Binary Synchronous Communications
Binary Synchronous Communication ( BSC) is a term used in computer science.
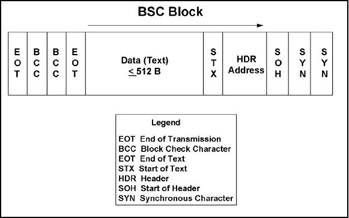
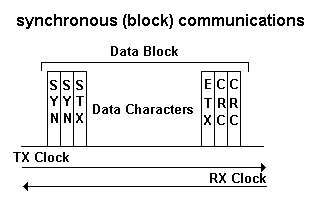
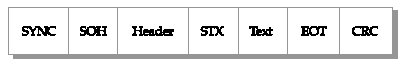
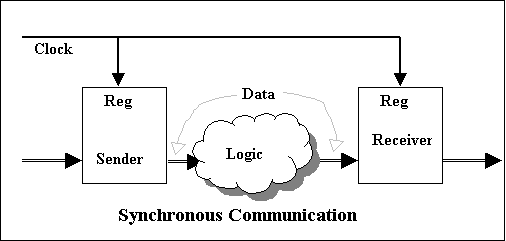
The Binary Synchronous Communication, or BSC for short, is a synchronous, character-oriented link protocol from IBM that settles its services at the data link layer. The method is also called BISYNC and uses a defined sequence of control characters for synchronized transmission of binary-coded data between stations of a communication system.
The data in blocks (character or bytes ) summarized, provided with control characters and marks and transmitted in half-duplex mode. The operation is done by request from a management station to a sub- station to transmit data. The received data is checked for transmission errors, and acknowledged or requested by the control station. BSC is suitable for point-to -point and point-to- multipoint connections.
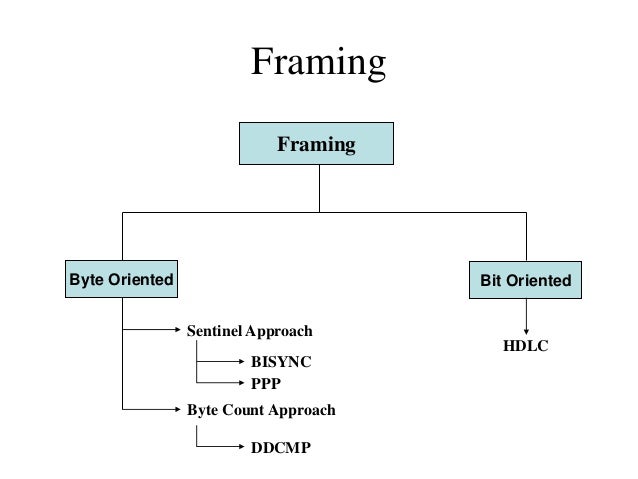
The BSC protocol was developed in the 1960s and was in the 1960s and 1970s, the most widely used form of communication on large IBM computers. It is still important, but has been increasing by more efficient, bit-oriented protocols such as HDLC (High- Level Data Link Control ) and SDLC ( Synchronous Data Link Control) replaced.