Fetal alcohol syndrome
Called Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS ), fetal alcohol also (AE), referred to the prenatal injury suffered by a child taken by the pregnant mother alcohol.
Is the organ formation already completed the child at the time of alcohol consumption, mostly caused little or no physical deformities and the child shows only minor exterior features. Damage to the central nervous system ( CNS), sometimes accompanied by cognitive and behavioral disorders, but may be present. For those in the attenuated symptoms, but not a flat rate to the implications for the child by "lighter " form of expression of the FAS Fetal Alcohol Effects ( FAE) is used.
As the boundaries between FAS and FAE are flowing, all relevant diagnoses under the umbrella term Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder ( FASD ) are summarized.
Definition
If an embryo ( up to the 9th week of pregnancy ) or fetus ( from the 9th week of gestation ) exposed to during its development alcohol and alcohol degradation products, it will not only inhibited in its development, but learns a function of stage of maturity, amount of alcohol and individual disposition more physical and cognitive development damage. This nachgeburtlich diagnosable damage you, acting under the terms fetal alcohol syndrome ( at full screen) or fetal alcohol effects together (with less severe, symptomatic ). As a generic term Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder is used.
History
The FAS, although certainly as old as the alcohol consumption itself, first described as a developmental disorder caused by alcohol consumption during pregnancy in 1968 by P. Lemoine in France, in 1973 again in the United States by KL Jones and DW Smith. The diagnostic criteria are essentially unchanged since the occurrence of a plurality of typical physical, cognitive and social developmental disorders.
Cause
The cause of FAS and FAE is always and exclusively maternal consumption of alcohol during pregnancy. Alcohol is one of the potentially toxic effect substances that can cross the placental barrier that separates the bloodstream of the mother and those of the child to penetrate, so that the fetus via the umbilical cord in a short time reached the same level of alcohol as his mother. The degradation takes place mainly on the organism of the mother, children develop only after birth its own powerful metabolism. Depending on maturity, amount of alcohol and individual disposition, the alcohol consumption of pregnant women affects irreversibly damaging effect on the physical- organic, cognitive and social development of the unborn child.
Some deficits are likely caused by the fact that it comes from alcohol damage to the Purkinje cells in the embryonic cerebellum, which are responsible for the balance and muscle coordination. As demonstrated in sheep, this damage, in turn caused by the acidic pH in the blood after consumption of alcohol in the circulation. All such resulting damage to children during their development in pregnancy are completely preventable by avoiding alcohol during pregnancy.
It must be currently assumed that any alcohol consumption at any time during pregnancy is a fundamental risk to the child and no limit can be named under the certainly no harm to the child is to be expected. Because so far could not be clearly established whether there is a tolerable, non-injurious amount of alcohol, and if so, where they would be to locate qualitatively and quantitatively. In addition to studies that evaluate a low alcohol consumption as not significant harmful, there are findings, according to which, even with only once greater alcohol consumption already occurred miscarriages. The magazine Baby and Family holds also in the edition of July 2007 together current study findings by British scientists. The research team had a group of children observed subjects whose mothers had drunk almost a glass of wine or beer per week during pregnancy. They came through their evaluation to the conclusion that even this commonly been considered a " small amount" of alcohol consumption often leads to behavioral problems in affected children than in children teetotal pregnant. General develop girls compared to boys rare emotional disorders and hyperactivity. In the study, however, an increase of abnormalities by 37 % was recorded especially among girls.
Alcohol consumption plays the father in terms of developmental disorders, according to previous studies not matter. This can also be deduced from the fact that FAS is not a genetic disorder, but represents a poisoning during pregnancy. But in terms of postnatal family situation, the alcohol consumption of the father as well as other ( close ) family members - such as the more maternal alcohol consumption also - for the promotion of the child's partly a material adverse effect. Many children, especially those with the full picture of the syndrome, grow due to the often persisting even after giving birth to alcohol problem in their family of origin in adoptive or foster families.
