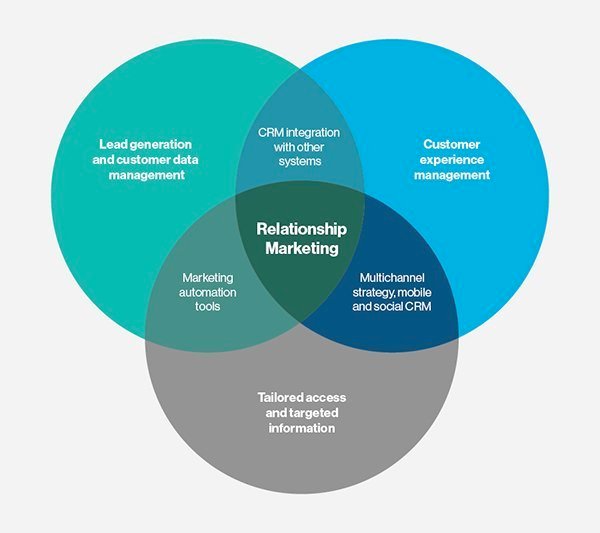
Relationship marketing
The relationship marketing or English Relationship Marketing is dedicated to the development and expansion of long-term customer relationships. It aims to attract more customers, satisfied customers and profitable customers for the company or brand. Unlike in the previous marketing the focus is therefore not placed on, for example, the price or the product, but on the relation of company or brand and customer.
Wholeness of relationship marketing
Customer relationships are subject to complex influences and can be most fully designed and captured in a holistic marketing system. This holistic approach combines qualitative and quantitative range. The qualitative range covers all strategic preparations and measures to promote relationship that can be accounted for indirectly. The quantitative range includes the economical instruments with immediate measurability. Qualitative and quantitative range are planned holistically, that is, the relationship marketing is long-term oriented content and is therefore not determined by short-term tactics.
A general broad definition of relationship marketing widens the viewing angle to the relations with stakeholders of the firm: Although the customer is the center of attention as before, the exchange with suppliers, employees, society and the competition will be given greater consideration.
Methodology
In order to include the various relevant to the relationship marketing issues, a methodical approach offers. For example, the relationship equity method are applied. The relationships with existing customers are analyzed, goal-oriented set up and expanded, custom- designed and systematically controlled. Customer relationships improve hereby in terms of number, satisfaction and profitability. The total value added is finally increased.
Basic understanding
Through relationship marketing or relationship marketing long-term customer relationships ( customer loyalty ) are to be built. This can only develop if the customer recognizes their needs and requirements, and for this purpose appropriate marketing measures are developed. This high- aligned relationship marketing considered interdisciplinary insights, for example, from the relationship psychology. So-called "soft" factors such as the positive basic emotion in a customer relationship are taken into account.
Dynamically designed marketing
The dialogic communication with customers through all channels is a crucial aspect for the relationship marketing and can assume a leadership role for the entire corporate culture. The relationship marketing takes on, in contrast to traditional marketing is no longer a management-related position. In a dynamic process, the customer has the opportunity to become the co-designer of the relationship. Pointing beyond merely instrumental marketing measures can here identify the customers with the company and develop an emotional attachment. There are emerging relationship values that increase the impact and effectiveness of marketing.
Individual customer relationship
Regular and thus rehearsed purchase transactions require less information and coordination of effort and stabilize the business. The main advantage is that they give rise to an individual relationship between companies and customers, which can be disrupted by competing only with considerable effort. This allows the individual customer relationship, very specifically to interact with the customers in the dialogue and thereby make effective marketing measures.
Business Background and objective
The necessary revenue to cover costs and make a profit may come from new customers or existing customers. Especially in the early phase of a Produkt-/Unternehmenslebenszyklus when the customer base is still small or even non-existent, but also at a later stage, namely, when the sales potential is exhausted for existing customers, new customer acquisition is the focus. In difficult economic times, in dynamically changing market conditions, with increased competition, arising from the cost side constraint to growth and the fight for market share, the expansion of relationships with existing customers is becoming increasingly important. In addition, the acquisition of new customers more costly is usually as a business expansion with existing customers.
The economic objective of relationship marketing is long-term profitable customer loyalty to the company. Customer contribution margin or customer lifetime value is eg possible control mechanisms here. This requires on the one hand to build a regular clientele and on the other hand their commitment to the company, what should a supplier or brand changeover reduce / prevent and increase the repurchase rate.
Economically -oriented marketing activities
In relationship marketing, the entire business relationship is with the customer in marketing focus. This is the one to variants of the classical marketing instruments and other customer- oriented management concepts. Some forms of relationship marketing should be listed here as examples: product development in cooperation with customers, integration of customers in the value chain, customized product customization, value added services, performance guarantees; Price concessions for regular customers, loyalty discounts, loyalty programs, price guarantees, cost escalation clauses; Customer Advisory Boards, stem customer service ( number), customer magazines, regulars events, subscriptions; Cross-selling, post- sale marketing, customer recovery; Customer clubs, loyalty cards, originating customer-friendly complaint management. In addition will be added to the special treatment of key accounts by key account manager for large customers.
Increased operational efficiency
The benefits of a high-quality relationship with customers is complex: on the one hand, increases with a positive history of a customer relationship, the willingness to pay the error tolerance and the sales volume per customer. With better knowledge of the needs of individual customers, or by the growing knowledge on buyer's side regarding the company's internal processes of care effort decreases. Third, a company can react through an intensive dialogue with customers quickly to changing demand and potential for improvement. And recently, a high level of customer loyalty - under certain circumstances - be considered as an entry barrier to potential competitors.
Data Management / CRM
An effective relationship marketing is facilitated by the growing availability of individual data. This data provides the customer relationship marketing software for CRM (Customer Relationship Management ). The CRM software can access databases of all Customer Data. The customer- specific evaluations of such powerful customer databases allow a very promising relationship marketing. However, the use of CRM systems alone is no guarantee of a successful relationship marketing. In many cases, the practical application of CRM successes behind expectations remain, which is often due to a unilateral application with insufficient integration into the company. Here is a holistic integration into the Relationship Marketing is required.
References
- Ian Gordon: Relationship Marketing. New Strategies, Techniques and Technologies to Win the Customer You Want and Keep Them Forever. John Wiley and Sons Publisher. In 1998.
- Adrian Payne, Martin Christopher, Helen Peck, Moira Clark: Relationship Marketing. Text and Cases. Oxford: 1999.
- Manfred Bruhn: Relationship Marketing. The management of customer relationships. Munich: Franz Vahlen GmbH. 2009
- Customer Relationship Management