Toric lens
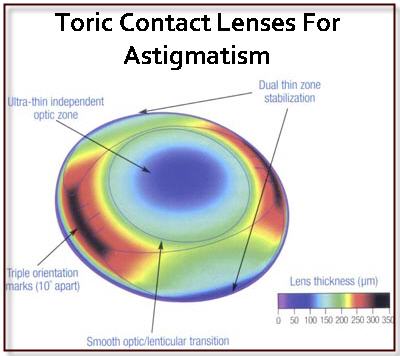
A toric lens is a lens having two different refractive indices in two mutually perpendicular directions. One of the lens surfaces has the shape of a " caplet " of a torus ( Fig. 1), the other is usually spherical. Toric lenses are used in particular for ophthalmic lenses, contact lenses and intraocular lenses for the correction of astigmatism.
Torus
A torus is formed when a circle having a radius rotated about an axis ( axis in Figure 2), which lies in the same plane as the circle. The center of this circle follows a circular path with a radius about the axis of rotation. If, you get a Ringtorus. If the opening has shrunk in the center of the rotation circuit; one speaks of a Horntorus. When, we speak of a Spindeltorus; stay here from the opening left only two wells whose depth vanishes when going. If, the torus degenerates into a sphere with the radius. ( See Figure 3 )
Description
The largest radius of curvature of the toric lens surface ( see Figure 2); The corresponding smallest refractive index, when the refractive index of the glass. The smallest radius of curvature, corresponding to the largest refractive index. As is, is. The difference is called in ophthalmology and optometry the cylinder correction. The glass behaves somewhat like a combination of a spherical lens with the refractive index and a cylindrical lens with the refractive index.
Note that the maximum and minimum curvature of both of which are circular. Contrary to what many believe, the toric lens surface is therefore not a part of an ellipsoid of revolution.
Effect
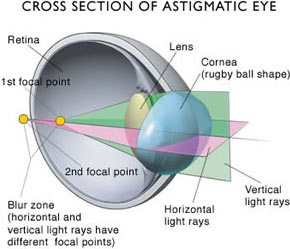
Light rays incident in the ( ) plane of the torus ( see Figure 2) are refracted according to the largest radius of curvature, that is the smallest refractive index.
Light rays in a plane through the axis of the torus (Fig. 2) corresponding to the smallest radius of curvature, which is the largest refractive index, broken.
There are thus two different refractive indices in mutually perpendicular directions. In the intermediate directions of the refractive index is gradual from smallest to largest or vice versa. This compensates for the astigmatic deviations of the eye.
Atoric lens
Computerized design, grinding and polishing procedures make it today to achieve in a larger field of view good corrections by introducing certain deviations from the torus. In this case, the term (literally, " non- toric " ) from a non-toroidal lens.