Frequency
Fetal alcohol syndrome is the leading cause of mental retardation that is not genetic. Alcohol has from the diverse during pregnancy on the child potentially toxic substances acting the most widely used and the largest social consumption acceptance. An FASD would be through responsible behavior of pregnant women completely avoidable. However, statistically, only one in five women consistently waives any alcohol consumption during pregnancy are alcohol-related harm is the most common cause of prenatal emergent cognitive and physical- organic damage without genetic influence:
On average, one out of 300 children in Germany with the full image of the fetal alcohol syndrome, including characteristic facial features ( facial syndrome ), bodily- organic malformations, cognitive disability and conduct disorder is born. The number of children with fetal alcohol effects, ie without or with only minor external characteristics and organic malformations, but with cognitive deficits and behavioral disorders, is about 4000 per year, or about 0.6 percent of all newborns. The real figure is estimated to be more about 11000-16000, since it is assumed that children with abnormalities of fetal alcohol effects in the sense often not diagnosed as such. Out of concern of mothers before own stigma and stigmatization of the child's consumption of alcohol during pregnancy is also often concealed or trivialized, so that research is being conducted for other causes.
In Germany, each year about 10,000 newborns are associated with alcohol-related harm to the world. About 4,000 of them have the full picture of the fetal alcohol syndrome and are life- long physical and mental severely disabled. In a study of the Charité, with 58 % of surveyed pregnant women who occasionally drink alcohol.
Prenatal developmental disorders
The poisoning of the unborn child with alcohol leads depending on the stage of maturation at different developmental disorders.
The embryo is characterized in the first trimester through the process of organogenesis from, that is to say the organs are created. Accordingly serious are the injuries that can occur at this time: microcephaly and microencephaly ( Kopf-/Gehirnminderentwicklung ), craniofacial hypoplasia ( face changes with structural developments ) and malformations of internal organs are the most common.
During this period, the main risk is a miscarriage in maternal alcohol consumption. Furthermore, there is growth retardation with residue or delay of physical development.
At this time the fetus grows physically and cognitively to the birth maturity. By the influence of alcohol is a risk of growth retardation (growth delay ), and damage to the central nervous system. This risk is greatest at that time.
Not only regular or excessive drinking has a harmful effect in this sense. The episodic ( occasional ) alcohol consumption can cause specific damage to the unborn child, depending on the development phase: During the fourth week of pregnancy, for example, the influence of alcohol affect the developing project of the head shape, in the sixth week may lead to deformities in the development of the kidney. Above the entire course of pregnancy, the brain in a process of maturation and is therefore the most susceptible and at risk of alcohol-related harm member.
Postnatal symptoms
Alcohol consumption of pregnant women can cause harm to the principle of all organs and organ systems of the unborn child, although in typical expression of FAS some body parts are particularly affected. The diagnosis of classical syndrome is based on hard-hit children especially on physical characteristics. These include: short stature, underweight, Kleinköpfigkeit ( microcephaly ), poor muscle development, typical facial changes, cognitive retardation and behavior disorder (s). The severity of alcohol-related injuries in children have as well as the individual qualitative and quantitative expression of maternal alcohol use a wide range, which must be considered and assessed in each individual case. The fact that not only maternal alcohol dependence has a negative effect on the child, but also can affect the hitherto largely socially tolerated and sometimes even required social occasion drinking toxic, only little attention so far. Despite the high medical importance with regard to permanent damage to the child, the trivialisation of alcohol consumption during pregnancy is still widespread even with gynecologists and pediatricians do primarily with the diagnosis of fetal alcohol effects sometimes very difficult.
Not all affected children show all the features and characteristics are not always equally strong expression available. With FAS show, mostly, more and more pronounced symptoms than in the FAE, the individual impairments may well weigh equally difficult, changes in the physical realm can be so inconspicuous in the child that a layman does not notice any difference to the healthy child, but also so pronounced that noticed it right away, and sometimes may have a socially stigmatizing effect ( " drunkard child "). The physical damage may be associated with disturbances in brain function ( learning difficulties through to intellectual disability) and disturbance of mental, affective and social development. However, it may not be a flat rate assumes a relation between physical characteristics and cognitive impairments.
