Pyrolysis
The pyrolysis or pyrolysis ( from Ancient Greek πῦρ pyr 'fire' and λύσις lysis, ( On ) solution ') is a thermo- chemical cleavage of organic compounds, due to high temperatures ( 200-900 ° C) a bond breakage within large molecules in smaller is enforced. In contrast to the gasification and combustion of this is done only under the effect of heat and without addition of oxygen supplied, the combustion air ratio is. In oxygen-containing fuels, such as biofuels like wood with an oxygen content of about 44 mass percent, but can still be involved in the oxidation reactions decomposition processes.
Older names for the pyrolysis are Pyrolysis, Dry distillation or degassing. The root word " Hot " in the names of chemical compounds such as catechol, furoic acid and pyruvic acid goes back to this. Also in the process of coking coal and charcoal production and wood gasification Pyrolysevorgänge take place, in addition to coke or charcoal is produced combustible gas and tar. Chemically and the cracking of petroleum is seen a pyrolysis process, but is not called that.
- 4.1 Application examples for pyrolysis in rotary kilns 4.1.1 of activated carbon and regeneration
- 4.1.2 Pyrolysis of waste
- 4.1.3 Altholzrecyling
- 4.1.4 Soil Remediation
History
By smoldering won tar and pitch are the oldest plastics of mankind. Already in the European Mesolithic period (8300-4000 BC) knew the tar and pitch extraction ( birch pitch ) by pyrolysis.
Over the centuries, different systems have been installed to Teergewinnung. They used mines, the double pot method and tar works or smolder. Depending on the target by smoldering ( charcoal or tar or charcoal and tar and other by-products), one can distinguish two main processes:
- Allothermic the process, here are reaction and firewood separated. Mention may be made, the double pot method, the two-chamber furnace ( Wiethagen ) and today the retort.
- The autothermal process, there is no separation between response and firewood. These include reactors, the tar pits, the ditch or slope kiln or kiln- oven ( single chamber ).
As starting material for the Teerherstellung resinous pine wood, obtained from the roots ( stump ) of old trees is particularly suitable. In the Slavic countries ( Teerschwelen of Nettelsee, Schleswig -Holstein) is used mainly the wood of the birch.
Museums and applications
On the forestry and Charcoal Wiethagen (Rostock) and in Düppel (Berlin), there are historical and tar works in a model park originals and models of the most important Holzverschwelungsanlagen from Central Europe.
Tar and pitch was used as an adhesive and sealing. When shoeing and stealing cutting wood tar is used as a disinfectant today.
The dry distillation is one of the oldest chemical processes used by man. The dry distillation of birch bark birch pitch delivered. Also the Stone Age man who died around 3340 BC on the Similaun and was found to be frozen mummy, named Ötzi, joined the shafts of his arrows with the tips of flint using plant fibers and birch pitch.
When fire behavior of wood is called pyrolysis also the time at which charred the top layer of wood slowly and thus forms an insulating protective layer for the remaining cross section. The so-called temperature firing time graph, the pyrolysis takes place in phase 1 ( ignition) at temperatures between 100 and 200 ° C.
Technical Process
Differentiation pyrolysis - gasification
Usually is called with the word gasification processes in which the addition of a gasifying agent ( steam, air or oxygen), the total organic content of the feedstock is converted to gaseous substances, wherein only the mineral ash or slag remains. Here, the solid is oxidized to carbon monoxide and partially combusted thereby.
The word pyrolysis is used in a narrower sense for processes in which remains in addition to the mineral constituents of the feedstock and solid carbon. This residue is called at an appreciable carbon content as pyrolysis.
Differentiation pyrolysis - thermolysis
Previous large-scale pyrolysis processes were mainly the destruction of waste, the so-called energy recovery. However, not only the continuous DGE method provides the technical requirements for the specific production of products in a defined process atmosphere.
Pyrolysis
Generally, gases, liquids and solids. The amounts and the composition will depend not only on the starting material, but also on the pyrolysis temperature, the added additives, and the pressure conditions of the treatment period. Depending on pyrolyzed product and reaction temperature arise, for example rather long-chain or short-chain molecules. During the pyrolysis of polymers, the corresponding monomer is produced in many cases, as a significant proportion of the pyrolysis gas.
On cold spots in the reactor vapor pyrolysis products can condense (eg creosote ) and may drip out at leaks.
Basic variants of the method
There are two basic variants, the one direct, and on the other the indirect pyrolysis.
