Cyclic compound
Chemical compounds are referred to as cyclic compounds, if at least a part of the constituent atoms in a molecule is linked to one or more rings are formed. Mainly occur in cyclic structures on carbon-containing organic compounds, but they can also occur in inorganic compounds. If large rings formed with a high number of participating atoms, is spoken of macrocyclic compounds. In contrast, acyclic compounds only have a chain-like structure.
Cyclic compounds can be prepared by appropriate cyclization ( ring-closing reactions).
Homocyclic and heterocyclic compounds
In homocyclic compounds of the ring consists only of atoms of the same element. A classic example of an inorganic compound is homocyclic λ of sulfur which forms crown-shaped rings 8 sulfur atoms.
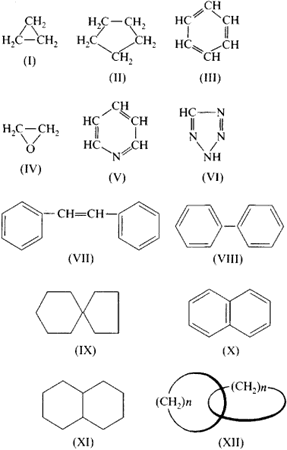
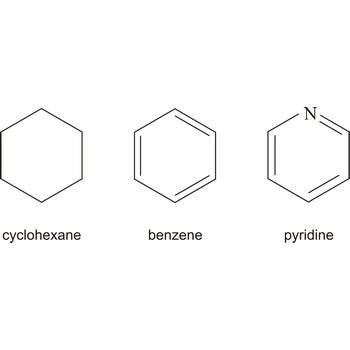
Compounds in which the ring-forming atoms are only carbon atoms are called carbocyclic compounds. The "smallest" compound of this class is the cyclopropane C3H6, which is part of the cycloalkanes. Other examples of carbocyclic molecules include cyclohexane, which is required for the production of nylon, naphthalene that has been previously used in moth balls and benzene, which increases the knock resistance of gasoline.
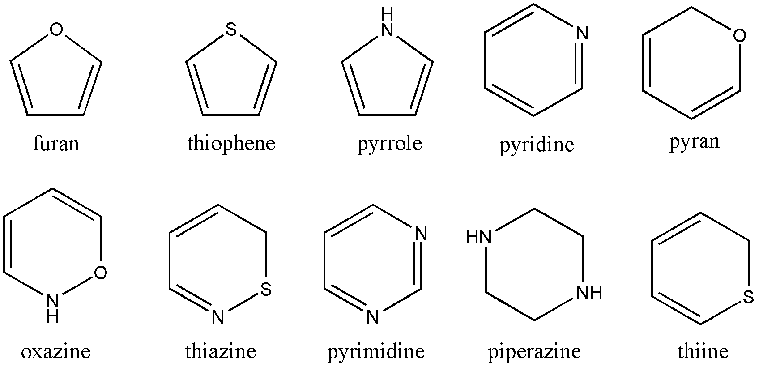
When in at least one ring of the whole molecule a hetero atom is contained, it is spoken of a heterocyclic compound. Heterocycles play an important role in biological processes. Everyday Examples are caffeine and nicotine. But heterocycles are also found in DNA and color, as well as odors. The inorganic heterocycles include meta, meta-silicic and borazine.
Nomenclature on the number of rings
- Monocyclic compounds or monocycles are cyclic compounds which contain only a single ring. You will Cyclo - referred to in the chemical nomenclature, the prefix. Examples include cyclohexane or cyclooctatetraene. Frequently aromatic or heterocyclic compounds, however, indicated by proper names, such as benzene or melamine.
- Polycyclic compounds, or polycyclic compounds, which consist of multiple rings. Their nomenclature is very complicated and dependent on the way down, where the rings are linked. Examples: anthracene, phenanthrene, pyrene For polycyclic compounds that consist of two rings, the designation or bicyclic bicyclic compound is in use. Example: naphthalene
- If several rings linked to two bridgehead atoms, one speaks of bridged bicyclic compounds. Example: norbornane
- Two directly adjacent rings having a common bond are also known as fused or fused ring system.
- In the laboratory jargon often of a " three-ring ", " four ring ", etc. is spoken. Here, only an indication of the number of ring atoms is made, but not on the nature of atoms ( such as carbon or heteroatoms).
Nomenclature according to functional groups
Cyclic esters are called lactones. Cyclic amides form the substance group of lactams. Cyclic sulfonamides are called sultams. Lactols are cyclic hemiacetals or hemiketals.
Aromatics ( or aromatics ) form a cyclic structural motif of conjugated double bonds, which have a special stability. Do they possess more aromatic ring structures, they are divided into the group of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons ( PAHs). Alicyclic compounds are cyclic hydrocarbons, not satisfying the aromaticity.
Spiro compounds are polycyclic organic compounds whose rings are connected at only one atom. Catenanes contain at least two chain-like intricate rings, rotaxanes, a ring that is penetrated by a dumbbell-shaped molecule.
Examples of mono rings to the number of ring atoms
- Cyclopropane, oxirane
- Cyclobutane, β -lactams, β - lactones
- Cyclopentane, furan, furanoses, γ -butyrolactone
- Benzene, cyclohexane, phenol, piperidine, pyran, pyranoses, pyridine, sulfur ( Cyclohexaschwefel )
- Azulene, benzodiazepines, caprolactam, caprolactone, chamazulene, cycloheptane, sulfur ( Cycloheptaschwefel ) Tropolone
- Octogen, sulfur ( cyclooctasulfur )