Respiratory epithelium
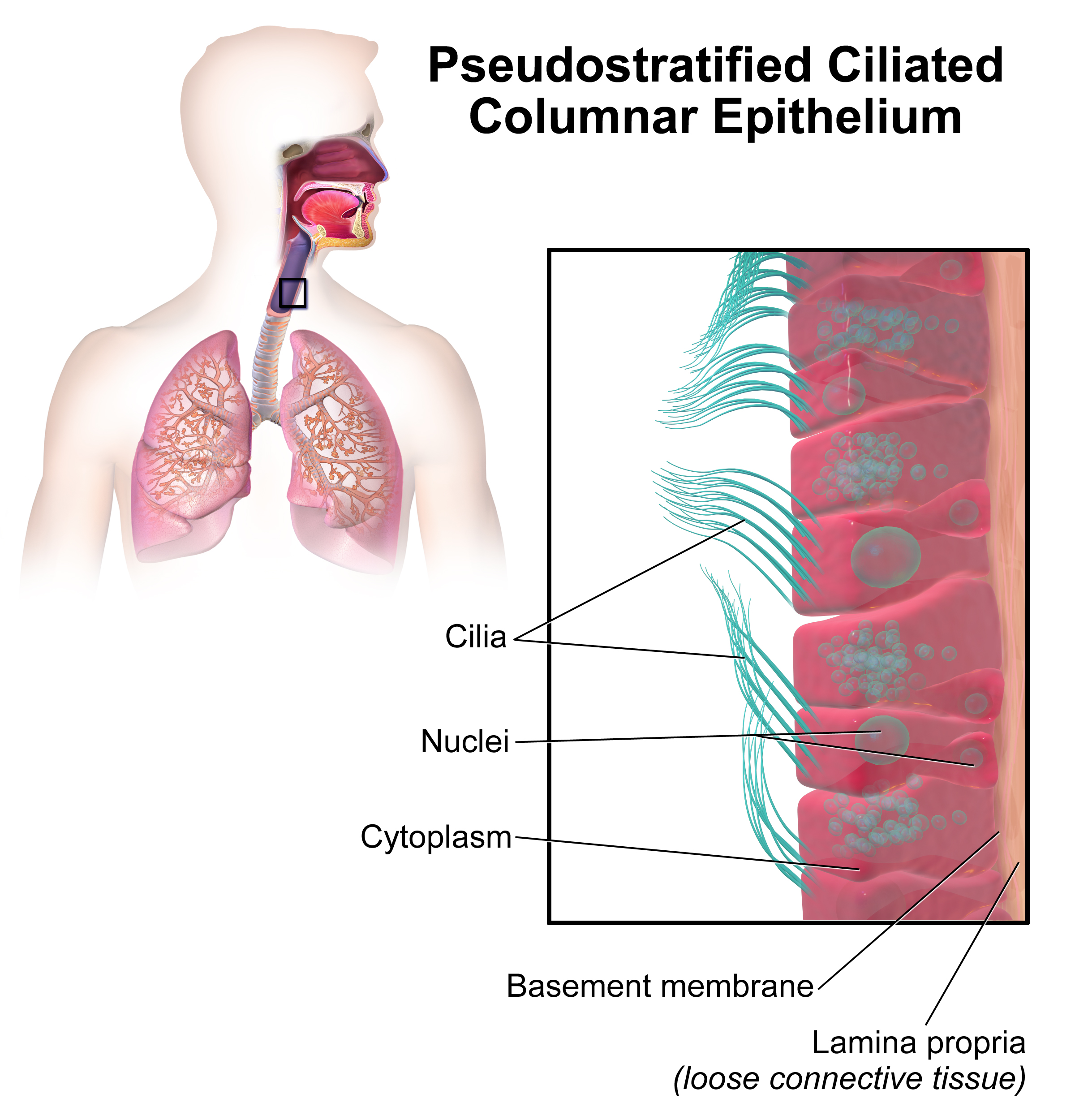
The ciliated respiratory epithelium, or is a layer of specialized epithelial cells lining most of the respiratory tract. It is characterized by cilia ( cilia ) on the luminal cell surface. The respiratory epithelium is used, even if the name suggests, non- gas exchange, but the cleaning of the airways.
