Asphalt volcano
Asphalt volcano is the name for an up to 800 m high volcano -like elevation on the ocean floor, which consists of salt and exits from the top of natural asphalt. The term was introduced without Asphaltvulkanismus that the process of asphalt outlet is understood so far - only the association of the asphalt with the crater and Rutschungsstrukturen and the morphological similarity of the asphalt layers with igneous lava flows has led to it. The beaten and cured on the seafloor asphalt currents are similar to AA lava fissured by numerous cracks and crevices.
The discovery of this geological peculiarity managed an international team of researchers led by the University of Bremen on board the research vessel "Sonne" in 2003. Researchers had become through images obtained from satellites, on which traces of oil were visible on the water surface, attentive to the locality.
The geology of the Asphaltvulkanismus
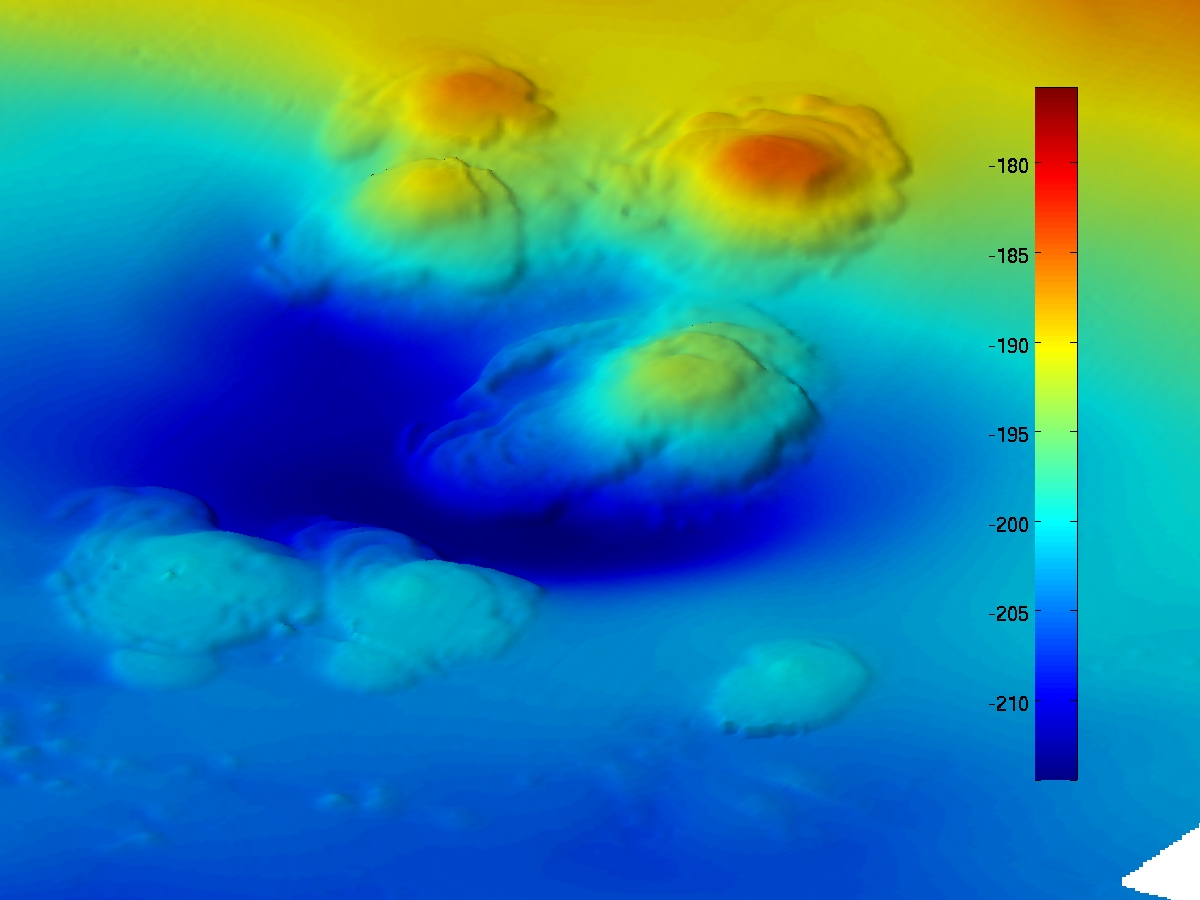
At the base of the Campeche Bay in about 3000 m water depth, in the southern part of the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest of the Mexican state of Campeche on the Yucatán Peninsula, there are diapirförmige salt domes, locally Campeche Knolls ( Campeche Hill ) called, exiting the tips of natural asphalt and lavaähnlich flows down the slopes.
Until this discovery, only smaller covered with asphalt sites were observed in the Campeche Bay, however, they discovered an area of about 1 km2. In this marine region crowd in the Jurassic period deposited salt deposits from 8-15 km depth up until about the level of the sea pelvic floor addition, while the asphalt from the decomposed by microorganisms and thermally altered petroleum shows. The at their base about 5 to 10 km wide Campeche Knolls are 450-800 m high and of different types of shape (morphology), most are elongated ridge, some have a round, dome- like shape. The slope is between 10 and 20%. One of the most closely investigated asphalt volcanoes 'was named after the derived from the Aztec language Nahuatl word Chapopote family or the borrowed them in the Mexican Spanish chapapote, both mean, asphalt ' by its discoverers, Chapopote.
A new ecosystem
The existence chemosynthetisierender organisms has long been known, for example from along the mid-ocean ridges encountered submarine black smokers. There, the rising hot sulphurous solutions serve as an energy source, while in the unprecedented global ecosystem of Campeche Knolls of asphalt fulfills this function. It is the basis of large collections of chemosynthetic bacteria and clams from the family vesicomyid and beard worms that are as seep indicators indicator for escaping fluids, also crabs and fish were observed. The use of asphalt as a source of food is exceptional and in this form for science a new phenomenon, as it represents the final stage in the conversion of petroleum represents and is therefore considered less friendly to life. What chemical compounds are used exactly by the organisms for chemosynthesis, is still unclear, as are the exact ecological relationships within this habitat.
The leader of the expedition, Prof. Gerhard Bohrmann, commented on the discovery: " Only rarely do you have as a researcher the opportunity to discover completely unknown things. On Earth offers to this extent only the deep sea. "
Asphalt volcanoes in the Santa Barbara Channel, California
In 2007, dome-shaped mounds were in the bathymetric mapping with sonar sensors on the seafloor of the Santa Barbara Channel, California, discovered in about 220 meters water depth. Further studies with submersibles by scientists at the University of California, Santa Barbara showed that these consist almost entirely of asphalt.
Near the asphalt volcanoes are crude oil production sites. The crude oil extracted from the Monterey Formation has the same chemical composition as the asphalt from the volcanoes. The journeys of researchers showed that no more oil wells were active under water in 2010. However, in some places came into smaller quantities of methane.
The asphalt found originated about 40,000 years ago. These drawings outlets cones were removed since the Ice Age by the currents in the channel. Today, only the recently discovered mounds are preserved. On the Origin of submarine outlets has been found in 2010 no clear, matching opinion.