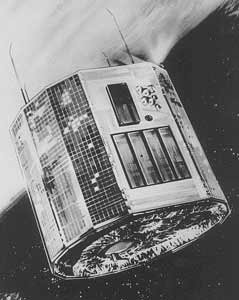
Ariel 5
Ariel V was a British-American -ray satellite in the 1970s, developed in cooperation of the British Science Research Council and NASA.
Ariel V ( called before the start UK5 ) was launched on 15 October 1974 by the San Marco platform off the coast of Kenya with a Scout rocket in a low, almost equatorial orbit. The mission ended on 14 March 1980 with the re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
Ariel V was a spin- stabilized satellite of every six seconds turned around its axis. Four instruments for the energy range 0.3-40 keV were looking into a small region of the sky of about 10 ° to the satellite axis. Two other instruments probed using the rotation of the satellite from almost the entire sky.
Ariel V monitored and studied the changes in brightness of cosmic X-ray sources. He introduced for the first time found that Seyfert 1 galaxies are X-ray sources, and found the emission line of iron at about 7 keV in the spectrum of galaxy clusters.