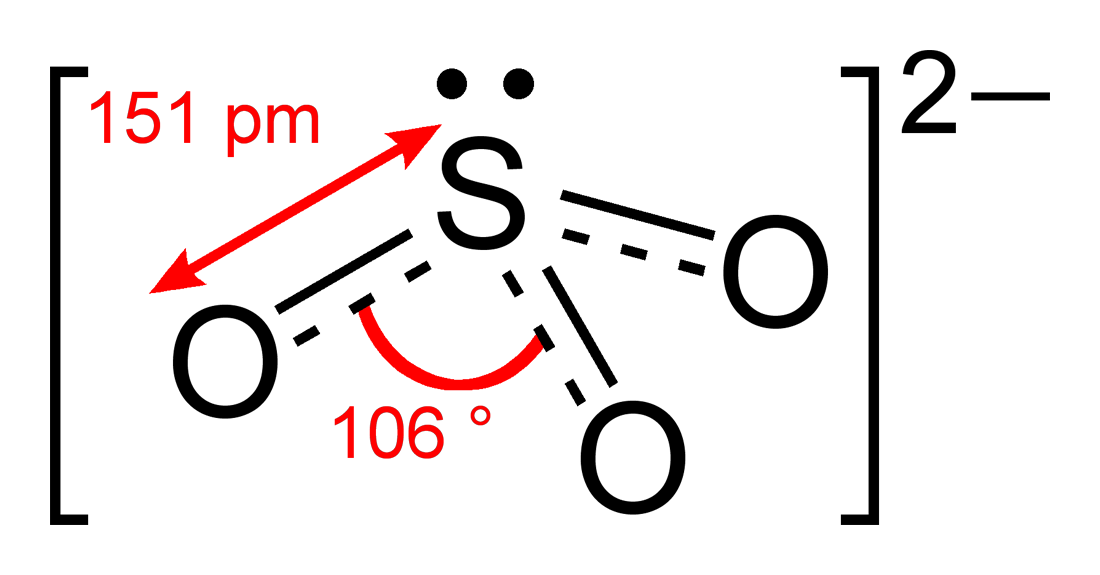
Sulfite
Sulfites are salts and esters of sulfurous acid H2SO3. The salts as anion sulfite ion ( SO32 - ). They are often used as a preservative in wine, dried fruit and potato products. However, sulfites also occur naturally in almost all wines.
Also be referred to as esters of sulfurous acid sulfites which having the general formula ROS ( = O)- OR ' ( with R and R' are organic radicals ).
The sulfurous acid is a dibasic acid. Therefore, among the salts exist
- Sulfites ( MI2SO3 ), also known as normal or neutral secondary sulfites and
- Hydrogensulfites ( MIHSO3 ), which are also called primary or acid sulfite or bisulfite.
Hydrogensulfites are non-existent as solid salts, and are just in aqueous solutions. During evaporation of a solution to respond hydrogensulfites elimination of water and formation of a sulfur -sulfur bond to disulfites ( S2O52 ):
Use
Sulfites are used as reducing agents. The bisulfite anion reacts in chemical reactions as a nucleophile (eg with aldehydes to form readily crystallizing salts). Important process for the production of pulp and paper from wood to work with sulfites (especially Calciumhydrogensulfit, according to Mitscherlich ).
Sulfites in wine
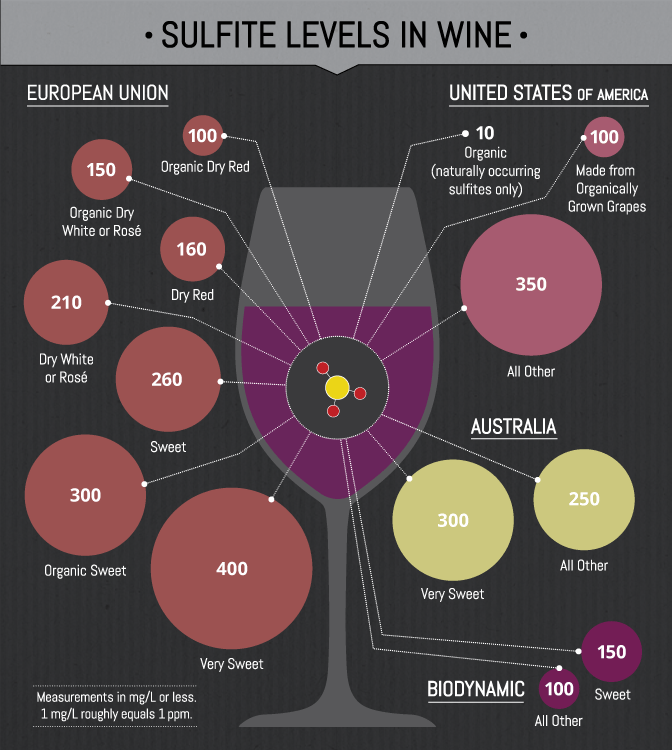
The label " contains sulphites " or " contains sulfur dioxide " is under Article 3, paragraph 3 of the wine market organization implementing regulation - Regulation (EC) 753/2002 - mandatory at concentrations greater than 10 mg / l. In the U.S., have wines that were bottled after mid-1987, contain a reference to sulfites on the label. The corresponding regulation in the EU has applied since 2005. Labeling goes back to being people with a hypersensitivity to sulfites in consumer and small amounts of sulfite intolerance reactions such as Bronchospasm and asthma, anaphylactic reactions, urticaria, and hypotension show.
Sulfites produced in small quantities ( 10-30 mg / l) in a natural way during the alcoholic fermentation (see alcoholic fermentation ) of the wine. Since the end of the 18th century, the antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of sulfur known. Since that time, the addition of sulfur in the world's wine production is firmly anchored. In quantities of wine are used sulfur dioxide between 90-400 mg / l. Sulfur dioxide ( SO2) is the wine gaseous, in aqueous solution, as " sulfur powder " ( potassium ) in the form of tablets or as before, added by burning barrels with sulfur chips.
Sulfites allow to store wines for long periods without the wines " upset " by oxidation completely. They also prevent undesirable secondary fermentation in the bottle filled with sweet wines, as it (such as yeasts) effectively prevent microorganisms in their work.
The addition of sulfites is permitted for wines from organic and also must be marked on the bottle.
There are some places efforts within the wine industry to make wines without sulfur dioxide. Club tents conventional as well as Bioweingütern manages this for several years with success, mainly thanks to the modern wine technology.
For sulfur dioxide in wine exist limits according to EC Reg.
Proof
Qualitative detection can be done indirectly with Permanganates. This discolor in a redox reaction when sulphites are present.
The reaction is not specific to, sulfites, and may, therefore, be used as proof of sulfites, when the presence of other reducing agents is excluded. Likewise, an iodine solution is decolorized by sulfites, where iodine is reduced to iodide and sulfite is oxidized to sulfate.
With sodium nitroprusside forms in the presence of zinc ions, a red precipitate of Zn2 [ Fe ( CN) 5SO3 ]. With barium chloride, a white precipitate of barium sulfite, the slightly soluble in acids, in contrast to barium sulfate forms.
Examples
Salts of sulfurous acid are
- Potassium
- Sodium sulfite
- Magnesium
- Sodium hydrosulfite ( sodium bisulfite )
- Calciumhydrogensulfit ( calcium bisulfite ).
Esters of sulfurous acid are
- Dimethyl