ARCNET
ARCNET ( Attached Resource Computer Network ) is a networking technology for local area networks (LANs). You define cable types and signaling for the physical layer (physical layer) and packet formats and protocols for the media access control ( Media Access Control, MAC) / data link layer of the OSI model.
On December 1, 1977 ARCNET was unveiled to the public after the computer manufacturer DataPoint, who had developed this technique was completed in the same year the installation of the first customers of Chase Manhattan Bank in New York City. ARCNET was developed at the same time as Ethernet, but kept a few years as a proprietary USP, to the Standard Microsystems Corporation, the production of the corresponding controllers took over in 1982 reached a release, and won a further partner Novell in 1985. Meanwhile, ARCNET, for example, one of the foundations of BACnet.
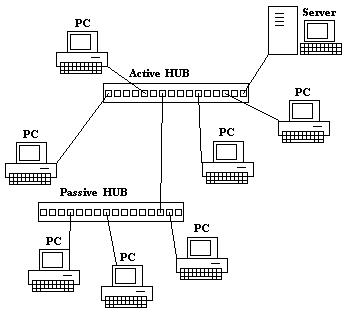
ARCNET is either physically built like a classic 10BASE2 Ethernet as a bus or alternatively as a star or tree. The switching components are in the bus version simple tees, or the star active or passive hubs, with active and passive hubs can be mixed. In the original form ARCNET was built with coaxial cables. In the course of development also UTP and fiber have been specified. The coaxial cables do not correspond to that of 10BASE2 (Thin Ethernet) known type RG -58 ( with a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms), but RG -62 with a characteristic impedance of 93 ohms. This circumstance made temporarily for faster dissemination of arcnet over Ethernet, as the RG -62 cable IBM's SNA corresponded cabling and so many places has already resorted to an existing infrastructure.
The connection to the hub and a computer either in star shape directly via BNC connectors without the well-known by 10BASE2 T- piece to the hub, with no terminator is required, since the termination of the cable directly in the hub or on the map is done. The bus version is just as wired with T-pieces like 10BASE2 and also has termination resistors (93 ohms) at the cable end. The possible distances between nodes are in the 2.5 - to 4 -fold of 10BASE2.
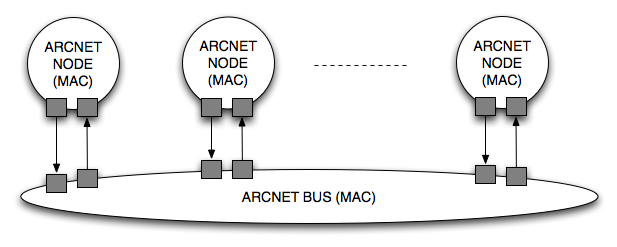
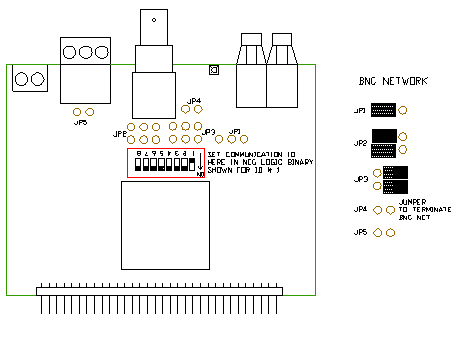
The access method of ARCNET token passing on a token bus. Here, similar to the access method token ring, token sent on their way, which is passed in a fixed order. Token ring, this is determined by the ring wiring. ARCNET in the token is always sent in the entire network, and the next station in a logical sequence takes the token. The order is to be handed to the cards as a node ID ( sequential numbering ) on an externally accessible DIP switch; with current products, the ARCNET ID is communicated via the software of the card.
The transfer rate is 2.5 Mbit / s ( 20 Mbit / s by using ARCNET Plus cards). Lower than Ethernet and Token Ring But, as with Token Ring, no collision slows the pace of the transfer, is - especially with high network load - even with 2.5 Mbit to achieve a higher speed than 4 times faster Ethernet networks. From U.S. network specialist Thomas Conrad in 1990 under the name " " TCNS "is also a (not specified ) 100- Mbit version of the ARCNET with RG -62 and fiber optic cabling was presented, which had all the advantages of ARCNET via Ethernet and Token Ring. Compaq let this system but after the takeover by Thomas Conrad in favor of the much cheaper has become the meantime Fast Ethernet drop. during the early years ARCNET was, however, much cheaper than Ethernet or Token Ring both the components, as well as the wiring and maintenance costs.
A special feature was the ARCNET cards. ARCNET was an open design and ordered especially for a standardized Maps API, so that cards from different manufacturers were able to operate with a standard driver. This practical simplification used later many manufacturers with the widespread NE2000 - compatible Ethernet cards. There, too, reduced development costs and this soon led to very inexpensive cards. Today's ARCNET cards require vendor-specific drivers.
An ARCNET network to a hub in the center was a good example in the explanation of network topologies: the wiring formed a star, electrically the net was a bus and a logical ring. ARCNET lost with the further spread of Fast Ethernet in local area networks in importance, but is still used in areas such as industrial production, printing technology, wind energy technology, but also medical and logistics.