Common symptoms of FASD are premature births, with not completely distinct limbs and open pubic area, as well as the formation of a third lung. ( Stamping an approach )
- Physical area Growth retardation, short stature, underweight
- Comparatively smaller head circumference ( microcephaly ), short development of the brain ( microencephaly )
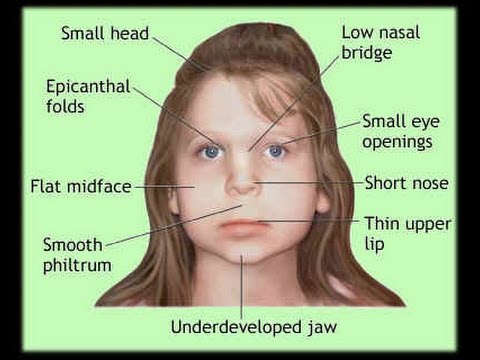
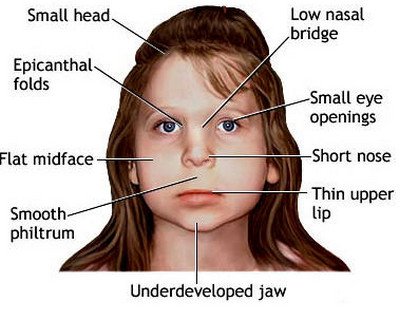
- Flat acting in profile with a flat midface maxillary region, receding chin and a short, flat nose (snubbed ) with an initial forward -facing nostrils ( nose socket )
- Small teeth, increased tooth spacing
- Specially shaped and low set ears
- Comparatively small eyes with narrow, sometimes drooping eyelids (ptosis )
- Crescent-shaped fold of skin at the inner edge angles of the eyes ( epicanthus medialis)
- Anti- mongoloid ( down the outside, lateral -caudal descending ) palpebral fissures
- Hemangioma ( haemangioma )
- Sacral dimple
- Muscle weakness ( hypotonia ), underdevelopment of the muscles
- Connective tissue, lack of subcutaneous fatty tissue
- Special hand furrows, flat hand line relief
- Organic range, physical malformations speech disorders
- Hearing impairment
- Sleep
- Eating and swallowing disorders, often missing or excessive hunger
- Eye malformations, heaped clefts, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, strabismus
- Heart defects, often septum defects
- Cleft palate
- Alkoholkardiomyopathie ( alcohol-induced heart muscle damage )
- Malformations in the urogenital: renal malformations, developmental disorder of urethra ( hypospadias ), undescended testicles ( cryptorchidism ), enlargement of the clitoris ( clitoral hypertrophy )
- Hernia
- Dislocation of the hip ( hip dislocation )
- Curvature of the spine (scoliosis )
- Anomalies of the ribs and vertebrae ( eg, block vertebra )
- Pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum
- Underdevelopment of the finger - end links
- Shortening and flexion of the little finger, sometimes lasting curvature
- Intergrowth of radius and ulna
- Neurologically - cognitive area general developmental retardation to the lack of independence
- Lack of concentration, learning disability, cognitive disability
- Difficulty in understanding abstract things and logical connections
- Problems with the collection of terms like soon, before, after, soon, the day after tomorrow.
- Problems in the field of mathematics, such as estimating numbers, understanding the time and dealing with money values
- Seizures, epilepsy
- Emotional instability, fluctuations of balance, moods and expressions of emotion
- Often long-lasting temper outbursts
- Hyperactivity
- Hyperexcitability ( hyperexcitability of the central nervous system )
- Over -or under- sensitivity with respect to often even slight pain, temperature, touch stimuli, etc.
