according to Pascal's law (named after Blaise Pascal ):
Unit: N / m² ( = Pa, Pascal ) or bar (1 bar = 100,000 N / m )
With:
Example water column (height 50 m): 50 m × 1000 kg / m³ x 9.80665 m / s ² ≈ 490 333 N / m ≈ 4.90 bar
The hydrostatic pressure does not depend on the shape of a vessel. Critical to the pressure at the bottom is only the level of the liquid, not the absolute amount of the liquid in the vessel. This phenomenon is known as hydrostatic paradox.
For a full description of the pressure in a fluid at rest you have to add the atmospheric pressure to the hydrostatic pressure yet. As the water pressure acting on a diver in a stationary water the amount of air pressure acting on the water surface and the hydrostatic pressure of the water corresponds to itself
For a description of the hydrostatic pressure is in part the non SI -compliant old unit " meter water column " ( abbreviation 1 m water column ) were used.
Examples
- For divers, it is important to know what pressure their bodies gases ( nitrogen), are exposed in order to avoid the bends.
- A bathyscaphe must withstand particularly high hydrostatic pressure.
- Water towers use the hydrostatic pressure in order to produce the necessary for the provision to the final line pressure.
- In hydrogeology flow between two points may be governed by the Darcy's law only set when the pressure difference is different from the difference between the hydrostatic pressures at the two points.
- A hoist is a device or a device with which you can decant a liquid from a container on the container rim into a lower reservoir or drain into the open without tipping the container and without that he has a hole or an outlet below the liquid level.
Gravitational pressure in stars
Stars in the balance
A special case of hydrostatic pressure, the gravitational pressure in stars dar. This results from the twitch the star gravity. On the other acts such as the radiation pressure as the star expanding force. With a stable star is doing an equilibrium of all forces and the star has a stable shape. This is approximately the condition of stars on the main sequence.
Examples of stars in the imbalance
With emerging stars, which contract outweighs the gravitational pressure compared to the sum of all the forces that build up back pressure. Examples of back pressure are the kinetic gas pressure of the gas itself and when starting the fusion reaction of the radiation pressure from all types of radiation occur. This is the hydrostatic pressure within the emerging star changed.
For some classes of variable stars occur periodic or transient changes in the stellar density, whereby the quantity of matter of the star that is within or outside a sphere with a fixed radius changed, and with it, the hydrostatic pressure at a given radius from the star center out.
Due to the stellar wind steadily losing star mass to the environment. Also by the hydrostatic pressure changes. For main sequence stars, however, this change is very slow.
In the late stages of a star's life, it also leads to changes in the stellar structure, which affect the hydrostatic pressure in the star.