Viridiplantae
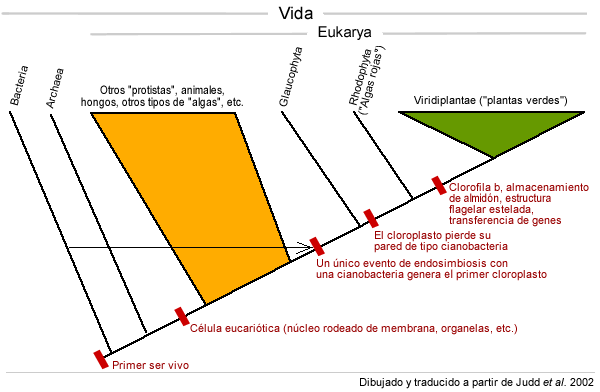
The Chloroplastida or Viridiplantae are a group of photosynthetic eukaryotes, ie organisms with cell nuclei. They include the green algae and plants.
Features
The vast majority of Chloroplastida have photosynthetic plastids with chlorophyll a and b, chloroplasts. Exceptions are organisms that have secondarily lost the ability to photosynthesis. These include, for example, the parasitic living Neottia or the colorless alga Polytoma. The plastids originate from a primary endosymbiosis with a cyanobacterium. Frequently plastide a pyrenoid is present. The Chloroplastida usually have a cell wall made of cellulose. The cristae of mitochondria are flat. As memory serves carbohydrate starch. With the exception of angiosperms, the cells have centrioles.
System
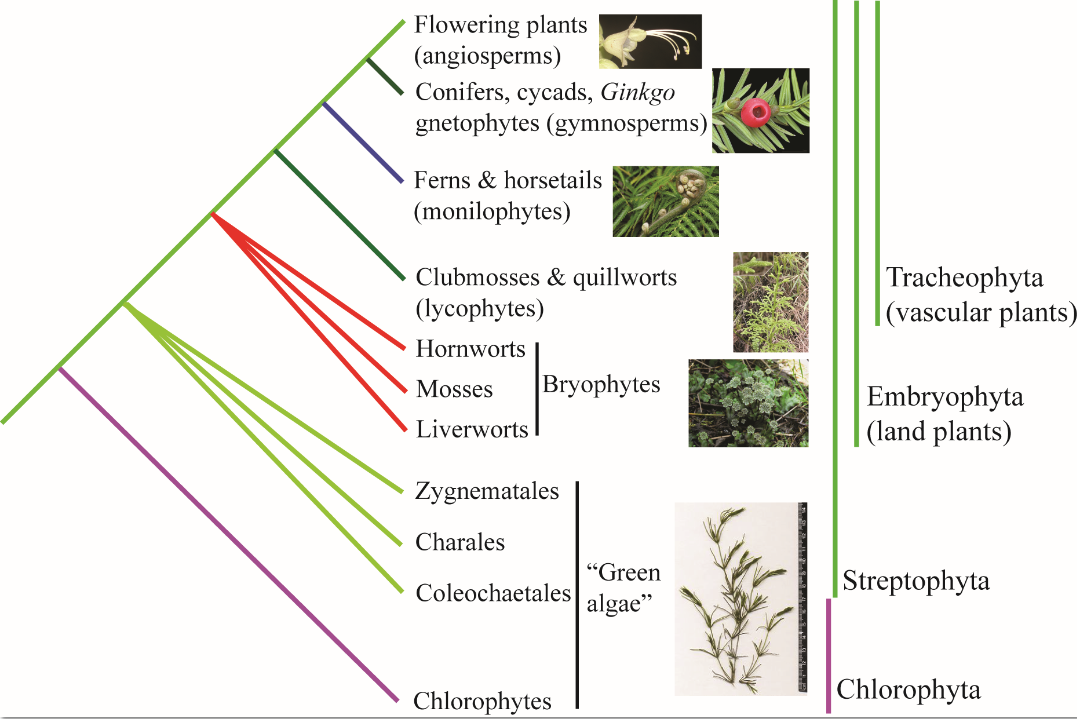
Within the Chloroplastida there are two major clades that are strongly separated: the Chlorophyta and the Charophyta ( which include the plants belong ). Both the Chlorophyta as well as several representatives of Charophyta are classically referred to as green algae. Thus, the term green algae is no longer usable for a taxon.
Et al Adl divided on the basis of Lewis and McCourt the Chloroplastida into the following groups without classical ranks ( in the Adl among others omitted small groups are re-inserted ):
- Chlorophyta Ulvophyceae
- Trebouxiophyceae
- Chlorophyceae
- Coleochaetales
- Chlorokybus
- Klebsormidium
- Zygnemophyceae Jochalgen ( Zygnematales )
- Desmids ( Desmidiales )
- Chara ( Charales )
- Plants (Plantae )
The Chloroplastida meet the Viridiplantae Cavalier- Smith, 1981; the Chlorobionta Jeffrey, 1982, emend. Lewis and McCourt, 2004; and the Chlorobiota Kendrick and Crane, 1997.