Malayo-Polynesian languages
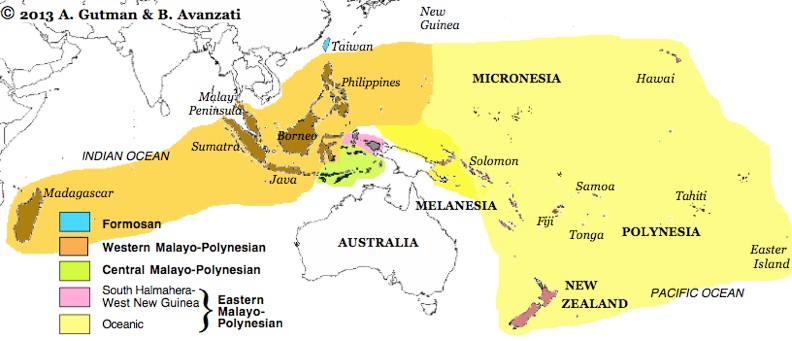
The Malayo -Polynesian languages are by far the most important and richest speaker subgroup of the Austronesian languages. They comprise about 1100 languages with nearly 300 million speakers. They are widespread on the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, a few members of this family of languages spoken on the Asian mainland. The Malagasy spoken in Madagascar is geographically from the rest far remote, the language of Easter Island ( Rapa Nui ) is the eastern extreme Represents the Malayo - Polynesian divides into two main groups, the Western Malayo - Polynesian and the Central - Eastern Malayo - Polynesian.
Characteristic of the Malayo -Polynesian languages are the tendency to productive reduplication ( repetition of parts of words or whole words ), the absence of consonant clusters, and the low number of vowels in the phonemic system (usually five).
The migration of the Malayo - Polynesian languages speakers in their present settlement areas, see Austronesian languages.
Classification and distribution areas of the Malayo -Polynesian languages
This section describes the internal structure (classification ) of the Malayo - Polynesian is shown in detail. In addition, the number of languages , current numbers of speakers and the distribution areas of the individual branches and sub-branches are given.
The Malayo -Polynesian than 1100 languages are spoken by around 300 million speakers in the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, East Timor, Papua New Guinea, Oceania, and Madagascar. They fall into two main branches:
- Western Malayo -Polynesian and
- Central - Eastern Malayo -Polynesian
Western Malayo -Polynesian
Western Malayo -Polynesian has about 290 million speakers and includes the Malay language, Javanese, Malagasy, Tagalog, Ilocano and Cebuano, as well as many other languages .
Western Malayo -Polynesian ( 445 languages , 284 million speakers, Philippines, Indonesia, Madagascar)
- Philippines (132 languages , 68 million speakers; Philippines, Sangir, North Sulawesi ) North Philippines (45 Languages , 13 million speakers; Bashi, Luzon, Northern Mindoro )
- Meso - Philippines (46 Languages , 49 million speakers; central Philippines, Mangyan, Palawan, Kalamian )
- Southern Philippines ( 21 languages , 2.6 million speakers; Manobo, Danao, Subanun )
- Southern Mindanao (4 languages 4,000 speakers; Southern Mindanao )
- Sangir languages ( 6 languages 600,000 speakers; North Sulawesi )
- Minahasa languages ( 3 languages, 250,000 speakers; North Sulawesi )
- Gorontalo Mongondow languages ( 7 languages , 2.2 million speakers; North and East Sulawesi ): Gorontalo, Mongondow
- Malay (60 Languages , 60 million speakers, Malaysia, Indonesia)
- Cham - Achin ( 8 languages , 3.9 million speakers; China: Hainan, Vietnam, Cambodia / Indonesia: North Sumatra )
- Embaloh - Taman (2 languages , 15,000 speakers; Central Borneo ( Kalimantan ) )
- Sunda (2 languages , 27 million speakers; Sunda )
- Madura (2 languages , 10 million speakers; Madura )
- Bali - Sasak - Sumbawa languages ( 3 languages, 6.3 million speakers; Bali, Sasak, Sumbawa )
- Barrier Islands ( 5 languages, 670,000 speakers; Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano )
- Batak ( 5 languages, 5.9 million speakers; West Sumatra: the Batak country)
- Gayo (1 language, 180,000 speakers; North Sumatra ( Takengon, Genteng, Lokon ) )
- Sabah ( 36 languages , 500,000 speakers; Northwest Borneo: Sabah )
- Northern Sarawak ( 24 languages , 100,000 speakers; Northwest Borneo: North Sarawak )
Central - Eastern Malayo -Polynesian
The approximately 680 Languages of the Central Malayo - Polynesian -east are spoken by some 7.5 million people in the Moluccas, Timor, Flores, in New Guinea and Oceania. It is divided into two main branches:
- Central Malayo-Polynesian and
- Eastern Malayo -Polynesian
Central Malayo -Polynesian
Go to Central Malayo - Polynesian languages include 151, spoken by 4.5 million people in the Moluccas, Timor, Flores, Sumba and West New Guinea. Tetum is an official language of East Timor. Other languages are national languages in East Timor.
