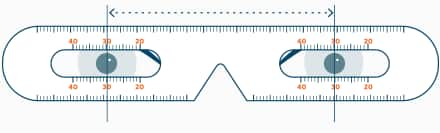
Pupillary distance
As viewing distance (synonyms: interpupillary distance (IPD ), Pupillardistanz (PD ), pupillary distance ) is called each other the indicated in millimeter distance between the two eyes in the ophthalmology and optometry. He has to be considered when customizing a pair of glasses and is used to align the optical axes of the lenses ( main visual point ) at which the eyes (eye axes).
Physiology
The viewing distance in humans is an average of 65 mm (men) or 62 mm ( women), but can vary depending on the constitution and size in the range between about 55 mm and 75 mm.
Scientific studies show that, the eye relief, even if only to a small extent, have an influence on the ability to distinguish distances.
The viewing distance is used as a biometric feature in face recognition.
By means of his own thumb and the interocular distance can be estimated to an object according to the theorem on the so-called thumb jump the distance.
Pathology
Too large or small eye relief may be pathologically related.
Hypertelorism
The term hypertelorism denotes a relatively long eye relief. Often hypertelorism is accompanied by a telecanthus. Hypertelorism is defined as a distance between the centers of the pupils ( interpupillary distance IPD ) above the 97 % percentile of a pro rata distribution in the normal population. In adult women, one interpupillary distance is greater than 65 mm, greater than 70 mm indicated in men than hypertelorism.
Hypertelorism is not necessarily a feature of the disease. Quite often it is an isolated anomaly, which is often perceived as a feature of women to a certain degree as attractive. Famous examples are Liza Minnelli and Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis. Pronounced or asynchronous hypertelorism can seriously affect as a serious cosmetic defect and speak for surgical correction of the distance between the eye sockets.
Hypertelorism is a component of a variety of syndromes, for example, it is found in people with cat cry syndrome ( 5p, Cri -du -chat syndrome), Wolf- Hirschhorn syndrome (4p - ), Zellweger syndrome, triploidy, Noonan syndrome, Gorlin - Goltz syndrome, Fraser syndrome, trisomy 14, Edwards syndrome ( trisomy 18), trisomy 22, LEOPARD syndrome, de Grouchy syndrome, Mabry syndrome, Crouzon 's disease and Dubowitz syndrome, down syndrome ( trisomy 21), Alagille syndrome.
Hypotelorism
The term hypotelorism denotes a comparatively small eye relief. It frequently happens in people with Patau syndrome ( trisomy 13), trisomy 8, trisomy 9, holoprosencephaly or fetal alcohol syndrome.
Measurement
Reference point for the measurement of the interpupillary distance, either the pupil or center of the outer edge of the iris. Because of the dynamic pupillary game latter is easier to assess, in particular for inexperienced examiner. The determination is carried out either by summing the left and right eyes, the pupil distance from center to center of the nose, or through the measurement of the distance between each right and left edges of the iris. In a spectacle pass the values will be listed separately for the distance between the right and left pupil center to the center of the face in general (eg, 32 mm / 33 mm ), which enables the documentation of asymmetries and thus to determine the visual points in the spectacle lens a higher precision allows the measurement of the eye to the eye ( for example, 65 mm).
The own interpupillary distance itself can be measured with some accuracy, if you only determines a distant point with the one and then targeted with the other eye on a kept at a small distance ruler and the difference of doing readings.
Optical Devices
To set the Okularabstände optical equipment that come with a binocular tube, there are special devices that take into account the individual eye relief and thus ensure an optimal view.
Another meaning of the term " viewing distance " is the distance from eye to the eyepiece, which should not exceed a certain value, to avoid triggering limitations of the visual field.