- Under-or over-reaction to tactile stimuli
- Trustfulness (eg with strangers go along)
- Increased risk-taking, daring greatly increased because of accident proneness
- Aggressiveness and destructiveness
- Longer than average response times
- Inattention, distractibility up to overstimulation by various environmental stimuli (lights, colors, sounds, movements, people, etc. )
- Motor coordination difficulties due to delays in development of fine and gross motor skills and poor eye -hand coordination ( " clumsiness " )
- Problem-solving difficulties ( again same approaches without variables )
- Self-stimulatory, partly self-injurious behavior
- Impatience and spontaneity on the one hand, decision difficulty on the other hand
- Antisocial and oppositional behavior
- Non-recognition of consequences
- Difficulties to adequately integrate into social relationships and to feel comfortable in it
- Ignorance of verbal instructions, uncooperative and oppositional behavior in verbally expressed setting limits ( non-acceptance of "No")
- Unresponsiveness or incomprehension of non-verbal signals through gestures, facial expressions and body language of others
- Meaningful contemporary understanding of instructions, but inability to adequately design
- Often anxious and worried and frustrated chronic setting
- Low frustration tolerance
- Fast fatigability
Diagnosis
FAE or FAS is after birth, partly only in the course of childhood, when manifest disorders diagnosed in the majority of literature on the following criteria:
FAE (FAS grade I- II)
FAS (Fullscreen)
The following three main criteria must be present:
The ICD -10 code O35.4 is specified in the care of pregnant women with (suspected ) damage to the unborn child due to alcohol consumption. For the newborn, however, the ICD -10 code Q86.0 used.
Follow
Children with consequences of FAS can achieve a normal IQ; but are often physically limited and susceptible to disease. Children with the full picture of FAS develop physically quite on, in part, some of the physical sub- developments grow out. Malformations can sometimes be surgically corrected, so they pose no harm. In the cognitive domain, however, this is different: Most children with FAS are mentally handicapped for life, albeit in varying degrees. This also has an optimal development of children who came to foster parents, showed no further development successes. Mental and social deficits could not be eliminated, the children need a simple clear structured environment, to avoid being overwhelmed.
Children with FAE often have little physical peculiarities, their IQ is often average. However striking they are in the (social) behavior. Most children require constant supervision and a lot more diverse to adulthood assistance with activities of daily life.
Prevention
The only effective prevention of alcohol-related harm to the unborn child is the full and consistent renunciation of the consumption of alcohol by pregnant women during the entire period of gestation. The greatest difficulty of each prevention approach is that many women of the risks of alcohol consumption with the possible consequences for the child are not aware of it or the risks are underestimated.
In the care of pregnant women, it should be standard to refer to the potential risks and responsible use of alcohol strongly to stop women. The Routine assessment of whether a pregnant woman is present a problematic consumer behavior or must be assumed to be a frivolous attitude may be part of the pension. The support or cooperation with a specialized counseling may be helpful. A broad-based prevention program for example, is carried out in 25 American states, Nurse -Family Partnership, which offers a beyond the two-year pregnancy care.
While an increasing number of gynecologists do so conscientiously and advised to refrain from alcohol in pregnancy and lactation and motivate, but especially the opportunity consumption is still often trivialized by physicians. Not infrequently, on the contrary even to the occasional drink encouraged ( " Good for blood pressure ", " Helps to relax "). Potential impairments are often underestimated, trivialized or denied entirely possible risks, while a safe limit, in the absence thereof, can not be called.
Stubbornly adheres also by the social prejudice that only children of alcoholic women suffer damage, although this is not applicable in this exclusivity. So it goes in the primary prevention efforts aim is to identify alcohol consumption as potentially always fruit -destructive behavior, to create an overall social awareness and make it easier for women in pregnancy and lactation accepted aware and especially socially and support to give up alcohol. At this point particular the responsibility of the child fathers to bear.
Day of the alcohol- impaired child
On the initiative of the organization " FASD Germany eV " is celebrated every year since 1999 on 9 September in many countries of the world, the "Day of the alcohol- impaired child ." It is through information campaigns, etc. made aware of the situation of children and young people who were born with an alcohol- related harm. The resulting difficulties for them and their families should get special social attention that day. Another important point of efforts to educate and inform the warning of the often underestimated dangers of alcohol consumption by the mother during pregnancy.
FAS in the literature
FAS is among others in " Tell him not from the mountains: The moving story of the Indian boy Adam " by Michael Dorris and flows like a river, the blood treated by my dreams of Timothy Patrick Barrus.