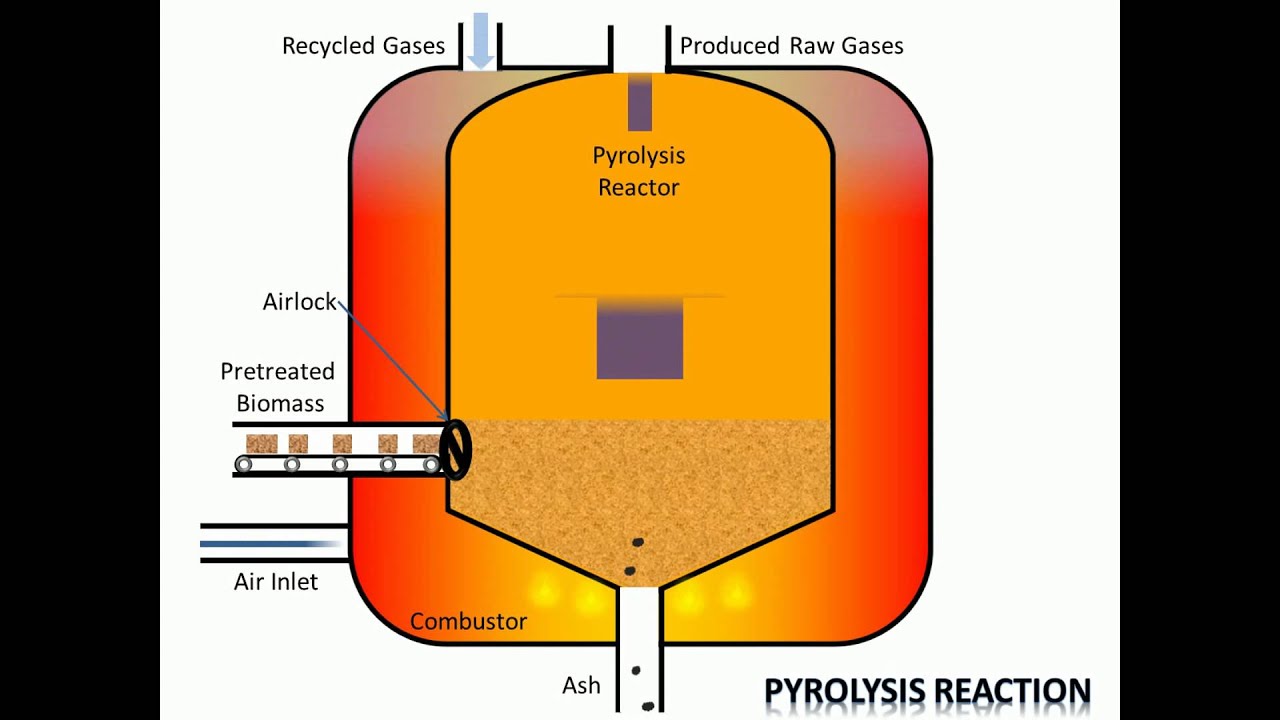
The direct pyrolysis heats the Good to be pyrolyzed by combustion gases. Pyrolysis may gain the required heat energy from the pyrolysis itself. Here, the reaction temperature is controlled by the supply of air in a closed container.
In the indirect pyrolysis ( closed, heated from the outside space ) oxygen-free atmospheres can be tailored. The heating is carried out from the outside, in most systems with hot gases. In particular, in laboratory equipment, there are also electric heating systems.
Usually the pyrolysis takes place under the exclusion of oxygen ( anaerobic) in order to prevent combustion. We also speak of smoldering. If necessary, dehydrogenation or dehydration agent are added during the process.
The so-called coal liquefaction is the reaction of carbon with the addition of hydrogen to hydrocarbons. It is not a pyrolysis process, although here is a solid to a liquid. The production of fuels from biomass, BtL fuel, however, is a pyrolysis and distillation process.
Technical Applications
Application examples for pyrolysis in rotary kilns
These methods are distinguished by the fact that the pyrolysis gas is almost no pressure in the entire system.
Of activated carbon and regeneration
After coal and binder are mixed to form a defined mass, pellets are pressed and heated in an oxygen -free atmosphere.
Spent, namely contaminated with the pollutant carbon is heated in an oxygen-free atmosphere and the pollutants are driven off at temperatures of about 800 ° C and partially cracked.
Pyrolysis of waste
The difficulty in the pyrolysis of waste is in the non-homogeneous product with a variety of contaminants. The actual pyrolysis is relatively easy. The problems include processing of the incoming waste, and the use of the pyrolysis gas. The interspersed with heavy metals pyrolysis must be disposed of as a rule only in landfills.
Altholzrecyling
Since 2005, a Drehrohrpyrolyseanlage (manufacturer TechTrade / MHI) is for waste wood recycling in operation in Japan. Produced a coke which can be used for further chemical processes.
Soil remediation
At the beginning of the 1980s, in the shadow of the large tanker accidents, the pyrolysis of the company PLEQ was brought to the soil remediation for the market and there were built several systems for the following substances:
- Dioxin- contaminated soil
- Oil-contaminated soils,
- Mercury- contaminated soils.
Organic contaminated soils are degassed in a directly or indirectly heated with oil or gas burners, rotary drum. The organic pollutants are expelled in this way from the material and destroyed in an afterburner. If included in the feed, volatile heavy metals (mercury ) are also mobilized and then deposited in a special flue gas cleaning. Dioxins and furans decompose above about 500 ° C in oxygen deficiency ( Hagen Maier process).
In contrast to direct firing arising from the indirect pyrolytic floor cleaning only small amounts of pyrolysis gas. This allows the Pyrolysegasreinigung be much smaller and cheaper. This advantage must, however, be paid for with a more elaborate system technology for indirect heating.
