Cardiotocography
Kardiotokografie or tomography (English: Cardiotocography, Abbr: CTG) refers to a method for the simultaneous ( concurrent ) registration and recording of the heart rate of the unborn child and the uterine contractions (Greek tokos ) in the expectant mother. The method is used both in pregnancy as well as care for monitoring during delivery.
Technology and evaluation
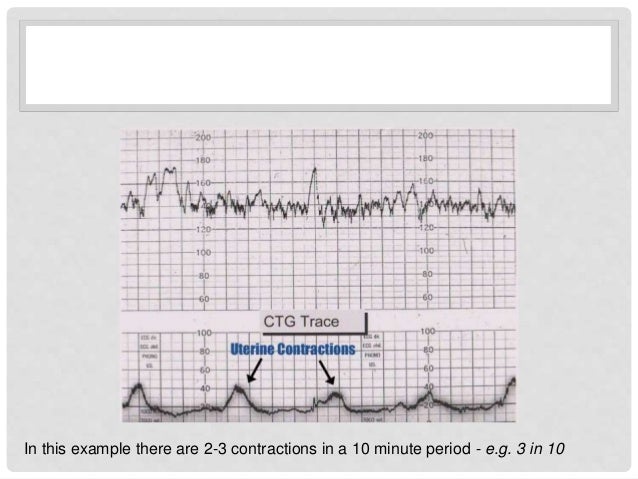
The fetal heart rate is usually determined by pulsed - wave Doppler ultrasound and in bpm (beats per minute ) (unit: min-1 ) was recorded. The contractions of the mother is measured with a separate Toco transducer, ie, a pressure gauge (transducer) and also recorded. There are two methods: intrauterine, direct pressure measurement rarely used, which can be only after the opening of the amniotic sac, so during childbirth, applied, and the usual external, indirect pressure measurement. Here, the pressure gauge responds to the change in waist circumference during a contraction, which is why it is used in the recording of uterine contractions to large individual variations: The girth of a very lean pregnant women (with very little subcutaneous fat ) changes much more clearly than that of a corpulent pregnant women. The range of recording differences ranges from large eruptions of Tokographen with small contractions of lean pregnant women up to a total lack of eruptions during the throes of a obese woman in travail. When interpreting a CTG therefore the constitution of the pregnant women and their data on the perceptibility of labor are taken into account.
Interprets the history of the changes of the child's heart rate taking into account the labor and gestational age ( in the care of pregnant women ) and since then the birth progress. If you suspect an insufficient supply of the Child ( uteroplacental dysfunction ), a labor load test can be performed with CTG control. But he has many false- positive results.
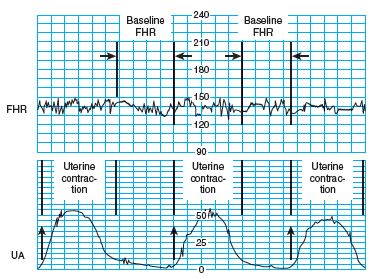
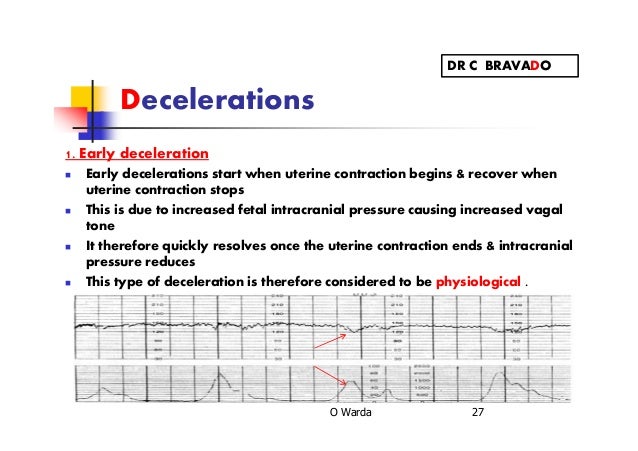
During childbirth, it can result from lack of oxygen, among other things caused a transient reduction in fetal heart rate (FHR ), come a so-called deceleration. This can be particularly "late" decelerations that occur each following a contraction, give evidence of risk to the child. " Early " decelerations that blow synchronously occur are rare signs of acute danger, but may, if they regularly occur already at the onset of labor, give rise to an obstetric intervention. In a three -minute pause existing FHR below 120 bpm is called a light, below 100 bpm by a severe bradycardia. Bradycardia upon the occurrence of the bowl into the basin is also called entry effect.
The evaluation of the CTG can be based on various schemes carried out, for instance by using the Fischer- scores. Guidelines for evaluating the CTG issued by the Fédération International de Gynécologie et d' Obstétrique ( FIGO ) and other national and international bodies. The introduction of computerized documentation and evaluation systems is the focus of current research programs.
History
About obstetric monitoring method was first reported in the early 18th century. Here was proof that an unborn child (still ) lives in the foreground. From the first decades of the 19th century, the auscultation of fetal heart tones was widespread. Since the mid 19th century was devoted to the fetal heart rate (FHR ) and its changes during birth more attention. However, a continuous recording was only possible due to the technological developments in the early 20th century. First, the fetal heart rate was phonokardiografisch, ie on the derivative of the heart sound by means of a microphone is determined. Other tests consisted of deriving the child's electrocardiogram in different ways and to determine the heart rate. A more elegant method is used since the late 1960s: the ultrasonic Doppler method. This pulsed ultrasonic signals are sent from a placed at the mother's abdomen transducer, reflected from the fetal heart and received by the ultrasound probe again. From the electronically processed signals the child's heart rate is determined. In conjunction with the simultaneous registration of uterine contractions today Phonokardiotokographie that Ultrasonokardiotokographie and fetal Elektrokardiotokographie are possible. Modern CTG devices ( FMP CTG) draw next fetal heart rate and maternal uterine contractions in addition to fetal movement ( movement = Greek kinesis ). These provide additional information about the child's condition. The transfer of data is now mostly from the battery-powered transducer on the abdominal wall of the mother by radio to the recording unit. Thus, the woman in labor can move freely while monitoring the child's condition. The photograph shows such a modern CTG.