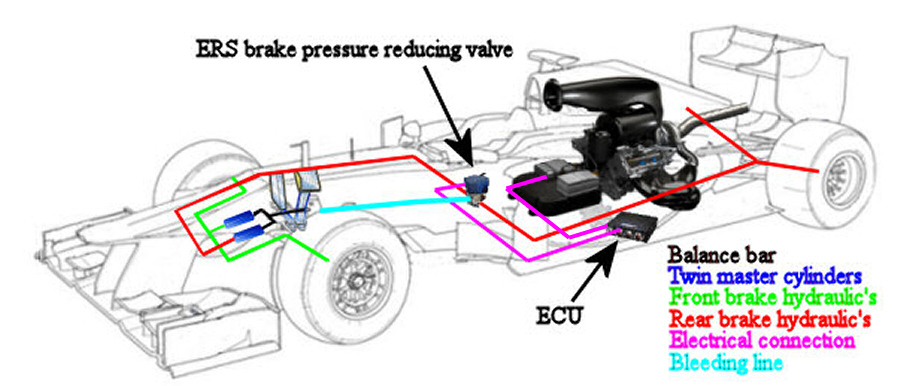
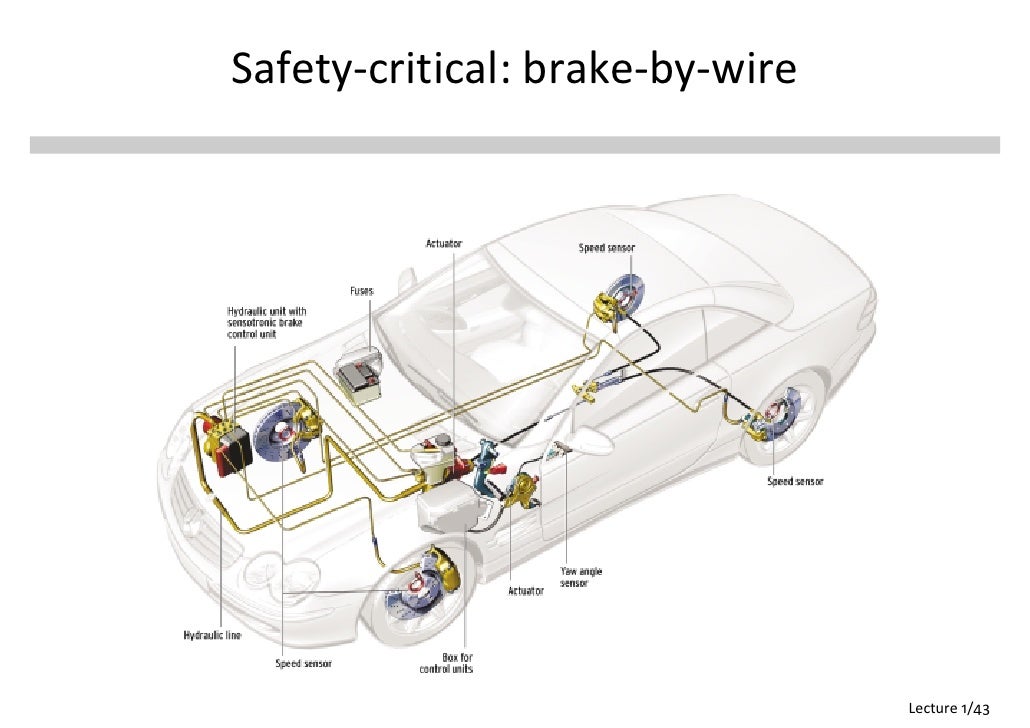
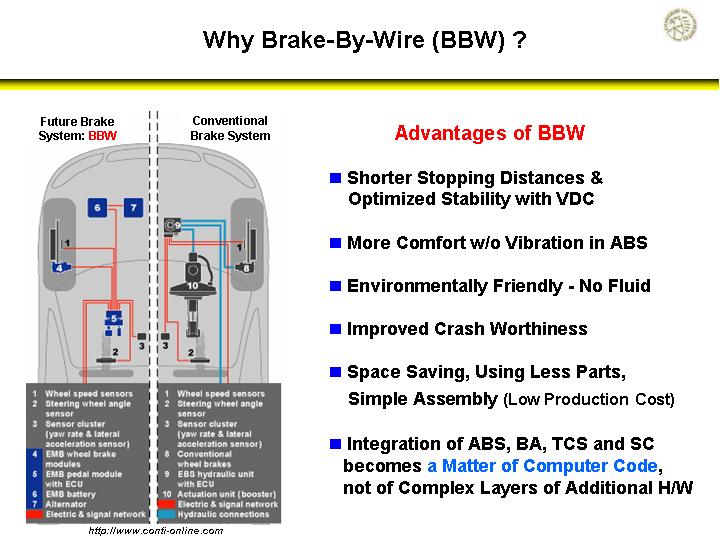
Brake-by-Wire
Brake-by- Wire (literally: Brake by Wire ) describes a braking system in which the actuator and transmission device is decoupled. In the conventional hydraulic brake system, the actuator, the brake pedal, and the transmission means is hydraulic. Here, between the electro-hydraulic brake, electropneumatic brake (for trucks) and the electromechanical brake distinguished.
Only the elimination of the hydraulic or pneumatic brake makes a genuine, so-called "dry " brake- by-wire application, since no fluid power systems be used. Siemens VDO Automotive presented at the IAA 2005 based on the wedge technology Passenger car brake, which should go up to 2010 in series.
The reason given for future use of this technology, especially with the inertia of currently used media in the brake system. Using only electro- mechanical solutions could be thus enable faster response, with this should be reflected in the achievable braking distances. An important advantage is the much cheaper manufacturability of the brake-by -wire technology, as in hydraulic systems in use is components such as brake master cylinder, brake booster and ABS must be manufactured comparatively expensive. Future are realized all the functions of the braking system via software.
A clear disadvantage is that is required by law that a fallback has to be present, so that in case of a failure of the electronics still the brakes can be operated. This means only one additional valve, which is opened and energized, the coupling between the brake pedal and a hydraulic circuit ( which is preferably the front axle ) is prepared again for the electro-hydraulic brake. In the electro-mechanical brake should have a second battery are made available and redundant signal lines are routed. A second battery provides, inter alia, but a significant difference in weight is, and thus is not practical.