Central Malayo -Polynesian
- North Bomberai (4 languages , speaker 2000, Irian Jaya: N. Bomberai Peninsula )
- South Bomberai (1 language, 600 speakers; Irian Jaya: Bomberai southern Peninsula )
- Central Moluccas ( 52 languages , 330,000 speakers; Banda, Seram, Ambon, Sula )
- Teor Cure (2 languages , 4,000 speakers; Teor, spa )
- Aru ( 13 languages , 50,000 people; Aru )
- Southeast Moluccas ( 5 languages, 180,000 speakers; Kai, Fordata, Yamdena, Tanimbarese )
- Babar ( 9 languages , 10,000 speakers; Babar )
- Timor- Flores ( 41 languages , 2 million speakers; Timor, Roti, Alor, Wetar, Flores ): Tetum, Uab Meto, Manggarai, Kambera, Lewotobi and others.
- Bima - Sumba ( 24 languages , 1.9 million speakers; Sumba, Sumbawa ): Bima
Eastern Malayo -Polynesian
For Eastern Malayo - Polynesian includes 527 languages , spoken by 2.8 million people in New Guinea, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia.
Eastern Malayo -Polynesian
- South Halmahera - West New Guinea ( SHWNG group) ( 39 languages , 135,000 speakers; South Halmahera, West New Guinea) South Halmahera ( 6 languages , 50,000 people; South Halmahera )
- West New Guinea ( 33 languages , 85,000 speakers; West New Guinea)
- Admiralty Islands ( 31 languages , 30,000 speakers; Admiralty Islands )
- Western Oceanic (231 languages , 770,000 speakers; North, East - Central New Guinea, Melanesia meso ) Northern New Guinea (102 languages , 210,000 speakers; North New Guinea)
- East Central Papua New Guinea (62 languages , 240,000 speakers)
- Meso - Melanesian (67 languages , 320,000 speakers; meso Melanesia: Vitu, UNEA, New Britain, New Ireland, Solomon Islands Northwest )
- Southeast Solomon Islands ( 26 languages , 220,000 speakers)
- Santa Cruz ( 6 languages , 1,200 speakers)
- North-Central Vanuatu ( 90 languages , 80,000 speakers)
- Southern Vanuatu ( 8 languages , 18,000 speakers)
- New Caledonia (30 languages , 33,000 speakers)
- Loyalty Islands ( 3 languages, 23,000 speakers)
- Micronesian (20 languages , 220,000 speakers; Micronesia: Ikiribati, Kosrae, Marshall Islands, Ponape, Truk, Nauru )
- Central Pacific ( 43 languages , 1.3 million speakers, Fiji, French Polynesia ) Western Fiji Rotuma ( 3 languages, 70,000 speakers; Western Fiji, Rotuma )
- Eastern Fiji ( 4 languages , 365,000 speakers)
- Polynesian ( 36 languages , 900,000 speakers) Tonga - Niue (2 languages , 130,000 speakers; Tonga, Niue )
- Nuclear -Polynesian Samoa Group ( 22 languages , 500,000 speakers; Samoa, Wallis, Tuvalu, Futuna, Pukapuka, Tokelau )
- Eastern Polynesian (12 languages , 270,000 speakers; Hawaii, Mangareva, Marquesas, Tahiti, Rarotonga, Tuamotu, Rakahanga, New Zealand (Maori ), Easter Island ( Rapa Nui ) and Others )
Malayo - Polynesian languages million
There are about 30 Malayo - Polynesian languages with at least one million speakers, of which 10 are in the Philippines, 18 in Malaysia and Indonesia and one spoken in Madagascar. In the table below next to the number of speakers ( native speakers) is given the Malayo - Polynesian subfamily of the to which the language belongs, and also the distribution area, if it is not clear from the name of the sub-group. The statement " S2" includes the number of native speakers and second speakers of this language. The table is arranged geographically.
All other Malayo -Polynesian languages have less than a million speakers. In particular, the oceanic languages are often very "small" and have less than 1000 speakers. A complete overview of all Austronesian languages with their classification within the Austronesian is also found in Ernst Kausen.