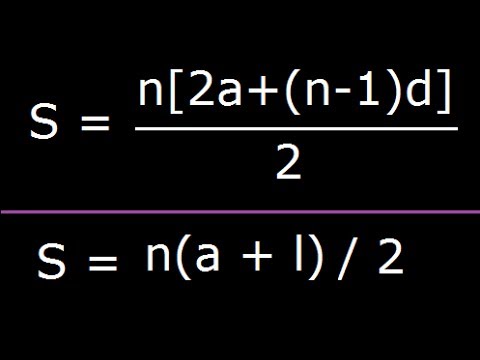Arithmetic progression
An arithmetic sequence (also arithmetic progression) is a regular mathematical number sequence with the characteristic that the difference between two adjacent follower members is constant. A simple arithmetic sequence are the odd natural numbers is:
- 3.1 Odd numbers
- 3.2 prime sequence
- 4.1 Calculation
- 4.2 tetrahedral numbers
- 4.3 square numbers
Calculation
The following applies:
The i- th term of an arithmetic progression with an initial term and the difference d is calculated from
Or spelled out:
Example
Arithmetic sequence with an initial term and the difference
If the members just write one behind the other, resulting
Arithmetic mean
The term " arithmetic sequence " is derived from the arithmetic mean. Each member of an arithmetic sequence with is in fact the arithmetic mean of its neighboring links:
The summation of the terms of the sequence results in the arithmetic series.
Difference sequence
The consequence of the differences between two successive links is called difference sequence.
In an arithmetic sequence, the difference sequence is constant: applies to each.
Odd numbers
The difference between two consecutive odd natural numbers is always 2 So is obtained as difference sequence, the sequence consisting only of twos:
Prime sequence
Example of an arithmetic progression of primes with the constant distance 210:
The episode ends after 10 members ( AP -10). The difference itself is a primorial (210 = 2.3.5.7 ). Terence Tao and Ben Green proved that it arbitrarily long arithmetic progressions of this kind must be of prime numbers. The date (2010) longest known of these sequences consists of 26 elements ( AP -26).
Arithmetic series of higher order
Consequences that can be attributed to an arithmetic sequence is called arithmetic sequences of higher order. It is exactly those consequences, which can be described by a polynomial function; The order here is the order of the polynomial.
Calculation
Formulas for calculating arithmetic consequences general order:
The Faulhabersche formula, is the -th Bernoulli number:
Tetrahedral numbers
The sequence of tetrahedral numbers is an arithmetic sequence 3rd order. The polynomial that describes the result is:
The greatest exponent determines the degree of polynomial, which is in this case the three.
As can be seen from the table, the sequence of triangular numbers ( first difference sequence ) is an arithmetic sequence 2nd order.
Square numbers
So too, in the wake of square numbers is an arithmetic sequence 2nd order.