Automotive electronics
Automotive Electronics covers the entire field of electronics in vehicles. These include the control devices which are distributed in the vehicle. At the electronics in the vehicle special demands on robustness, temperature range, vibration and shock resistance and reliability are provided. The development of control units has taken since the 1990s along with the increase of the performance of microprocessors, a rapid development.
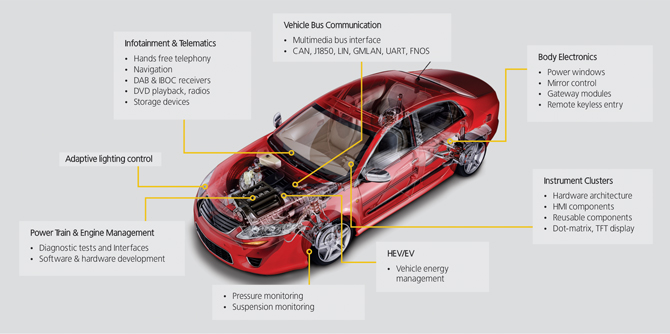
Examples of electronic applications in the vehicle
- Instrument panel cluster ( used to display the data in a car)
- Motor control with control of the ignition system or the injection system
- Anti -lock brakes and vehicle dynamics control
- Airbag ( electronics detect collision and triggers the airbag off)
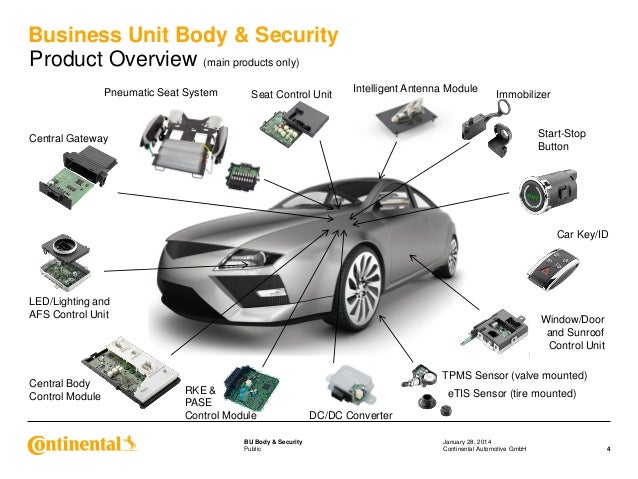
- Body Control Unit
- Driver Assistance Systems
- Car Alarm Systems
- Multimedia devices (navigation system, TV tuner, etc.)
Data communication between control units
Meanwhile, more than 20 ECUs are distributed in each new mid-range model that communicate via CAN bus, LIN bus or other vehicle-specific bus systems with each other. Full expansion of the upper class segment, the importance of the automotive electronics knocks especially - there you can sometimes find up to 80 control units, m 3000 lines and 3800 contacts. However, it is this complexity of today's vehicles, which repeatedly caused failures and malfunctions.
Requirements for electrical components
Electronic components for motor mounting must be specified for a temperature range of -40 to 125 ° C. For other areas, such as the interior a temperature range of -40 to 85 ° C is specified. In many chip manufacturers, there is a special section for ICs that may be used in the automotive industry.