FFmpeg
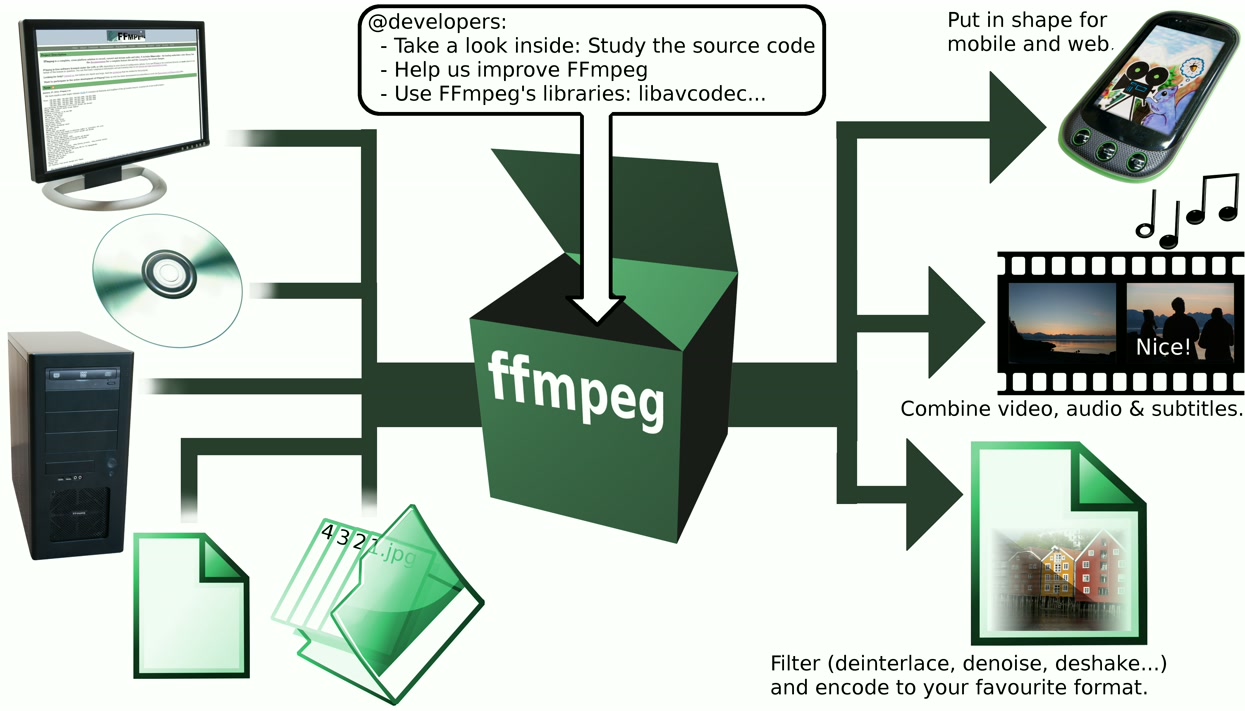
The FFmpeg project consists of a series of free computer programs and program libraries which receive digital video and audio, convert, send ( stream ) and can pack into various container formats. Among other things, it contains libavcodec with a collection of different audio and video codecs.
Technical details
FFmpeg is developed under Linux and other Unix-like systems ( Unix-like ) and has also been ported to other operating systems and platforms. Known programs that use FFmpeg under Unix-like and Windows are the programs MPlayer, VLC, xine and HandBrake, Windows Mobile and Palm OS TCPMP.
The project consists of several components:
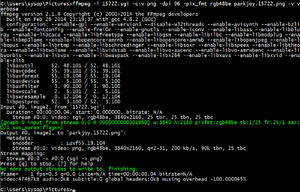
- Ffmpeg is a command line program to convert from one video, audio or image format to another. It also supports the recording and encoding from a TV card in real time.
- Ffserver is an HTTP or RTP and multimedia streaming server RTSP for audio and video transmissions (including live) on the Internet.
- Libavcodec contains all the ffmpeg audio and video encoder and decoder. All native codecs have been written from scratch, this also includes a H.264 decoder. This library can be used by other programs, and then present the films themselves.
- Libavformat container contains the parser and creator for all common audio and video container formats (such as AVI, MOV, MKV, Ogg / Ogg Media etc.).
Since FFmpeg also includes implementations of codecs, on the - particularly in the U.S. - made claims, the use of these formats in countries that recognize such claims, under certain circumstances the payment of fees to license organizations (such as the MPEG LA) require.
Furthermore, the FFmpeg project come from two new video codecs: One only lossless codec called working FFV1 and an almost finished codec called Snow, which is based on wavelet transforms and an intelligent variant of the coding region.
In March 2011 it was announced that the libraries of the project were expanded to include additional multithreading functions whose development began in the Google Summer of Code in 2008.
Libav
On 18 January 2011 it was announced by several FFmpeg developers to want to take over the FFmpeg project. It justified this step by a dissatisfaction with the previous lead developer Michael Niedermayer. The organization of additional FFmpeg development should be more strongly oriented in the future of the Linux kernel.
After the takeover of the project had failed, the developers split off under the name Libav from FFmpeg project on 13 March 2011. The two Linux distributions Debian and Ubuntu provide since by default from Libav. At the same time the output of the program was supplemented with the ffmpeg Note that FFmpeg will not be deprecated on Debian and Ubuntu. Once users had complained that this is not the truth, because FFmpeg is developed further still, the issue has been changed, it is now claimed that ffmpeg is outdated ( deprecated ).
Legal consideration of the codec collection
FFmpeg ( libavcodec or as part of FFmpeg ) contains implementations of more than 100 codecs, of which a part of patent holders could be challenged.
" In some jurisdictions, could, on the basis of vague references, possibly claims against various standards that support FFmpeg, be asserted. "
Furthermore, many of these codecs have been published under Terms of Use which prohibit reverse engineering; itself to ensure interoperability. These conditions are not valid in some countries, for example, it is in the German Copyright Act ( Copyright Act) in § 69e, under certain circumstances, allows decompilation.
Logo
The FFmpeg logo represents a zig- zag scan pattern, which in MPEG codecs the data for the entropy coding provides. The logo was taken from Libav, when the project was split off.