5-Hydroxymethylcytosine
- 4-amino- 5-( hydroxymethyl) -1H- pyrimidin- 2-one
- 5 - Formylcytosin
Fixed
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
5 - hydroxymethylcytosine is a heterocyclic organic compound with a Pyrimidingrundgerüst. It is a derivative of the nucleobase cytosine. It forms the nucleosides 5 - Hydroxymethylcytidin ( 5hmC, hm5C ) in the RNA and 5 Hydroxymethyldesoxycytidin (5- HOMedC ) in the DNA.
Biological Significance
5 - hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine is adjacent to the single base modified DNA, which was found in mammals. Therefore, 5 -methylcytosine is often called the fifth and 5- hydroxymethylcytosine often referred to as the sixth DNA base. 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine, in vivo postreplikativ ( after DNA synthesis) from cytosine by addition of a methyl group (see DNA methylation ) and subsequent oxidation is formed. It is believed that 5- hydroxymethylcytosine such as 5- methylcytosine play an important role in epigenetics and are involved in the buying and silencing genes.
Occurrence
5 - hydroxymethylcytosine was discovered in the early 1950s in bacteriophage DNA. Here the hydroxymethyl group protects the DNA of the phage from degradation by bacterial restriction enzymes.
2009 found two groups of researchers that 5- hydroxymethylcytosine is also a part of the DNA of mammals. Meanwhile, it is known that virtually any mammalian cell 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine, and in that the largest quantities occurring in the central nervous system. The amount of 5- hydroxymethylcytosine increases during development, but appears to be stable in adulthood. This has been demonstrated in the cerebellum and hippocampus of mice. Due to this finding can be found in embryonic and neural stem cells, only small amounts of 5- hydroxymethylcytosine.
Biosynthesis
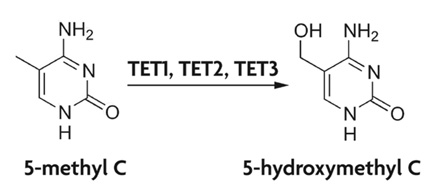
In DNA, 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine is the base of the nucleoside 5 - Hydroxymethylcytidin. It is formed by oxidation of 5- methyl cytidine. This reaction is catalyzed by the iron (II) - catalyzed and TET ketoglutarate dependent enzymes. In vitro, however, it was shown that methyltransferases can directly convert cytosine with formaldehyde, which is also 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine forms.
Function
The exact function of 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine is unknown. However, it seems likely that the DNA base plays an important role in epigenetics and could affect gene expression crucial. It has also been speculated that 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine is involved in active demethylation, the enzymatic cleavage of the methyl group of 5-methylcytosine. 5 now has Formylcytosin, an intermediate of the oxidative demethylation mechanism postulated to be detected in the DNA of embryonic stem cells. 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine could play a special role in the central nervous system, as there were in particularly high amounts (~ 0.25 % of all DNA bases ) is present.
Wider impacts
Through the discovery of 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine studies on the distribution of 5 -methylcytosine be questioned, since the standard detection methods such as Bilsulfit sequencing can not distinguish between 5 - hydroxymethylcytosine and 5- methylcytosine.