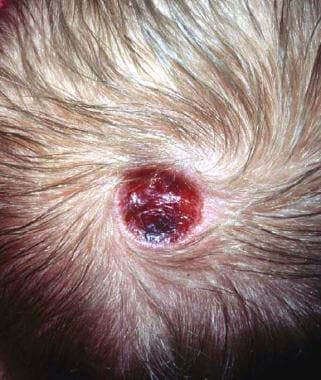
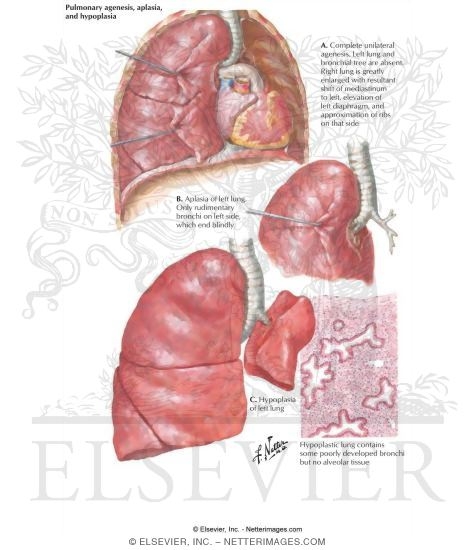
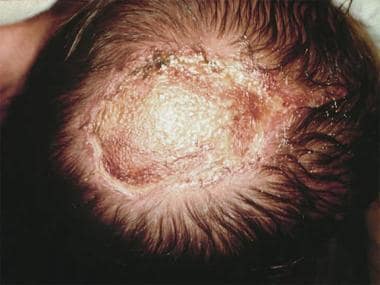
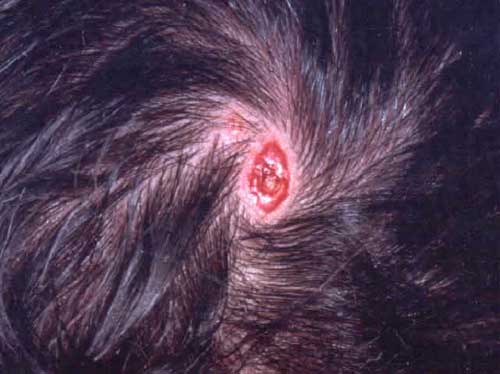
Aplasia
As aplasia or Aplasia ( from Ancient Greek ἀπλασία in Modern Greek, απλασία, neulateinisch aplasia "not training " ) is the non- formation of an organ in medicine despite the presence of organ system called (in contrast to agenesis ). In embryonic development may lead to a complete absence of the organ in virtually every organ. If the organ is designed to be small, so we speak of a hypoplasia.
Aplasia result in vital organs to the death of the fetus and cause miscarriage. However, some organs are not vital or their function can otherwise, for example, in paired organs are replaced by the institution of the other side. Then, a aplasia remain without life-threatening consequences (eg aplasia of the gallbladder, a thyroid lobe, a kidney or genitals ).
In total there is aplasia rare ( usually < 1:1000) and its exact cause can not often recognize. Under the influence of teratogenic agents (eg thalidomide ), teratogenic viruses or radioactive rays are they found more frequently ( see, eg, amniotic band syndrome).
The same terminology is used in dentistry in teeth. That is, if teeth are not created ( a frequently occurring phenomenon in wisdom teeth ), so it is a dental aplasia. Too small teeth are called analogous hypoplastic.
In tumor medicine is referred to patients who, as a result of a Zytostatikumbehandlung an extreme decrease in white blood cells ( leukocytes), located as aplastic or in the state of aplasia.