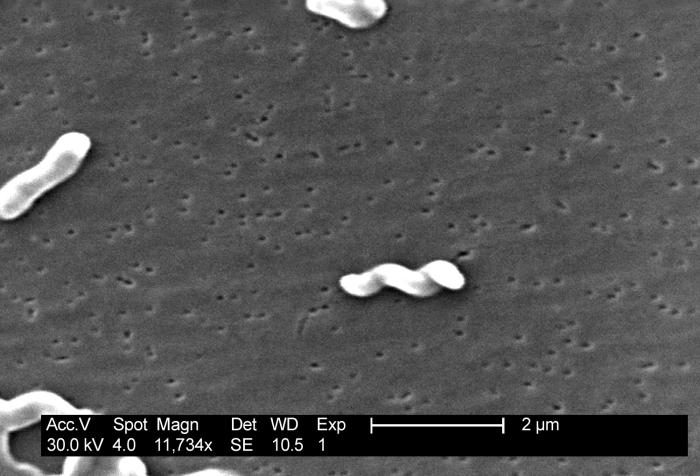
Campylobacter jejuni
Campylobacter jejuni
Campylobacter jejuni is a microaerophilic, gram-negative bacterium of the genus Campylobacter, which can mainly of diarrheal diseases ( Campylobacter enteritis ) appear in humans as a pathogen. The genome of this kind was completely sequenced in 2005.
Description
Morphologically, Campylobacter jejuni slender, spirally curved rods that are 0.2-0.5 microns thick and 0.5 to 5 microns long. There is a single flagellum at both poles.
The pathogens are transmitted from animals through food and drinking water to the people. A direct smear infection occurs, especially in children. Often the infection occurs in summer and autumn.
The incubation period after infection was 2 to 5 days. The optimal growth temperature for the cultivation is 42-45 ° C. When stored at 25 ° C, the bacteria die off, but they paradoxically survive refrigerator temperatures for weeks. To kill these germs in foods rich usually from 55 ° C. Therefore, the thorough cooking of meat, especially poultry meat, and the cooking of raw milk important measures of prevention.
Medical importance
Possible sources of infection
As possible sources of infection is not known to:
- Raw cow's milk (untreated)
- Contaminated, non-chlorinated drinking water (especially in southern countries )
- Contaminated animal food ( especially meat, for example, not cooked poultry meat but also pork, and raw clams and other shellfish )
- Contact with animals ( especially cats, dogs, birds, cattle and poultry)
- Smear infection from person to person
It should be noted that for an infection suffice about 500 seeds.
Pathogenicity
On the mechanisms of pathogenicity of these pathogens are known no more details. However, Campylobacter jejuni is a heat-stable enterotoxin, which is similar to that of Escherichia coli.
Course of the infection
After an incubation period of two to five days (in some cases 1-10 days) can make the following noticeable symptoms:
- Severe, colicky abdominal pain
- Frequent, watery diarrhea ( diarrhea ), sometimes with mucus and blood deposits
- High fever
- Occasionally vomiting
It often occurs before the onset of symptoms of diarrhea, for developing an one - to two-day Vorstadiums, which is characterized by high fever, severe malaise, muscle pain and headaches. The elimination of the pathogen occurs in the faeces, the duration of the excretion after the disease is usually three to four weeks. During this period, an infection is possible.
Possible infectious diseases and disease consequences
Campylobacter jejuni wanders through the intestinal epithelium and subepithelial spread.
- Enterocolitis with watery diarrhea
- Campylobacter enteritis
- Fever
- Arthritis
- Cholecystitis
- Salpingitis
- Sepsis
- Meningitis
- Peritonitis
- Erythema nodosum
The Guillain -Barré syndrome occurs more frequently after infection with Campylobacter jejuni. The cause of this molecular mimicry is discussed.
Therapy
Antibiotic therapy is only in individual cases with erythromycin, usually there is a spontaneous healing under symptomatic therapy, ie Fluid and electrolyte replacement. In Germany, Switzerland and Austria must be reported, it engages in Germany the Infection Protection Act (IfSG ). According to § 7 IfSG the detection of intestinal pathogenic Campylobacter species in an infection is notifiable under § 6 IfSG the suspected disease and illness when the person concerned an activity in certain food businesses ( § 42 IfSG ) have been notifiable exercises.
Diagnosis
For detection is a culture that was isolated from stool. Campylobacter jejuni can be cultured on blood agar plates under a microaerophilic atmosphere containing 10% CO2 and 5 % O2. This selected antibiotics the culture medium are added to suppress the growth of the accompanying flora (eg Enterobacteriaceae ) in the chair. The optimum growth temperature for C. jejuni is 42 ° C, while the related species Campylobacter fetus grows better at 25 ° C.
The detection of C. jejuni and Campylobacter coli to related species ( the detection of the antigens ) or by means of the PCR method (detection of the nucleic acids ) can be carried out faster in the stool by means of the direct ELISA method.