Histologic structure
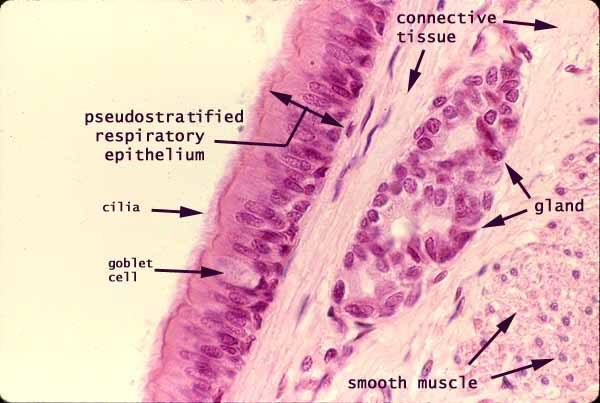
The respiratory epithelium is a multi-row columnar epithelium, which is equipped with cilia and goblet cells. The goblet cells located within the epithelium make physiological, between 15-20 % of the epithelium. All cells are associated with the basement membrane.
The thickness of the epithelium decreases along the bronchial tree toward the alveoli continuously. The past just before the alveoli bronchioles ( terminal bronchioles ) have only a single layer epithelium.
Cilia -bearing cells
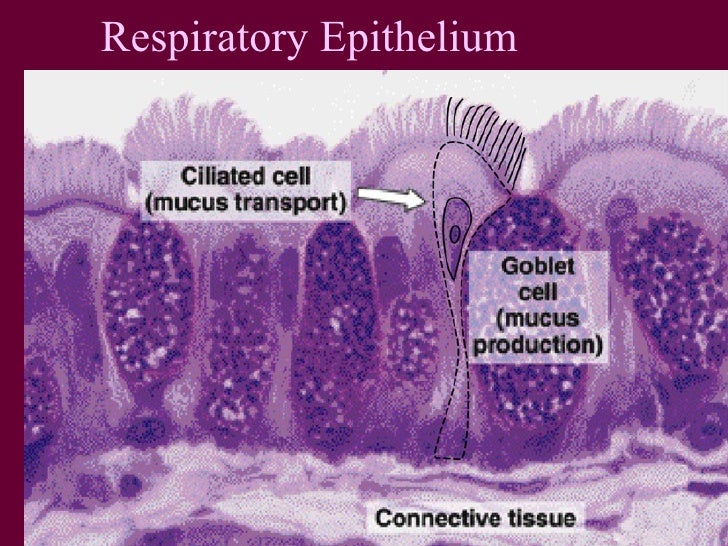
You are the body of the cells of the ciliated epithelium. Cilia are moving protrusions of the cell membrane at the apical pole of the cell, which are about 7-10 microns in length and have a diameter of about 0.3 microns. Motility is provided by so-called microtubules. These cilia move symbolically as stalks in the wind and transported by this movement mucus and unwanted substances from the lungs and resolve as a rule to cough out. According to the latest research results they have in addition to this purely mechanical task nor a sensory function. For example, bitter substances such as nicotine or quinine meet cilia -bearing cells, as the calcium concentration increases inside the cell, the cell is activated and the total reaction starts to remove harmful substances from the lungs.
Goblet cells
The goblet cells are unicellular, cup-shaped glands that - in addition to the serous and mucous glands of the lamina propria - produce bronchial mucus. The their secreted mucins covering the epithelium and moisturize the past trending breath.
Other cells
Besides these two cell types the ciliated epithelium still has sensory cells that have contact with afferent nerve fibers at their basal pole. You loose in a irritation from the cough or sneeze reflex -. The basal cells represent a precursor of the mature epithelial cells and provide the cell replenishment.
Physiology
The epithelium has a sophisticated self-cleaning mechanism. The moving cilia line the airways of like a dense turf. Their coordinated movement is geared toward the throat. Thus, the bronchial and have penetrated into the airways smaller foreign particles and microorganisms are constantly being transported from the respiratory tract.
Occurrence
Respiratory epithelium is found in the following locations:
- Upper respiratory tract: Sinuses, such as sinus or antrum
- Nasal respiratory region
- Epiglottis ( epiglottis ) on the side of the larynx ( laryngeal page )
- Velum ( soft palate ) on the side of the nose
- Nasopharynx ( epipharynx )
- Larynx (voice box )
- Eustachian tube ( auditory tube )
- Windpipe (trachea )
- Bronchia
- Bronchioles