Axenfeld syndrome
Rieger syndrome
The term Rieger syndrome (syn. irido - dental dysplasia, Axenfeld syndrome, Rieger - Axenfeld syndrome and dysgenesis mesodermalis Corneal et iridis ) denotes a Hemmungsmißbildung the mesoderm due to a gene mutation. The syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Affected are the chromosomes 4, 6, 11 and 18, specifically are currently the loci 4q25 -27, 13q14, 6p25 and 6q24 known.
Clinical picture
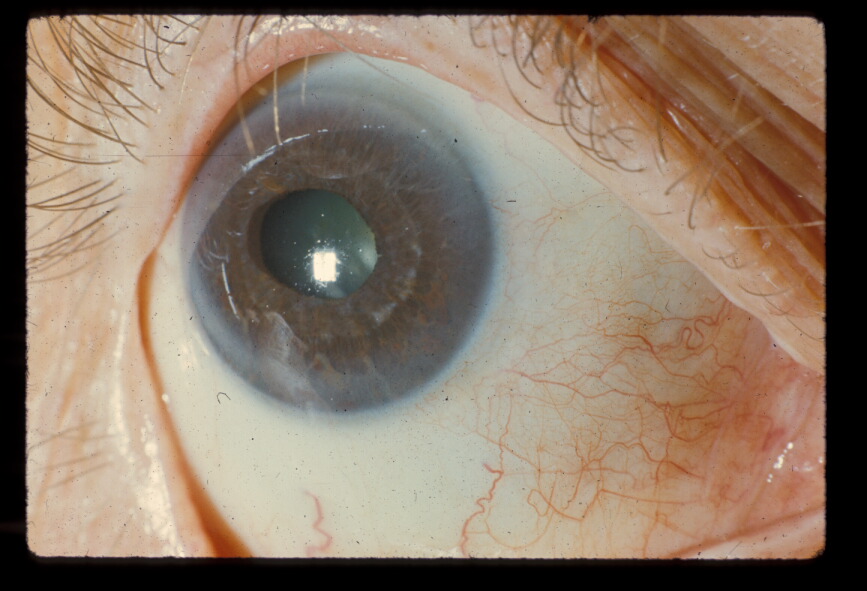
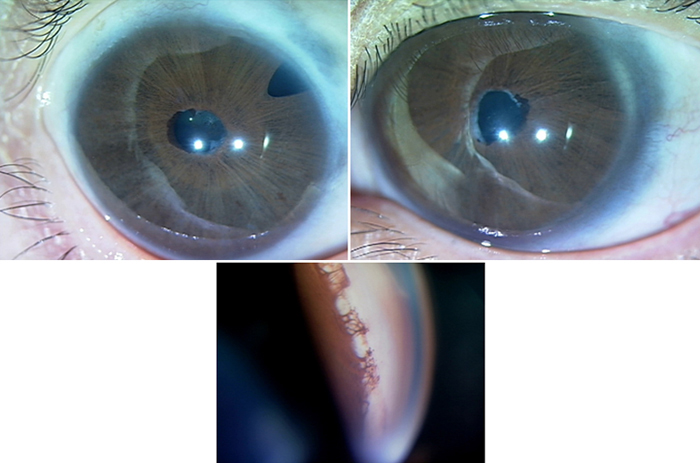
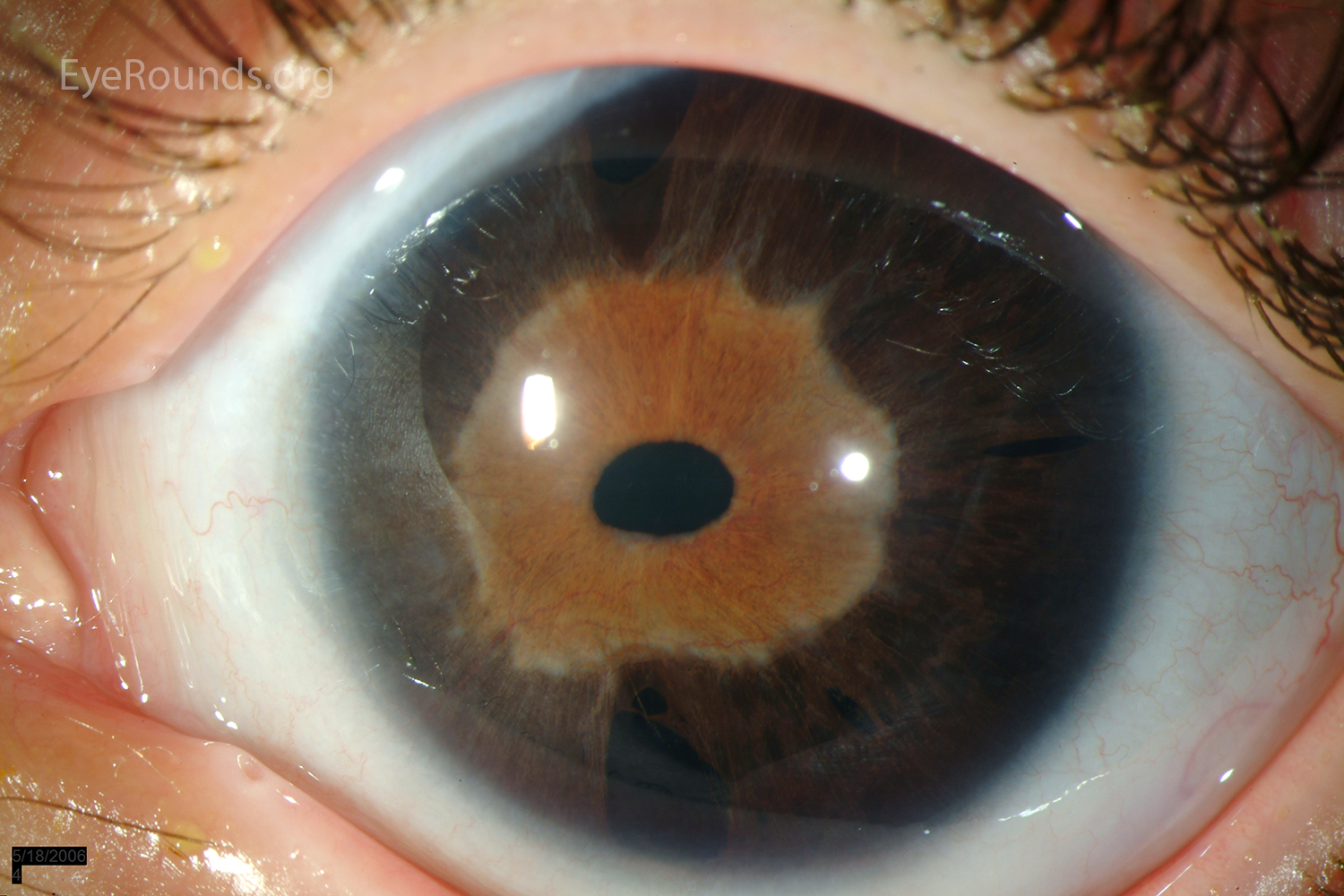
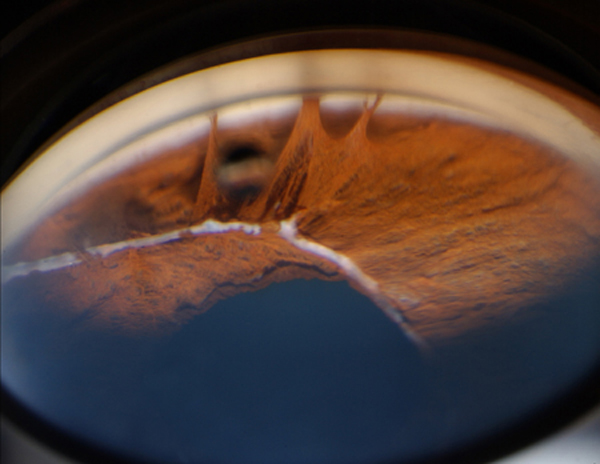
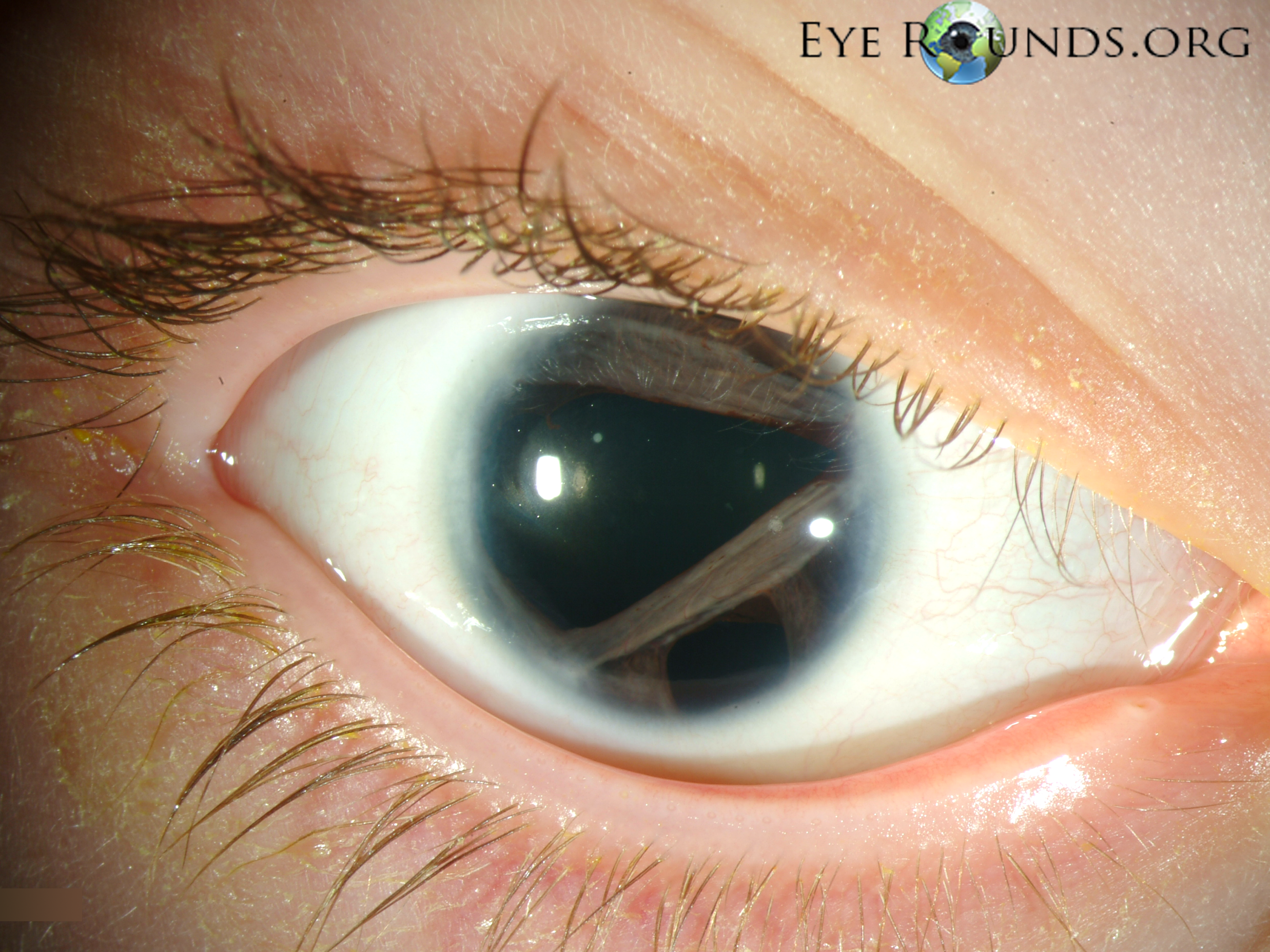
Typical is a Irisdysplasie, which presents as coloboma, hole formation, deformation of the pupil or synechiae. You can usually run in conjunction with malformations in the chamber angle of the eye to glaucoma. The pathomechanism for the development of glaucoma in the Rieger syndrome is variable.
As more serious symptoms are Mittelohrschwerhöigkeit, cerebral retardation, dental and maxillofacial skull malformations (decreased number of teeth see hypodontia ), umbilical hernia, and bone formation disorders of the skeleton system known.
Therapy
A causal therapy is not yet known, with unsatisfactory success Symptomatic plastic- surgical corrections are possible and necessary, especially in relation to the vision.