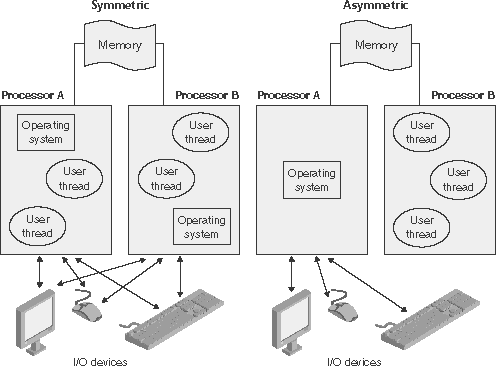
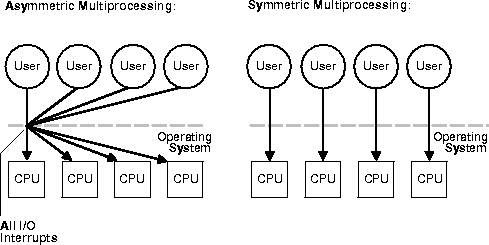
Asymmetric multiprocessing
An asymmetric multiprocessor system is a multiprocessing architecture in which a given processor is executing the operating system and processes distributed to itself, and the other processors. However, it can also execute a plurality of processors, certain parts of the operating system in order to reduce the load. This means that in case of unavailability (freezing through full utilization or failure) of a primary processor, the entire system is no longer usable. That's why today almost exclusively symmetric multiprocessors systems are used.
In the classical sense, the processors are identical. In contrast, the usual today variants use a main processor and more focused on specific tasks subordinated processors. The IBM Cell processor, for example, utilizes a PowerPC compatible main processor and 8 subordinated specialized calculations processors.
The combination of main processor, graphics card (s ), physics accelerator (s ) may be regarded as a kind of asymmetric multiprocessor system.
- Computer Architecture