Wood drying
As wood drying method is called for the withdrawal of moisture from wood.
Target
Target controlled drying process is used to achieve the moisture content of the wood. This is usually between 8% and 16 % moisture content (based on the weight of the oven dry wood ). For comparison: Forest Fresh wood contains about 40 % water. Only through controlled drying, drying can damage ( tearing, Planking, discarding the timber ) should be avoided. During the drying process of wood for combustion to generate energy (firewood drying) is a rapid removal of water in the foreground to improve combustion characteristics and heat output of the fuel.
Method
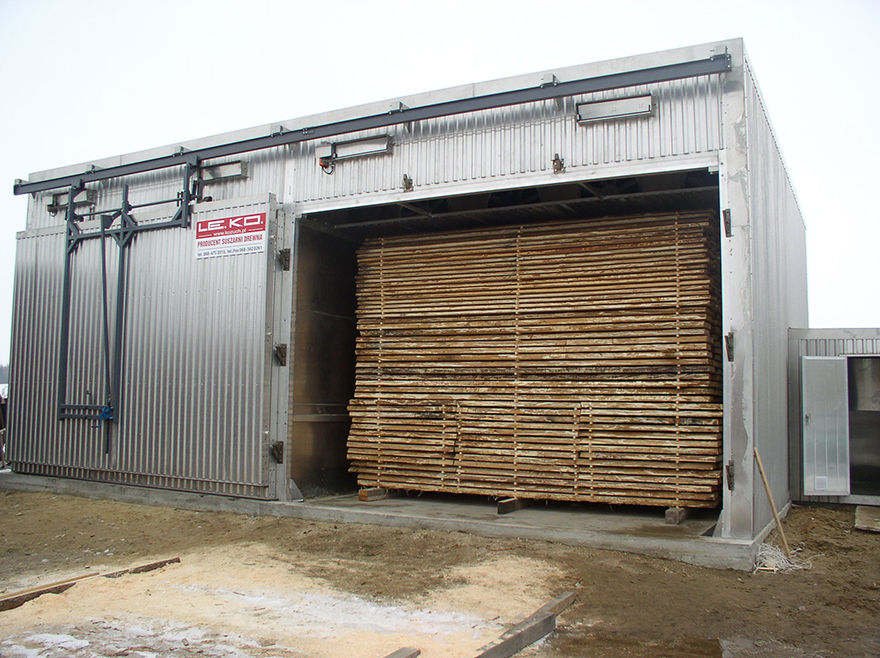
The wood drying takes place during the wood processing either by open-air drying (especially firewood) or by technical means of thermal drying process (evaporation, evaporation) in dryers. Other methods for fast drying very permeable and therefore easy to be dried woods are the high-temperature drying and the high frequency drying.
Convection
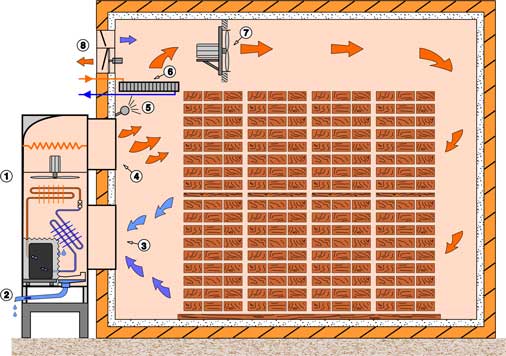
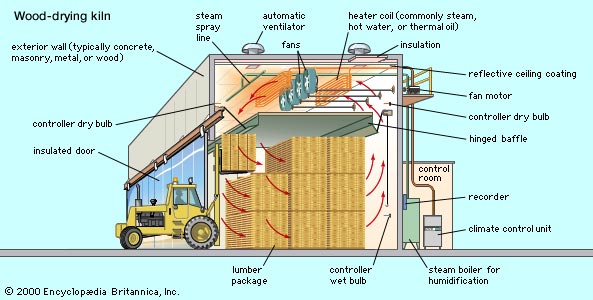
The most common method is the convection, usually in the form of the fresh-air air - drying, in the drying gap is controlled by controlling the temperature, the flow rate of the drying air and the relative humidity in the drying chamber. In the warm-up phase, the relative humidity is first for better heat transfer is maintained at a high level, partly enhanced by spraying water into the drying chamber. In the drying phase, the Trockungsgefälle is then optimized according to the type of wood. The conditioning phase at the end of the process is the moisture balance within the wood. A partial recovery of the applied energy can be done by use of the heat of condensation from the exhaust air.
Open air drying
The open air drying as the original form of convection has lost importance in the field of timber drying. For the firewood drying is still the most widely used method. The wood to be dried is stored protected against precipitation at free air circulation as possible outdoors. Drying is carried out without external energy through the evaporation of water from the wood and by air movement ( convection). The open air drying is the simplest and most energy-efficient drying process. Disadvantage, the relatively long drying time (in case of split logs four to twelve months).
Wood vacuum drying
The short drying time of vacuum drying and the associated rapid availability of wood have the vacuum drying developed a solid scope in the wood sector. Basic principle of this method, which is mainly for value woods and difficult to dry timbers used, the pressure dependence of the boiling point of water. The pressure in a vacuum system is lowered below the pressure at which to boil the water in the timber at a given timber temperature and vaporize, so this leads to a total pressure drop across the board cross-section, and thus a uniform and rapid running steam flow in the timber towards the surface. This makes possible a relatively fast drying at low temperatures. Here, however, the specific properties of the timber are to be considered in relation to its moisture conductivity and to control the parameters pressure and temperature in a suitable manner. The drying takes place in a pressure-tight container in which a reduced pressure of 95-150 hPa is generated.
Firewood drying
In the drying of firewood cost effective and energy efficient removal of moisture from the fuel is in the foreground - the calorific value of firewood increases linearly with decreasing moisture content. The other hand, drying damage do not matter. For cost reasons, and to the environmental benefit of the biogenic fuel to get wood, the value obtained by the drying energy gain in the use of firewood must be significantly higher than the energy required for drying. In the open air drying, the energy consumption is minimal. In the convection of the financial cost and energy use can be optimized by otherwise non- usable waste heat is used to dry the wood. However, since 2009 only in the commercial dry wood chips - If waste heat from the production of bioenergy (eg combined heat and power generation with biogas plants ) used for wood drying, the operator of the bioenergy plant shall receive additional remuneration for the injected current ( CHP bonus ) or the drying of sawdust for the production of fuel pellets. In addition to the Kammertrockung there for firewood other methods of convection (eg drum dryer ) and the Kontaktttrocknung (eg screw dryer for wood chips).