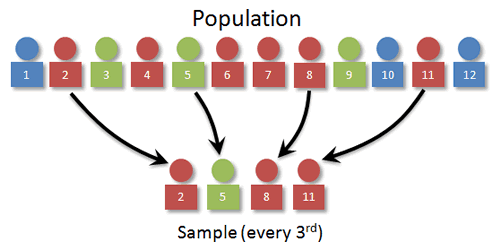
Systematic sampling
As a systematic sample ( also conscious selection ) is called selection, where subjective considerations determine the selection of the target persons.
It can be used preliminary information on the cases to be selected. Generalizations are not possible on the basis of mathematical and statistical models in conscious selections.
Types of conscious selection:
- Theoretical sampling,
- Selection of typical cases / Typical selection: selection of such items that are considered to be particularly typical or characteristic.
- Snowball selection and
- Quota sampling ( quota sample ): As in the stratified random sample will first give a classification of the elements of the population into groups. After that, the share of each group in the total population is determined. The sample is now to draw so that this group ratio in the sample as possible looks exactly like in the population.
- Cut - off method (concentration principle): Selection of such elements, which are of particular importance, for example in the capital goods market research, such as interviewing leading large enterprises, allowing the number of respondents / investigation units to reduce without much loss of information concerning the object under investigation by that only those elements are included in the selection that are relevant with regard to the investigation target.
- Sampling theory
- Empirical Social Research