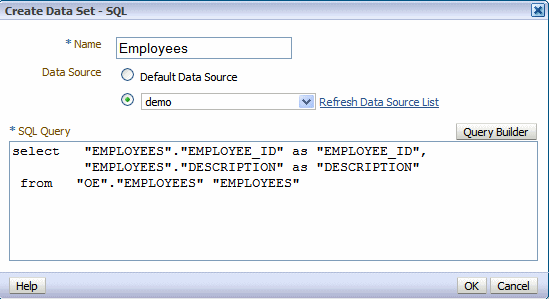
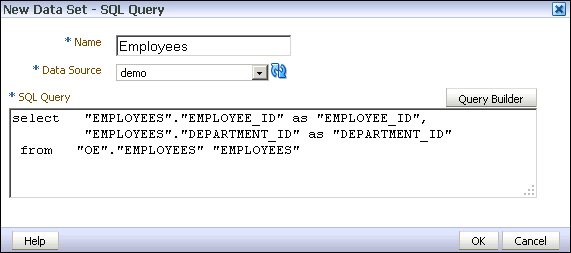
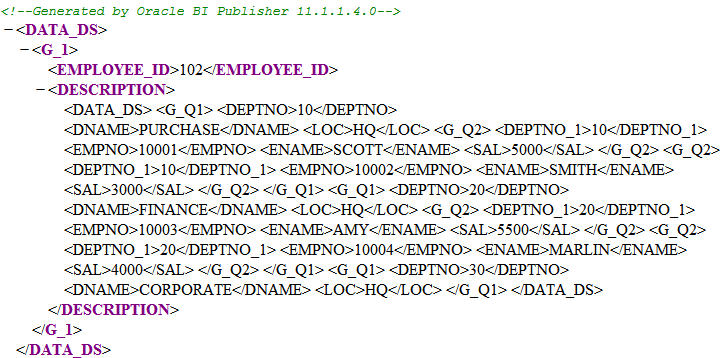
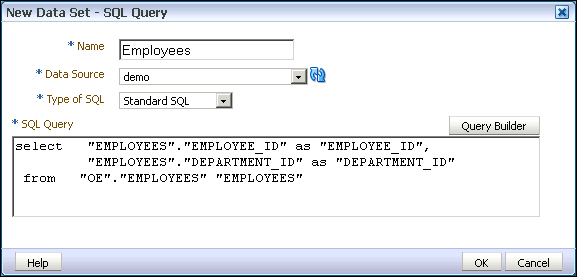
Character Large Object
Character Large Object ( CLOB ) is a data type that is used to store very long strings in databases.
This data type is called differently in different database systems. In Oracle and DB2 CLOB his name, while other database systems use other names. So there are in MySQL and PostgreSQL a corresponding type called TEXT. The database systems also differ in the type of data storage. While some systems store only a reference to the CLOB in the table, store other smaller CLOBs directly in the table and use only above a certain size the reference mechanism.
A CLOB has a specific character encoding and is lexically sortable. This differs from the Binary Large Object ( BLOB), which can only be sorted numerically according to the byte values . How BLOBs also CLOBs very high size limits in the order of several GiB. Not all database systems, all string functions are also available for CLOBs. Also, CLOBs can indeed be used in indexes, but only the first substring of fixed length is used, otherwise the index would need as much space as the CLOB itself
CLOBs are well suited for storing XML data in a database. Some database vendors are now offering for XML data specific data types that provide optimized access methods. So for fast access to the XML components special indexes have been developed to support and speed up access with XPath and XQuery.
For international projects, storing Unicode data is often required. Many database vendors offer special LOB data types where multiple bytes can be used for the storage of the individual characters. These are used in Oracle NCLOB ( National Character Large Object) and in DB2 as DBCLOB ( Double Byte Character Large Object) respectively. Thus, data can be stored in all common languages.