In Germany, a plant from the SITA operates. 2007 pyrolysis and heating muffle increased by TechTrade type MAXI- 08 Type MASTER 09.
A design like facility for cleaning of dioxin - contaminated soil in Spolana is now shut down because the project was successfully completed.
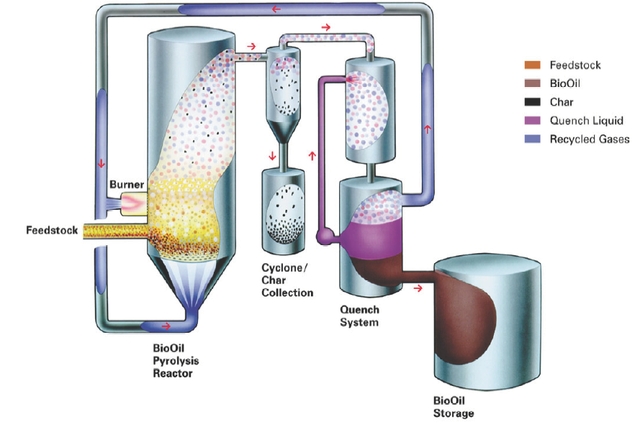
Flash pyrolysis of biomass
Flash pyrolysis is a patented in multiple variants method, which is applied to different configuration of the starting materials. The method approaches differ, particularly in the design of the reaction zone, the hydro- mechanical guidance of the stream and the process conditions for the cleavage of precursors to a desired end product for further thermal or chemical yield.
The known processes generally require all of a reduction in the oxygen content of the process atmosphere in order to reduce the burning of the starting material to the subset required for a thermal reaction. The finished product is depending on the process surrounding solid ( coke ) or liquid (tar). Because of the high content of complex phenols the liquid products are highly toxic and require distillation before use in non- completed processes.
The methods can be used for wood products and for other less carbonated raw materials, such as power plants or dried organic waste. So far, the method no role to play in terms of quantity and value in reactions of biomass for the establishment of sustainable energy production. In particular, the allegedly environmentally beneficial production methods of the feedstocks from agriculture are controversial.
In the flash pyrolysis condensates are obtained as a rule with an acetic acid content of up to 40%. Acetic acid is a decomposition product of the biomass pyrolysis and cracking starting only with increasing temperature from 330 ° C to 620 ° C. Since the process temperature is in the condensate production often not mentioned in the literature, this leads to irritating generalizations in the terminology pyrolysis oil.
Wood or biomass gasification
Main article: Biomass Gasification
At a biomass gasification process, it is understood in the biomass is converted into a synthesis or fuel gas. The biomass is carbonized via pyrolysis, the pyrolysis gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO ), hydrogen ( H2), carbon dioxide (CO2 ), methane (CH4 ) and a number of trace gases and metal contaminations as raw materials are used in the biomass gasification especially lignocellulosereiche agricultural commodities and forest wood into consideration, a special form is the wood gasification, in which wood is used as a raw material. Existing biomass gasification systems are designed for the gasification of wood in the form of forest wood and wood residues, which are supplied as wood chips.
For biomass gasification different technical carburetor can be used, which differ primarily by the type of contact between biomass and gasification agent (air, oxygen or hydrogen). There are three basic types of reactors are generally used: fixed-bed gasifier, fluidized bed gasifier and entrained flow gasifier. The gasification in a rotary tube seems entirely unknown in the general literature, but was successfully tested in 2009.
Types of procedure for the pyrolysis of scrap tires
When Altreifenpyrolyse different procedural approaches are preferred. For one, there are batch furnaces operating in batches, on the other, continuously operating furnaces. In the continuous pyrolysis furnaces are divided into two shaft furnace and rotary kiln.
From the tire granules 40% result soot / carbon 50 % oil (on the diesel -like properties ) and 10% of the permanent gas. The permanent gas is used for the process. Depending on process parameters, the values can vary significantly.
Favorited offered is currently the size of the plant MIDImit a throughput of 600 kg / h
Plastic recycling
For plastics recycling a fluidized bed pyrolysis is used by the so-called Hamburger process.
Other pyrolysis and application fields
- Acetylene by the HTP method
- Cracking as a process for the production of petrochemicals aromatenreichem gasoline, which is characterized by good anti-knock properties ( pyrolysis gasoline )
- Flash vacuum pyrolysis for the synthesis of complex structures such as fullerenes
- Charcoal production
- Industrierußherstellung
- Carbon fiber -reinforced carbon: In the production of such materials, pyrolysis is an essential step.
- Coking (Coke production from lignite or hard coal)
- Pyrolysis in combination with gas chromatographic methods (eg, GC / MS ) for the investigation and determination of polymeric materials
- Torrefaction as partial pyrolysis under mild temperatures to increase the calorific value of biomass
- Hydrogen from water using plasma torches
Explosion safety
If the temperature of the reaction chamber is too low or is sucked in through faulty seals on cooling oxygen, an explosive mixture can form. However, from about 450 ° C, the free oxygen reacts immediately in the case of a partial combustion of the combustible contents of the reactor (gas, carbon) and may form explosive mixtures more.