Bodo language
Spoken in
- Sino - Tibetan Tibeto- Burmese Tibetan
-
Sit ( other Sino Tibetan languages)
Brx
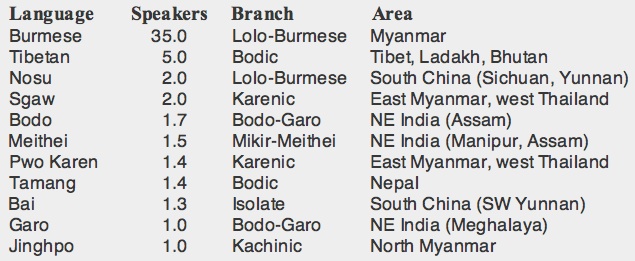
Bodo ( Boro also ) is a Tibeto - Burmese language from the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is spoken mainly in the northwest of the northeastern Indian state of Assam, there are also minorities in the north of West Bengal, Manipur and Meghalaya and in parts of eastern Nepal. In India, there were, according to 1991 census total of approximately 1.2 million native speakers, in Nepal about 3300 (as of 2001). Since 2003, Bodo in Assam enjoys the status of an official language.
Until the 19th century Bodo was exclusively a spoken language, then first the Bengali script has been introduced. In the course of the Christianization of many members of the Bodo people and the Latin alphabet was used frequently. Today the language is, however, usually written in Devanagari. The separatist National Democratic Front of Boroland argue for the single letters in the Latin alphabet.
Dialects
Bodo can be roughly divided into three dialect groups: a western, eastern and southern. The individual dialects differ mainly in pronunciation and vocabulary. As standard, the western dialect has been established.
Grammar
Bodo is an inflectional language. The language has seven cases ( nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, instrumental, ablative, locative ), two numbers (singular, plural ) and two grammatical genders ( masculine and feminine ). They are distinguished only in animals but not in objects. In the verbs, there is only one tense for the future, past and present. In the latter the verbs times be adapted to the aspect, in the presence of three elements can be distinguished in the past two.